Related Research Articles

Unemployment, according to the OECD, is people above a specified age not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period.
Full employment is a situation in which there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. Full employment does not entail the disappearance of all unemployment, as other kinds of unemployment, namely structural and frictional, may remain. For instance, workers who are "between jobs" for short periods of time as they search for better employment are not counted against full employment, as such unemployment is frictional rather than cyclical. An economy with full employment might also have unemployment or underemployment where part-time workers cannot find jobs appropriate to their skill level, as such unemployment is considered structural rather than cyclical. Full employment marks the point past which expansionary fiscal and/or monetary policy cannot reduce unemployment any further without causing inflation.

The United States had an official estimated resident population of 334,914,895 on July 1, 2023, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. This figure includes the 50 states and the District of Columbia but excludes the population of five unincorporated U.S. territories as well as several minor island possessions. The United States is the third most populous country in the world. The Census Bureau showed a population increase of 0.4% for the twelve-month period ending in July 2022, below the world average annual rate of 0.9%. The total fertility rate in the United States estimated for 2022 is 1.665 children per woman, which is below the replacement fertility rate of approximately 2.1.

The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System. The BLS collects, processes, analyzes, and disseminates essential statistical data to the American public, the U.S. Congress, other Federal agencies, State and local governments, business, and labor representatives. The BLS also serves as a statistical resource to the United States Department of Labor, and conducts research measuring the income levels families need to maintain a satisfactory quality of life.
An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment rate, quits rate, housing starts, consumer price index, Inverted yield curve, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production, bankruptcies, gross domestic product, broadband internet penetration, retail sales, price index, and changes in credit conditions.

In economics, a discouraged worker is a person of legal employment age who is not actively seeking employment or who has not found employment after long-term unemployment, but who would prefer to be working. This is usually because an individual has given up looking, hence the term "discouraged".
The following is a list of California unemployment statistics.
The Current Population Survey (CPS) is a monthly survey of about 60,000 U.S. households conducted by the United States Census Bureau for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The BLS uses the data to publish reports early each month called the Employment Situation. This report provides estimates of the unemployment rate and the numbers of employed and unemployed people in the United States based on the CPS. A readable Employment Situation Summary is provided monthly. Annual estimates include employment and unemployment in large metropolitan areas. Researchers can use some CPS microdata to investigate these or other topics.
A jobless recovery or jobless growth is an economic phenomenon in which a macroeconomy experiences growth while maintaining or decreasing its level of employment. The term was coined by the economist Nick Perna in the early 1990s.

The misery index is an economic indicator, created by economist Arthur Okun. The index helps determine how the average citizen is doing economically and is calculated by adding the seasonally adjusted unemployment rate to the annual inflation rate. It is assumed that both a higher rate of unemployment and a worsening of inflation create economic and social costs for a country.
The Conference Board Leading Economic Index is an American economic leading indicator intended to forecast future economic activity. It is calculated by The Conference Board, a non-governmental organization, which determines the value of the index from the values of ten key variables. These variables have historically turned downward before a recession and upward before an expansion. The per cent change year over year of the Leading Economic Index is a lagging indicator of the market directions.

Income in the United States is measured by the various federal agencies including the Internal Revenue Service, Bureau of Labor Statistics, US Department of Commerce, and the US Census Bureau. Additionally, various agencies, including the Congressional Budget Office compile reports on income statistics. The primary classifications are by household or individual. The top quintile in personal income in 2019 was $103,012. The differences between household and personal income are considerable, since 61% of households now have two or more income earners.
The New York State Department of Labor is the department of the New York state government that enforces labor law and administers unemployment benefits.
Shadowstats.com is a website that analyzes and offers alternatives to government economic statistics for the United States. Shadowstats primarily focuses on inflation, but also keeps track of the money supply, unemployment and GDP by utilizing methodologies abandoned by previous administrations from the Clinton era to the Great Depression.
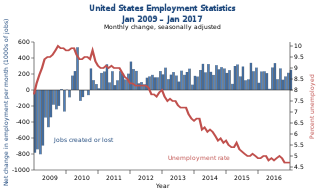
Unemployment in the United States discusses the causes and measures of U.S. unemployment and strategies for reducing it. Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as economic conditions, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage levels.

The United States entered a recession in 1990, which lasted 8 months through March 1991. Although the recession was mild relative to other post-war recessions, it was characterized by a sluggish employment recovery, most commonly referred to as a jobless recovery. Unemployment continued to rise through June 1992, even though a positive economic growth rate had returned the previous year.

The United States entered recession in January 1980 and returned to growth six months later in July 1980. Although recovery took hold, the unemployment rate remained unchanged through the start of a second recession in July 1981. The downturn ended 16 months later, in November 1982. The economy entered a strong recovery and experienced a lengthy expansion through 1990.
References
- ↑ John E. Bregger and Steven E. Haugen (1995). "BLS introduces new range of alternative unemployment measures" Monthly Labor Review, October: p. 24. , U.S. Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics, retrieved March 6, 2009.