Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme.

In organic chemistry, an oxime is an organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula RR’C=N−OH, where R is an organic side-chain and R' may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of amides with general structure R1C(=NOH)NR2R3.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.

An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which two carbonyl moieties react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone, and this is then followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone.

In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C−Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C−Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.
The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. The reaction was reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912.
A sigmatropic reaction in organic chemistry is a pericyclic reaction wherein the net result is one σ-bond is changed to another σ-bond in an uncatalyzed intramolecular reaction. The name sigmatropic is the result of a compounding of the long-established sigma designation from single carbon–carbon bonds and the Greek word tropos, meaning turn. In this type of rearrangement reaction, a substituent moves from one part of a π-bonded system to another part in an intramolecular reaction with simultaneous rearrangement of the π system. True sigmatropic reactions are usually uncatalyzed, although Lewis acid catalysis is possible. Sigmatropic reactions often have transition-metal catalysts that form intermediates in analogous reactions. The most well-known of the sigmatropic rearrangements are the [3,3] Cope rearrangement, Claisen rearrangement, Carroll rearrangement, and the Fischer indole synthesis.
The Sandmeyer reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts using copper salts as reagents or catalysts. It is an example of a radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution. The Sandmeyer reaction provides a method through which one can perform unique transformations on benzene, such as halogenation, cyanation, trifluoromethylation, and hydroxylation.
The Bischler–Napieralski reaction is an intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction that allows for the cyclization of β-arylethylamides or β-arylethylcarbamates. It was first discovered in 1893 by August Bischler and Bernard Napieralski, in affiliation with Basel Chemical Works and the University of Zurich. The reaction is most notably used in the synthesis of dihydroisoquinolines, which can be subsequently oxidized to isoquinolines.

The Robinson–Gabriel synthesis is an organic reaction in which a 2-acylamino-ketone reacts intramolecularly followed by a dehydration to give an oxazole. A cyclodehydrating agent is needed to catalyze the reaction It is named after Sir Robert Robinson and Siegmund Gabriel who described the reaction in 1909 and 1910, respectively.
The Barton–Kellogg reaction is a coupling reaction between a diazo compound and a thioketone, giving an alkene by way of an episulfide intermediate. The Barton–Kellogg reaction is also known as Barton–Kellogg olefination and Barton olefin synthesis.

