Related Research Articles

A quorum is the minimum number of members of a deliberative assembly necessary to conduct the business of that group. According to Robert's Rules of Order Newly Revised, the "requirement for a quorum is protection against totally unrepresentative action in the name of the body by an unduly small number of persons." In contrast, a plenum is a meeting of the full body. A body, or a meeting or vote of it, is quorate if a quorum is present.

The Texas Legislature is the state legislature of the US state of Texas. It is a bicameral body composed of a 31-member Senate and a 150-member House of Representatives. The state legislature meets at the Capitol in Austin. It is a powerful arm of the Texas government not only because of its power of the purse to control and direct the activities of state government and the strong constitutional connections between it and the Lieutenant Governor of Texas, but also due to Texas's plural executive.

For about a hundred years, from after Reconstruction until the 1990s, the Democratic Party dominated Texas politics.

Gregory Wayne Abbott is an American politician, attorney, and former jurist serving as the 48th governor of Texas since 2015. A member of the Republican Party, he served as the 50th attorney general of Texas from 2002 to 2015 and as a member of the Texas Supreme Court from 1996 to 2001.
The National Popular Vote Interstate Compact (NPVIC) is an agreement among a group of U.S. states and the District of Columbia to award all their electoral votes to whichever presidential ticket wins the overall popular vote in the 50 states and the District of Columbia. The compact is designed to ensure that the candidate who receives the most votes nationwide is elected president, and it would come into effect only when it would guarantee that outcome. As of February 2023, it has been adopted by fifteen states and the District of Columbia. These states have 195 electoral votes, which is 36% of the Electoral College and 72% of the 270 votes needed to give the compact legal force.
In American politics, straight-ticket voting or straight-party voting refers to the practice of voting for every candidate that a political party has on a general election ballot. The term can also refer to a straight-ticket voting option, sometimes known as a master lever, that allows voters to check a box and vote for all of a party's candidates, instead of voting for each race individually.

Senfronia Calpernia Thompson is a Democratic member of the Texas House of Representatives, representing the 141st District since 1972.

Electoral reform in California refers to efforts to change election and voting laws in the U.S. state of California.

Douglas Bryan Hughes is an American attorney and politician who is a Republican member of the Texas State Senate for District 1. He was first elected to the Texas Senate in November 2016. Previously, Hughes was a member of the Texas House of Representatives from 2003 through January 2017 as state representative for District 5, which includes Camp, Harrison, Upshur, and Wood counties in northeastern Texas.

Jason Villalba is a politician and attorney who is a Republican former member of the Texas House of Representatives for District 114 in Dallas County. He works for the law firm Frost Brown Todd.

Kelly Gene Hancock is an American businessman and Republican State Senator for District 9, which encompasses portions of Tarrant and Dallas counties, including all or part of the following communities in Tarrant County: Arlington, Bedford, Colleyville, Euless, Fort Worth, Grand Prairie, Grapevine, Haltom City, Hurst, Keller, North Richland Hills, Richland Hills, Saginaw, Southlake, Trophy Club, Watauga and Westlake. In Dallas County, Senate District 9 includes portions of Dallas, Grand Prairie, and Irving. Hancock was elected to the Texas Senate in November 2012, having previously served three terms in the Texas House of Representatives.

Steve Hixson Toth is an American businessman and politician serving as a member of the Texas House of Representatives from District 15.
Matthew McDade Phelan is an American real estate developer and Republican member of the Texas House of Representatives for District 21, which includes most of Jefferson and Orange Counties in the southeast corner of the state. He has served as Speaker of the Texas House of Representatives since January 2021.

Kenneth Kyle Biedermann, known as Kyle Biedermann, is an American politician who served as a member of the Texas House of Representatives for District 73 from 2017 to 2023. Biedermann owns and operates a hardware store within the district.

Briscoe Cain is an American attorney and Republican member of the Texas House of Representatives for District 128.
Gregory David Whitley is an American attorney and consultant to the Republican Party who asked to be appointed to the position of Acting Secretary of State of Texas by Texas Governor Greg Abbott. He served from December 2018 to May 2019. Whitley's confirmation was marred by his miscalculation calling for the investigation of 95,000 voters he identified as illegal. Republican President Donald Trump used this alleged information to claim wide spread illegal voting in the United States. Whitley could not muster enough votes in the Texas Senate to be confirmed and he resigned shortly before their session ended.

