
The national flag of Denmark is red with a white Nordic cross, which means that the cross extends to the edges of the flag and the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side.

Eric of Pomerania, ruled over the Kalmar Union from 1396 until 1439. He was initially co-ruler with his great-aunt Margaret I until her death in 1412. Eric is known as Eric III as King of Norway (1389–1442), Eric VII as King of Denmark (1396–1439) and has been called Eric XIII as King of Sweden. Eric was ultimately deposed from all three kingdoms of the union, but in 1449 he inherited one of the partitions of the Duchy of Pomerania and ruled it as duke until his death in 1459. His epithet of Pomerania was a pejorative intended to insinuate that he did not belong in Scandinavia.

Christian I was a German noble and Scandinavian monarch under the Kalmar Union. He was king of Denmark (1448–1481), Norway (1450–1481) and Sweden (1457–1464). From 1460 to 1481, he was also duke of Schleswig and count of Holstein. He was the first king of the House of Oldenburg.

Frederick I was King of Denmark and Norway. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over Denmark and Norway, when subsequent monarchs embraced Lutheranism after the Protestant Reformation. As king of Norway, Frederick is most remarkable in never having visited the country and was never crowned as such. Therefore, he was styled King of Denmark, the Vends and the Goths, elected King of Norway. Frederick's reign began the enduring tradition of calling kings of Denmark alternatively by the names Christian and Frederick.

John was a Scandinavian monarch under the Kalmar Union. He was king of Denmark (1481–1513), Norway (1483–1513) and as John II Sweden (1497–1501). From 1482 to 1513, he was concurrently duke of Schleswig and Holstein in joint rule with his brother Frederick.

Christopher of Bavaria, was King of Denmark, Sweden (1441–48) and Norway (1442–48) during the era of the Kalmar Union.

Götaland is one of three lands of Sweden and comprises ten provinces. Geographically it is located in the south of Sweden, bounded to the north by Svealand, with the deep woods of Tiveden, Tylöskog and Kolmården marking the border.

Three Crowns is the national emblem of Sweden, present in the coat of arms of Sweden, and composed of three yellow or gilded coronets ordered two above and one below, placed on a blue background. Similar designs are found on a number of other coats of arms or flags.
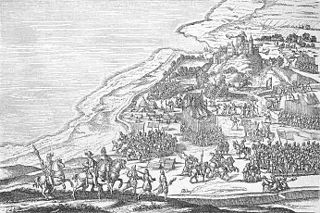
The Northern Seven Years' War was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden and a coalition of Denmark–Norway, Lübeck, and Poland–Lithuania between 1563 and 1570. The war was motivated by the dissatisfaction of King Frederick II of Denmark with the dissolution of the Kalmar Union, and the will of King Eric XIV of Sweden to break Denmark's dominating position. The fighting continued until both armies had been exhausted, and many men died. The resulting Treaty of Stettin was a stalemate, with neither party gaining any new territory.

Swedish heraldry encompasses heraldic achievements in modern and historic Sweden. Swedish heraldic style is consistent with the German-Nordic heraldic tradition, noted for its multiple helmets and crests which are treated as inseparable from the shield, its repetition of colours and charges between the shield and the crest, and its scant use of heraldic furs. Because the medieval history of the Nordic countries was so closely related, their heraldic individuality developed rather late. Swedish and Finnish heraldry have a shared history prior to the Diet of Porvoo in 1809; these, together with Danish heraldry, were heavily influenced by German heraldry. Unlike the highly stylized and macaronic language of English blazon, Swedish heraldry is described in plain language, using only Swedish terminology.

The coat of arms of Norway is the arms of dominion of King Harald V of Norway, and as such represents both the monarch and the kingdom. It depicts a standing golden lion on a red background, bearing a golden crown and axe with silver blade.

A Nordic cross flag is a flag bearing the design of the Nordic or Scandinavian cross, a cross symbol in a rectangular field, with the centre of the cross shifted towards the hoist.

The coat of arms of Denmark has a lesser and a greater version.

Philippa of England, also known as Philippa of Lancaster, was Queen of Denmark, Norway and Sweden from 1406 to 1430 by marriage to King Eric of the Kalmar Union. She was the daughter of King Henry IV of England by his first spouse Mary de Bohun and the younger sister of King Henry V. Queen Philippa participated significantly in state affairs during the reign of her spouse, and served as regent of Denmark from 1423 to 1425.

The flag of the Swedish-speaking Finns is an unofficial red flag with a yellow cross used in the Swedish-speaking parts of Finland to represent the Finland-Swedes. It may be flown in addition to the Finnish blue and white flag. This flag is unfamiliar to many in Finland but there have been attempts to introduce it again to a broader audience as what is known as "household pennants" demonstrating one's identity as Swedish-speaking, are more common and can be seen on many flagpoles in areas where there live many Swedish-speaking Finns, especially in countryside.

Socialist-style emblems usually follow a unique style consisting of communist symbolism. Although commonly referred to as coats of arms, most are not actually traditional heraldic achievements. Many communist governments purposely diverged from heraldic tradition in order to distance themselves from the monarchies that they usually replaced, with coats of arms being seen as symbols of the monarchs.
Finnish heraldry has a common past with Swedish heraldry until 1809 and it belongs to German heraldric tradition.

Russian heraldry involves the study and use of coats of arms and other heraldic insignia in the country of Russia. Compare the socialist heraldry of the Soviet period of Russian history (1917–1991).

The Dano-Hanseatic War, also known as the Kalmar War with the Hanseatic League, or the Danish-Hanseatic War of 1426-1435, was an armed trade conflict between the Danish-dominated Kalmar Union and the Hanseatic League led by the Free City of Lübeck.

The Countship of Larvik aka Landgraviate of Larvik was created on 29 September 1671 when Brunla amt was made into the county of Laurvigen. It covered today's Larvik and Tjøme municipality, and parts of Sandefjord municipality.





