The Wolff rearrangement is a reaction in organic chemistry in which an α-diazocarbonyl compound is converted into a ketene by loss of dinitrogen with accompanying 1,2-rearrangement. The Wolff rearrangement yields a ketene as an intermediate product, which can undergo nucleophilic attack with weakly acidic nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, and amines, to generate carboxylic acid derivatives or undergo [2+2] cycloaddition reactions to form four-membered rings. The mechanism of the Wolff rearrangement has been the subject of debate since its first use. No single mechanism sufficiently describes the reaction, and there are often competing concerted and carbene-mediated pathways; for simplicity, only the textbook, concerted mechanism is shown below. The reaction was discovered by Ludwig Wolff in 1902. The Wolff rearrangement has great synthetic utility due to the accessibility of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, variety of reactions from the ketene intermediate, and stereochemical retention of the migrating group. However, the Wolff rearrangement has limitations due to the highly reactive nature of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, which can undergo a variety of competing reactions.
The Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley (MPV) reduction in organic chemistry is the reduction of ketones and aldehydes to their corresponding alcohols utilizing aluminium alkoxide catalysis in the presence of a sacrificial alcohol. The advantages of the MPV reduction lie in its high chemoselectivity and its use of a cheap environmentally friendly metal catalyst. MPV reductions have been described as "obsolete" owing to the development of sodium borohydride and related reagents.
In organic chemistry, the Paal–Knorr synthesis is a reaction used to synthesize substituted furans, pyrroles, or thiophenes from 1,4-diketones. It is a synthetically valuable method for obtaining substituted furans and pyrroles, which are common structural components of many natural products. It was initially reported independently by German chemists Carl Paal and Ludwig Knorr in 1884 as a method for the preparation of furans, and has been adapted for pyrroles and thiophenes. Although the Paal–Knorr synthesis has seen widespread use, the mechanism wasn't fully understood until it was elucidated by V. Amarnath et al. in the 1990s.
In organic chemistry, the Buchwald–Hartwig amination is a chemical reaction for the synthesis of carbon–nitrogen bonds via the palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions of amines with aryl halides. Although Pd-catalyzed C–N couplings were reported as early as 1983, Stephen L. Buchwald and John F. Hartwig have been credited, whose publications between 1994 and the late 2000s established the scope of the transformation. The reaction's synthetic utility stems primarily from the shortcomings of typical methods for the synthesis of aromatic C−N bonds, with most methods suffering from limited substrate scope and functional group tolerance. The development of the Buchwald–Hartwig reaction allowed for the facile synthesis of aryl amines, replacing to an extent harsher methods while significantly expanding the repertoire of possible C−N bond formations.
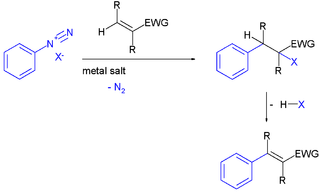
The Meerwein arylation is an organic reaction involving the addition of an aryl diazonium salt (ArN2X) to an electron-poor alkene usually supported by a metal salt. The reaction product is an alkylated arene compound. The reaction is named after Hans Meerwein, one of its inventors who first published it in 1939.
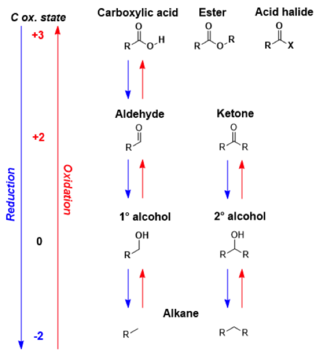
In organic chemistry, carbonyl reduction is the conversion of any carbonyl group, usually to an alcohol. It is a common transformation that is practiced in many ways. Ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, and acid halides - some of the most pervasive functional groups, -comprise carbonyl compounds. Carboxylic acids, esters, and acid halides can be reduced to either aldehydes or a step further to primary alcohols, depending on the strength of the reducing agent. Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced respectively to primary and secondary alcohols. In deoxygenation, the alcohol group can be further reduced and removed altogether by replacement with H.

Bis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium(III) chloride, also known as the Nugent–RajanBabu reagent, is the organotitanium compound which exists as a dimer with the formula [(C5H5)2TiCl]2. It is an air sensitive green solid. The complex finds specialized use in synthetic organic chemistry as a single electron reductant.

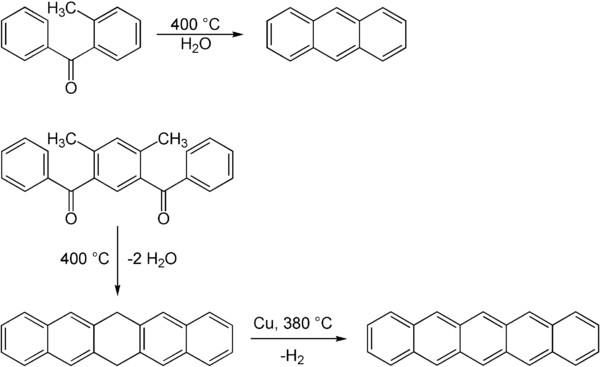
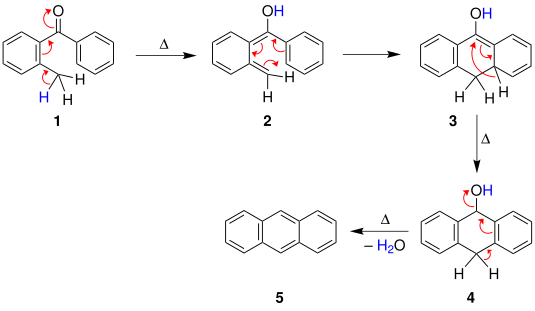
1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran is a highly reactive diene that can scavenge unstable and short-lived dienophiles in a Diels-Alder reaction. It is furthermore used as a standard reagent for the determination of singlet oxygen, even in biological systems. Cycloadditions with 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran and subsequent oxygen cleavage provide access to a variety of polyaromatics.