
Chives, scientific name Allium schoenoprasum, is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaryllidaceae that produces edible leaves and flowers. Their close relatives include the common onions, garlic, shallot, leek, scallion, and Chinese onion.

The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion. Until 2010, the shallot was classified as a separate species, Allium ascalonicum. The taxon was synonymized with Allium cepa in 2010, as the difference was too small to justify a separate species.
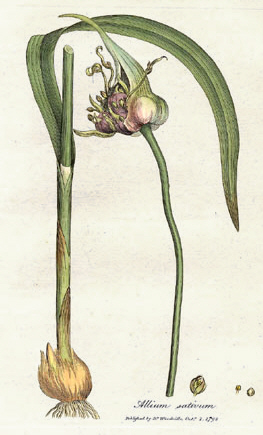
Garlic is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus Allium. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Welsh onion, and Chinese onion. It is native to South Asia, Central Asia and northeastern Iran and has long been used as a seasoning worldwide, with a history of several thousand years of human consumption and use. It was known to ancient Egyptians and has been used as both a food flavoring and a traditional medicine. China produces 76% of the world's supply of garlic.

An onion, also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus Allium. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion which was classified as a separate species until 2011. Its close relatives include garlic, scallion, leek, and chive.

Allium ursinum, known as wild garlic, ramsons, cowleekes, cows's leek, cowleek, buckrams, broad-leaved garlic, wood garlic, bear leek, Eurasian wild garlic or bear's garlic, is a bulbous perennial flowering plant in the amaryllis family Amaryllidaceae. It is native to Europe and Asia, where it grows in moist woodland. It is a wild relative of onion and garlic, all belonging to the same genus, Allium. There are two recognized subspecies: A. ursinum subsp. ursinum and A. ursinum subsp. ucrainicum.

Allium tricoccum is a bulbous perennial flowering plant in the amaryllis family Amaryllidaceae. It is a North American species of wild onion or garlic widespread across eastern Canada and the eastern United States. Many of the common English names for this plant are also used for other Allium species, particularly the similar Allium ursinum, which is native to Europe and Asia. An edible plant, Allium tricoccum is used in a variety of North American and indigenous cuisines, and has also been used by Native Americans in traditional medicine.

Allium fistulosum, the Welsh onion, also commonly called bunching onion, long green onion, Japanese bunching onion, and spring onion, is a species of perennial plant, often considered to be a kind of scallion.

The tree onion is a perennial plant similar to the common onion (A. cepa), but with a cluster of bulblets where a normal onion would have flowers. Tree onions are also known as topsetting onions, walking onions, or Egyptian onions. Genomic evidence has conclusively shown that they are a diploid hybrid of the shallot and the Welsh onion (A. fistulosum). However, some sources may still treat the tree onion as A. cepa var. proliferum or A. cepa Proliferum Group.

Allium vineale is a perennial, bulb-forming species of wild onion, native to Europe, northwestern Africa and the Middle East. The species was introduced in Australia and North America, where it has become a noxious weed.

Allium ampeloprasum is a member of the onion genus Allium. The wild plant is commonly known as wild leek or broadleaf wild leek. Its native range is southern Europe to western Asia, but it is cultivated in many other places and has become naturalized in many countries.

The pearl onion, also known as button, baby or silverskin onions in the UK, is a close relative of the leek, and may be distinguished from common onions by having only a single storage leaf, similar to cloves of garlic. In French they are known as oignon grelot. One English-speaking reference also mentions the term petit poireau antillais.

The sand leek, also known as rocambole and Korean pickled-peel garlic, is a Eurasian species of wild onion with a native range extending across much of Europe, Middle East, and Korea. The species should not be confused with rocambole garlic, which is A. sativum var. ophioscorodon.

Solo garlic, also known as single clove garlic, monobulb garlic, single bulb garlic, or pearl garlic, is a type of Allium sativum (garlic). The size of the single clove differs from approximately 25 to 50 mm in diameter. It has the flavour of the garlic clove but is somewhat milder and slightly perfumed. The appearance is akin to that of a pickling onion, with white skin and often purple stripes. Compared to traditional garlic, Solo garlic offers the advantage of being easy to peel quickly.

Garlic powder is a spice that is derived from dehydrated garlic and used in cooking for flavour enhancement. The process of making garlic powder includes drying and dehydrating the vegetable, then powdering it through machinery or home-based appliances depending on the scale of production. Garlic powder is a common component of spice mix. It is also a common component of seasoned salt.

White onion or Allium cepa are a cultivar of dry onion which have a distinct light and mild flavour profile. Much like red onions, they have a high sugar and low sulphur content, and thus have a relatively short shelf life. White onions are used in a variety of dishes, such as those of Mexican and European origin. Their uses in dishes often relate to their mild nature, they are often included in dishes to provide a light, fresh and sour taste to dishes and are often added uncooked to dishes such as salads.

Allium bisceptrum, also known as the twincrest onion or aspen onion, is a high elevation plant native to western United States. It is a perennial that thrives under damp and shady conditions or open meadows in California, Arizona, New Mexico, Nevada, Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and Utah.

Allium stipitatum, Persian shallot, is an Asian species of onion native to central and southwestern Asia.
Stromatinia cepivora is a fungus in the division Ascomycota. It is the teleomorph of Sclerotium cepivorum, the cause of white rot in onions, garlic, and leeks. The infective sclerotia remain viable in the soil for many years and are stimulated to germinate by the presence of a susceptible crop.

Allium is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants with hundreds of species, including the cultivated onion, garlic, scallion, shallot, leek, and chives. The generic name Allium is the Latin word for garlic, and the type species for the genus is Allium sativum which means "cultivated garlic".

The leek is a vegetable, a cultivar of Allium ampeloprasum, the broadleaf wild leek. The edible part of the plant is a bundle of leaf sheaths that is sometimes erroneously called a stem or stalk. The genus Allium also contains the onion, garlic, shallot, scallion, chives, and Chinese onion. Three closely related vegetables, elephant garlic, kurrat and Persian leek or tareh, are also cultivars of A. ampeloprasum, although different in their uses as food.




















