Plurality voting refers to electoral systems in which the candidate in an electoral district who poll more than any other are elected.
The politics of Grenada takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democracy, whereby the prime minister is the head of government. Grenada is an independent Commonwealth realm. It is governed under a multi-party parliamentary system whose political and legal traditions closely follow those of the United Kingdom; it has a prime minister and a cabinet, and a bicameral Parliament with an elected House of Representatives and an appointed Senate. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. Constitutional safeguards include freedom of speech, press, worship, motion, and association. Grenada is a member of the eastern Caribbean court system. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. Jurisprudence is based on English common law.

Elections in Bermuda have been taking place since 1620. Bermuda's current electoral system, with a lower house elected by all Bermudian status-holders, each casting a single vote, voting in single-member districts on the first-past-the-post method, came into effect with the 1968 constitution.

The Cayman Islands elect a legislature on the territorial level. The Parliament has 21 members, 19 elected members for a four-year term in 19 single member constituencies elected by first past the post and 2 members ex officio.

The Republic of the Congo elects on the national level a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president is elected by the people. The Parliament (Parlement) has two chambers. The National Assembly has 153 members, for a five-year term in single-seat constituencies. The Senate (Sénat) has 66 members, elected for a six-year term by district, local and regional councils. The Republic of Congo is a one party dominant state with the Congolese Labour Party in power. Opposition parties are allowed, but are widely considered to have no real chance of gaining power.

Elections in Dominica have been taking place since 1832. Dominica elects on national level a legislature. The House of Assembly has 32 members, 21 members elected for a five-year term in single-seat constituencies, 9 appointed senators, the Speaker and 1 ex officio member. A head of state—the president—is elected by the House of Assembly.

The Northern Marianas elect a governor and a legislature. The governor is elected for four-year term by the people. The Northern Mariana Islands Commonwealth Legislature has two chambers. The House of Representatives has 20 members, elected for a two-year term in single-seat constituencies. The Senate has 9 members, elected for a two-year term in single-seat constituencies. The Northern Marianas has a multi-party system, with two or three strong parties and a third party that is electorally successful.
Guadeloupe elects a legislature on the regional and departmental level. The legislature consists of two councils with diverging powers. The Regional Council of Guadeloupe has 41 members, elected for a four-year term by proportional representation. The Departmental Council of Guadeloupe, known as the General Council until 2015, has members elected for a six-year term in single-seat constituencies. Guadeloupe has a multi-party system, with numerous parties in which no one party often has a chance of gaining power alone, and parties must work with each other to form coalition governments.

Réunion elects on regional/départemental level a legislature. The legislature consists out of two councils with diverging powers. The Regional Council has 45 members, elected for a six-year term by proportional representation. The General Council has members elected for a five-year term in single seat-constituencies. Reunion has a multi-party system, with numerous parties in which no one party often has a chance of gaining power alone, and parties must work with each other to form coalition governments.

Elections in Kiribati are held every 4 years or, earlier, after a no confidence vote. They consist in the national elections of the Maneaba ni Maungatabu from whom is then elected the Beretitenti, shortly after, by the people. They are also local elections of the Councils.

Madagascar elects on the national level a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people, by absolute majority through a two-round system. The Parliament has two chambers. The National Assembly has 151 members, elected for a five-year term in single-member and two-member constituencies. In single-member constituencies, representatives are elected by simple majority, in the two-member constituencies, closed party lists are used, with the two seats distributed using a highest averages method. The Senate (Sénat) has 33 members, 22 members elected by the regions by provincial electors, and 11 members appointed by the president, all for 5 year terms.

Saint Kitts and Nevis elects a legislature on the national level. The National Assembly has fifteen members, eleven members elected for a five-year term in single-seat constituencies, three appointed members and one ex officio member. Saint Kitts and Nevis each have a two-party system, which means that there are two dominant political parties, with extreme difficulty for anybody to achieve electoral success under the banner of any other party.

Saint Lucia elects on the national level a legislature. The Legislature has two chambers. The House of Assembly has 17 members, elected for a five-year term in single-seat constituencies. The Senate has 11 appointed members. Saint Lucia has a two-party system, which means that there are two dominant political parties, with extreme difficulty for anybody to achieve electoral success under the banner of any other party.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines elects a legislature on the national level. The House of Assembly has 21 seats: 15 members elected for a five-year term in single seat constituencies and six appointed senators. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines has a two-party system, which means that there are two dominant political parties, with extreme difficulty for anybody to achieve electoral success under the banner of any other party.

Montenegro holds national election for the Parliament and the office of President. Montenegro has a multi-party system with numerous parties. The Parliament has 81 members elected by a system of proportional representation using D'Hondt method for a four-year term. To enter the national parliament, parties have to surpass the electoral threshold of 3%, except for minority lists, for which that threshold does not apply. President is elected at large, with a second round runoff between the two first placed candidates, if no candidate receives an absolute majority in the first round.
An electoral system or voting system is a set of rules that determine how elections and referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices.
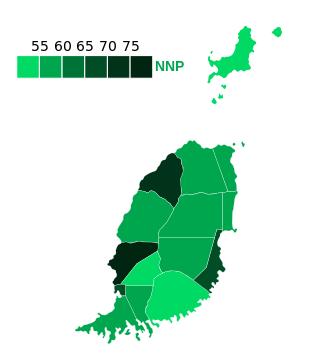
General elections were held in Grenada on 13 March 2018. The result was a victory for the New National Party and incumbent Prime Minister Keith Mitchell, winning his fifth term in office.

General elections were held in Barbados on 24 May 2018. The result was a landslide victory for the opposition Barbados Labour Party (BLP), which won all 30 seats in the House of Assembly, resulting in BLP leader Mia Mottley becoming the country's first female Prime Minister. The BLP's victory was the first time a party had won every seat in the House of Assembly. Previously, the most one-sided result for a Barbadian election had been in 1999, when the BLP won 26 of the 28 seats. The BLP's 73.5 percent vote share was also the highest on record.

Snap general elections were held in Grenada on 23 June 2022. The incumbent Prime Minister Keith Mitchell sought a sixth term. National Democratic Congress (NDC) made a return to parliament after nine years of absence, defeating the ruling party New National Party (NNP), which led to Dickon Mitchell becoming the new prime minister of Grenada. This is also the first election since 2008 where the NDC gained seats.
















