
Piezoelectricity is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure and latent heat. It is derived from Ancient Greek πιέζω (piézō) 'to squeeze or press', and ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron) 'amber'. The German form of the word (Piezoelektricität) was coined in 1881 by the German physicist Wilhelm Gottlieb Hankel; the English word was coined in 1883.
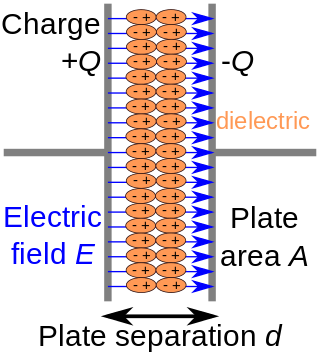
In electromagnetism, a dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in an electrical conductor, because they have no loosely bound, or free, electrons that may drift through the material, but instead they shift, only slightly, from their average equilibrium positions, causing dielectric polarisation. Because of dielectric polarisation, positive charges are displaced in the direction of the field and negative charges shift in the direction opposite to the field. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarised, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.
Ferroelectricity is a characteristic of certain materials that have a spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field. All ferroelectrics are also piezoelectric and pyroelectric, with the additional property that their natural electrical polarization is reversible. The term is used in analogy to ferromagnetism, in which a material exhibits a permanent magnetic moment. Ferromagnetism was already known when ferroelectricity was discovered in 1920 in Rochelle salt by Joseph Valasek. Thus, the prefix ferro, meaning iron, was used to describe the property despite the fact that most ferroelectric materials do not contain iron. Materials that are both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic are known as multiferroics.
The Rayleigh law describes the behavior of ferromagnetic materials at low fields.

Polyvinylidene fluoride or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive thermoplastic fluoropolymer produced by the polymerization of vinylidene difluoride. Its chemical formula is (C2H2F2)n.
In physics, the electromagnetic dual concept is based on the idea that, in the static case, electromagnetism has two separate facets: electric fields and magnetic fields. Expressions in one of these will have a directly analogous, or dual, expression in the other. The reason for this can ultimately be traced to special relativity, where applying the Lorentz transformation to the electric field will transform it into a magnetic field. These are special cases of duality in mathematics.
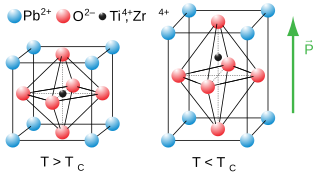
Lead zirconate titanate, also called lead zirconium titanate and commonly abbreviated as PZT, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb[ZrxTi1−x]O3(0 ≤ x ≤ 1). It is a ceramic perovskite material that shows a marked piezoelectric effect, meaning that the compound changes shape when an electric field is applied. It is used in a number of practical applications such as ultrasonic transducers and piezoelectric resonators. It is a white to off-white solid.

In physics, the electric displacement field or electric induction is a vector field that appears in Maxwell's equations. It accounts for the electromagnetic effects of polarization and that of an electric field, combining the two in an auxiliary field. It plays a major role in topics such as the capacitance of a material, as well the response of dielectrics to electric field, and how shapes can change due to electric fields in piezoelectricity or flexoelectricity as well as the creation of voltages and charge transfer due to elastic strains.
An electroactive polymer (EAP) is a polymer that exhibits a change in size or shape when stimulated by an electric field. The most common applications of this type of material are in actuators and sensors. A typical characteristic property of an EAP is that they will undergo a large amount of deformation while sustaining large forces.
Electroceramics are a class of ceramic materials used primarily for their electrical properties.
Piezomagnetism is a phenomenon observed in some antiferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic crystals. It is characterized by a linear coupling between the system's magnetic polarization and mechanical strain. In a piezomagnetic material, one may induce a spontaneous magnetic moment by applying mechanical stress, or a physical deformation by applying a magnetic field.
Flexoelectricity is a property of a dielectric material whereby it exhibits a spontaneous electrical polarization induced by a strain gradient. Flexoelectricity is closely related to piezoelectricity, but while piezoelectricity refers to polarization due to uniform strain, flexoelectricity refers specifically to polarization due to strain that changes from point to point in the material. This nonuniform strain breaks centrosymmetry, meaning that unlike in piezoelectiricty, flexoelectric effects can occur in centrosymmetric crystal structures. Flexoelectricity is not the same as Ferroelasticity. Inverse flexoelectricity, quite intuitively can be defined as generation of strain gradient due to polarization. Similarly extending on that, Converse flexoelectricity would refer to the process where a polarization gradient induces strain in a material.

Piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM) is a variant of atomic force microscopy (AFM) that allows imaging and manipulation of piezoelectric/ferroelectric materials domains. This is achieved by bringing a sharp conductive probe into contact with a ferroelectric surface and applying an alternating current (AC) bias to the probe tip in order to excite deformation of the sample through the converse piezoelectric effect (CPE). The resulting deflection of the probe cantilever is detected through standard split photodiode detector methods and then demodulated by use of a lock-in amplifier (LiA). In this way topography and ferroelectric domains can be imaged simultaneously with high resolution.
In its most general form, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) denotes any coupling between the magnetic and the electric properties of a material. The first example of such an effect was described by Wilhelm Röntgen in 1888, who found that a dielectric material moving through an electric field would become magnetized. A material where such a coupling is intrinsically present is called a magnetoelectric.
The acoustoelastic effect is how the sound velocities of an elastic material change if subjected to an initial static stress field. This is a non-linear effect of the constitutive relation between mechanical stress and finite strain in a material of continuous mass. In classical linear elasticity theory small deformations of most elastic materials can be described by a linear relation between the applied stress and the resulting strain. This relationship is commonly known as the generalised Hooke's law. The linear elastic theory involves second order elastic constants and yields constant longitudinal and shear sound velocities in an elastic material, not affected by an applied stress. The acoustoelastic effect on the other hand include higher order expansion of the constitutive relation between the applied stress and resulting strain, which yields longitudinal and shear sound velocities dependent of the stress state of the material. In the limit of an unstressed material the sound velocities of the linear elastic theory are reproduced.
Relaxor ferroelectrics are ferroelectric materials that exhibit high electrostriction. As of 2015, although they have been studied for over fifty years, the mechanism for this effect is still not completely understood, and is the subject of continuing research.

Kenji Uchino is an American electronics engineer, physicist, academic, inventor and industry executive. He is currently a professor of Electrical Engineering at Pennsylvania State University, where he also directs the International Center for Actuators and Transducers at Materials Research Institute. He is the former associate director at The US Office of Naval Research – Global Tokyo Office.
Nickel niobate is a complex oxide which as a solid material has found potential applications in catalysis and lithium batteries.