Texas state elections in 2020 were held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. Its primaries were held on March 3, 2020, with runoffs taking place on July 14.
Christopher George Hollins is an American attorney and politician who served as interim Harris County Clerk from June 2020 to November 2020. He is known for overseeing the 2020 United States presidential election in Harris County; many of his policies received resistance from state Republican officials.

The Eighty-seventh Texas Legislature was a meeting of the legislative branch of the U.S. state of Texas, composed of the Texas Senate and the Texas House of Representatives. The Texas State Legislature met in Austin, Texas, from January 12, 2021, to May 31, 2021. Governor Greg Abbott has announced three special legislative sessions during summer 2021.
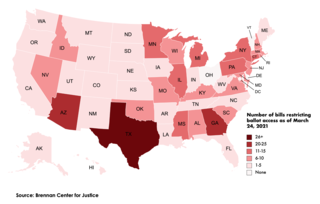
Following the 2020 United States presidential election and the unsuccessful attempts by Donald Trump and various other Republican officials to overturn it, Republican lawmakers initiated a sweeping effort to make voting laws more restrictive within several states across the country. According to the Brennan Center for Justice, as of October 4, 2021, more than 425 bills that would restrict voting access have been introduced in 49 states—with 33 of these bills enacted across 19 states so far. The bills are largely centered around limiting mail-in voting, strengthening voter ID laws, shortening early voting, eliminating automatic and same-day voter registration, curbing the use of ballot drop boxes, and allowing for increased purging of voter rolls. Republicans in at least eight states have also introduced bills that would give lawmakers greater power over election administration after they were unsuccessful in their attempts to overturn election results in swing states won by Democratic candidate Joe Biden in the 2020 election.
References
- ↑ VILLAFRANCA, ARMANDO (2001-02-15). "Lawmaker supports lowering voting age to 14". Chron. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- ↑ Nichols, John (2002-05-07). "A Voting Reform That Works Is Transforming Texas". The Nation. ISSN 0027-8378 . Retrieved 2018-04-17.
- ↑ Reding, Andrew (May 29, 2003). "Beyond Gerrymandering and Texas Posses: US Electoral Reform". Christian Science Monitor. 128: 9.
- 1 2 Pollock, Alexa Ura and Cassandra (2021-07-12). "Texas House Democrats flee the state in move that could block voting restrictions bill, bring Legislature to a halt". The Texas Tribune. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- 1 2 Ura, Alexa (2021-08-26). "Texas House passes new voting restrictions as Democratic hopes of killing the legislation wane". The Texas Tribune. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- 1 2 Corasaniti, Nick (7 September 2021). "Abbott Signs Texas Election Law, Ending a Fierce Voting Rights Battle". New York Times. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ↑ "Texas Legislature Online - 85(R) History for HB 496". capitol.texas.gov. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- ↑ "FAQ - Texans for Voter Choice". Texans for Voter Choice. Retrieved 2018-04-17.
- ↑ "87(2) SB 1 - Enrolled version - Bill Text". capitol.texas.gov. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- ↑ "Voting Laws Roundup: January 2021 | Brennan Center for Justice". www.brennancenter.org. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- ↑ "SB 1: Omnibus Voter Suppression". ACLU of Texas. 2021-07-19. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- 1 2 3 "EXPLAINER: Details of the final version of Texas voting bill". AP NEWS. 2021-08-31. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- ↑ Barragán, James (2021-09-23). "Despite his victory in Texas and no credible evidence of widespread fraud, Donald Trump calls for election audit legislation". The Texas Tribune. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- 1 2 3 Lindell, Chuck. "From polls to ballots, here's what a new Texas voting law means for you". Austin American-Statesman. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- ↑ Killough, Keith Allen,Ashley (2021-06-22). "Texas governor announces special session of state legislature | CNN Politics". CNN. Retrieved 2023-02-09.
- ↑ Ura, Alexa (7 September 2021). "Gov. Greg Abbott signs Texas voting bill into law, overcoming Democratic quorum breaks". Texas Tribune. Retrieved 15 September 2021.