
The Bahamas are a group of about 700 islands and cays in the western Atlantic Ocean, of which only between 30 and 40 are inhabited. The largest of the islands is Andros Island, located north of Cuba and 200 kilometres southeast of Florida. The Bimini islands are to its northwest. To the North is the island of Grand Bahama, home to the second-largest city in the country, Freeport. The island of Great Abaco is to its east. In the far south is the island of Great Inagua, the second-largest island in the country. Other notable islands include Eleuthera, Cat Island, San Salvador Island, Acklins, Crooked Island, and Mayaguana. Nassau is the capital and largest city, located on New Providence. The islands have a tropical savannah climate, moderated by the Gulf Stream. The total size is 13,878 km2 (5,358 sq mi). Due to the many widespread islands it has the 41st largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 654,715 km2 (252,787 sq mi).

The Abaco Islands lie in the north of The Bahamas, about 193 miles east of Miami, Florida. The main islands are Great Abaco and Little Abaco, which is just west of Great Abaco's northern tip. There are several smaller barrier cays, of which the northernmost are Walker's Cay and its sister island Grand Cay. To the south, the next inhabited islands are Spanish Cay and Green Turtle Cay, with its settlement of New Plymouth, Great Guana Cay, private Scotland Cay, Man-O-War Cay, and Elbow Cay, with its settlement of Hope Town. Southernmost are Tilloo Cay and Lubbers Quarters. Also of note off Abaco's western shore is Gorda Cay, now a Disney-owned island and cruise ship stop renamed Castaway Cay. Also in the vicinity is Moore's Island. On the Big Island of Abaco is Marsh Harbour, the Abacos' commercial hub and The Bahamas' third-largest city, plus the resort area of Treasure Cay. Both have airports. A few mainland settlements of significance are Coopers Town and Fox Town in the north and Cherokee and Sandy Point in the south. Administratively, the Abaco Islands constitute seven of the 31 Local Government Districts of The Bahamas: Grand Cay, North Abaco, Green Turtle Cay, Central Abaco, South Abaco, Moore's Island, and Hope Town.

The 1893 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1893. The 1893 season was fairly active, with 12 tropical storms forming, 10 of which became hurricanes. Of those, five became major hurricanes. This season proved to be a very deadly season, with two different hurricanes each causing over 2,000 deaths in the United States; at the time, the season was the deadliest in U.S. history. The season was one of two seasons on record to see four Atlantic hurricanes active simultaneously, along with the 1998 Atlantic hurricane season. Additionally, August 15, 1893 was the only time since the advent of modern record keeping that three storms have formed on the same day until 2020 saw Wilfred, Alpha, and Beta forming on the same day; and for the first time, there were two high-intensity hurricanes simultaneously in one month of August, and this was not repeated until the year 2023.
Marsh Harbour is a town in Abaco Islands, Bahamas, with a population of 6,283 as of 2012.
Man-O-War Cay is a small island in the Abaco region of the Bahamas. It had a population of 215 at the 2010 census.

Great Harbour Cay is the major island in the north Berry Islands. It has a population of 353.

Hope Town is one of the districts of The Bahamas, on the Abaco islands as well as a small village on Elbow Cay, located in Abaco. The area had a population of 458 in 2010.
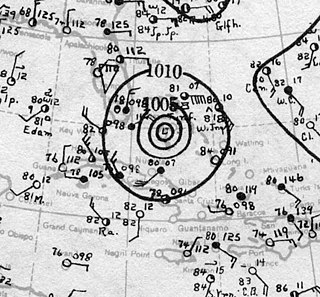
The 1929 Bahamas hurricane was a high-end Category 4 tropical cyclone whose intensity and slow forward speed led to catastrophic damage in the Bahamas in September 1929, particularly on Andros and New Providence islands. Its erratic path and a lack of nearby weather observations made the hurricane difficult to locate and forecast. The storm later made two landfalls in Florida, killing eleven but causing comparatively light damage. Moisture from the storm led to extensive flooding over the Southeastern United States, particularly along the Savannah River. Across its path from the Bahamas to the mouth of the Saint Lawrence River, the hurricane killed 155 people.

The 1932 Bahamas hurricane, also known as the Great Abaco hurricane of 1932, was a large and powerful Category 5 hurricane that struck the Bahamas at peak intensity. The fourth tropical storm and third hurricane in the 1932 Atlantic hurricane season, it was also one of two Category 5 hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean that year, the other being the 1932 Cuba hurricane. The 1932 Bahamas hurricane originated north of the Virgin Islands, became a strong hurricane, and passed over the northern Bahamas before recurving. The storm never made landfall on the continental United States, but its effects were felt in the northeast part of the country and in the Bahamas, especially on the Abaco Islands, where damage was very great. To date, it is one of four Category 5 Atlantic hurricanes to make landfall in the Bahamas at that intensity, the others having occurred in 1933, 1992, and 2019.

Great Guana Cay is an islet in The Bahamas. It is a long, narrow islet, 7 miles (11 km) long. It is in the centre of the Abaco Islands and is near Gumelemi Cay. It is about 8 miles from Marsh Harbour. Approximately 150 people live on the island, mostly along the five and a half mile long stretch of beach.
Treasure Cay, is a parcel of land connected to Great Abaco Island in The Bahamas. It has a population of 1,187 as of the 2010 Bahaman census.

Green Turtle Cay is one of the barrier islands off mainland Great Abaco, The Bahamas. It can only be reached via ferry from the mainland or boat. There is not an airport on the island. It is considered part of the "Abaco Out Islands" and is 3 miles (4.8 km) long and ½ mile wide. It was named after the once abundant green turtles that inhabited the area. In 1977, Key West, Florida became a sister city to New Plymouth, Green Turtle Cay's village.
The Hope Town District Council is a local government council in the Bahamas. It is a third schedule district council located within the Abaco Islands of the northwest Bahamas.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Commonwealth of The Bahamas.

The 1933 Treasure Coast hurricane was the second-most intense tropical cyclone to strike the United States during the active 1933 Atlantic hurricane season. The eleventh tropical storm, fifth hurricane, and the third major hurricane of the season, it formed east-northeast of the Leeward Islands on August 31. The tropical storm moved rapidly west-northwestward, steadily intensifying to a hurricane. It acquired peak winds of 140 mph (220 km/h) and passed over portions of the Bahamas on September 3, including Eleuthera and Harbour Island, causing severe damage to crops, buildings, and infrastructure. Winds over 100 mph (160 km/h) affected many islands in its path, especially those that encountered its center, and many wharves were ruined.
Spring City is a town in the Abaco Islands, Bahamas. It is almost directly south of Marsh Harbour. It is also a part of the Marsh Harbour-Spring City Township. It is located 4 meters above sea-level, making it prone to global warming. As of 2010, its population was 500.

Hurricane Dorian was an extremely powerful and catastrophic tropical cyclone, which became the most intense on record to strike The Bahamas. It is tied with the 1935 Labor Day hurricane for the strongest landfall in the Atlantic basin in terms of maximum sustained winds. It is regarded as the worst natural disaster in The Bahamas' recorded history. With winds peaking at 185 mph (295 km/h), it was also one of the most powerful hurricanes recorded in the Atlantic Ocean in terms of 1-minute sustained winds, and the strongest since Wilma in 2005. Dorian was the fourth named storm, second hurricane, the first major hurricane, and the first Category 5 hurricane of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season. Dorian struck the Abaco Islands on September 1 with maximum sustained winds of 185 mph (295 km/h), tying with the 1935 Labor Day hurricane for the highest wind speeds of an Atlantic hurricane ever recorded at landfall. Dorian went on to strike Grand Bahama at similar intensity, stalling just north of the territory with unrelenting winds for at least 24 hours. The resultant damage to these islands was catastrophic; most structures were flattened or swept to sea, and at least 70,000 people were left homeless. After it ravaged through The Bahamas, Dorian proceeded along the coasts of the Southeastern United States and Atlantic Canada, leaving behind considerable damage and economic losses in those regions.
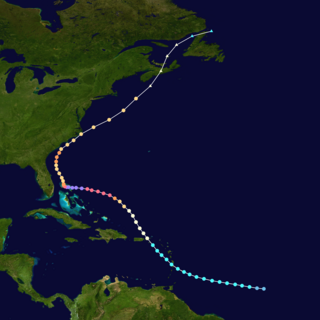
Hurricane Dorian was the strongest hurricane to affect The Bahamas on record, causing catastrophic damage on the islands of Abaco Islands and Grand Bahama, in early September 2019. The cyclone's intensity, as well as its slow forward motion near The Bahamas, broke numerous records. The fifth tropical cyclone, fourth named storm, second hurricane, and first major hurricane of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season, Dorian originated from a westward-traveling tropical wave, that departed from the western coast of Africa on August 19. The system organized into a tropical depression and later a tropical storm, both on August 24.

Hurricane Dorian became the costliest hurricane in the Bahamas on record. It struck the Abaco Islands as a Category 5 hurricane on September 1, and a day later hit Grand Bahama Island at the same category. The hurricane then stalled over Grand Bahama for another day, finally pulling away from the island on September 3. Damage amounted to US$3.4 billion, and there were at least 74 deaths in the country. Another 282 people were left missing after the hurricane.

The Bahama Archipelago, also known as the Lucayan Archipelago, is an archipelago comprising the Commonwealth of The Bahamas and the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands. The archipelago is in the western North Atlantic Ocean, north of Cuba along with the other Antilles, and east and southeast of Florida. The archipelago has experienced the effects of at least 22 Atlantic hurricanes, or storms that were once tropical or subtropical cyclones, including 17 since 2000. The storms collectively killed 101 people.
















