
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive 2002/95/EC, short for Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, was adopted in February 2003 by the European Union.

EU Directive 92/75/EC (1992) established an energy consumption labelling scheme. The directive was implemented by several other directives thus most white goods, light bulb packaging and cars must have an EU Energy Label clearly displayed when offered for sale or rent. The energy efficiency of the appliance is rated in terms of a set of energy efficiency classes from A to G on the label, A being the most energy efficient, G the least efficient. The labels also give other useful information to the customer as they choose between various models. The information should also be given in catalogues and included by internet retailers on their websites.

The presence of the logo on commercial products indicates that the manufacturer or importer affirms the goods' conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is not a quality indicator or a certification mark. The CE marking is required for goods sold in the European Economic Area (EEA); goods sold elsewhere may also carry the mark.
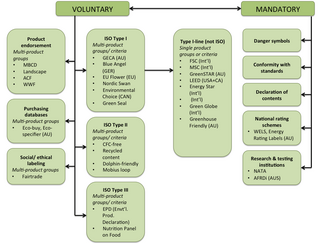
Ecolabels and Green Stickers are labeling systems for food and consumer products. The use of ecolabels is voluntary, whereas green stickers are mandated by law; for example, in North America major appliances and automobiles use Energy Star. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it easy to take environmental concerns into account when shopping. Some labels quantify pollution or energy consumption by way of index scores or units of measurement, while others assert compliance with a set of practices or minimum requirements for sustainability or reduction of harm to the environment. Many ecolabels are focused on minimising the negative ecological impacts of primary production or resource extraction in a given sector or commodity through a set of good practices that are captured in a sustainability standard. Through a verification process, usually referred to as "certification", a farm, forest, fishery, or mine can show that it complies with a standard and earn the right to sell its products as certified through the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing ecolabel.
Type approval or certificate of conformity is granted to a product that meets a minimum set of regulatory, technical and safety requirements. Generally, type approval is required before a product is allowed to be sold in a particular country, so the requirements for a given product will vary around the world. Processes and certifications known as type approval in English are often called homologation, or some cognate expression, in other European languages.

The Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS) is a voluntary environmental management instrument, which was developed in 1993 by the European Commission. It enables organizations to assess, manage and continuously improve their environmental performance. The scheme is globally applicable and open to all types of private and public organizations. In order to register with EMAS, organisations must meet the requirements of the EU EMAS-Regulation. Currently, more than 4,600 organisations and more than 7,900 sites are EMAS registered.
Building regulations in the United Kingdom are statutory instruments or statutory regulations that seek to ensure that the policies set out in the relevant legislation are carried out. Building regulations approval is required for most building work in the UK. Building regulations that apply across England and Wales are set out in the Building Act 1984 while those that apply across Scotland are set out in the Building (Scotland) Act 2003. The Act in England and Wales permits detailed regulations to be made by the Secretary of State. The regulations made under the Act have been periodically updated, rewritten or consolidated, with the latest and current version being the Building Regulations 2010. The UK Government is responsible for the relevant legislation and administration in England, the Welsh Government is the responsible body in Wales, the Scottish Government is responsible for the issue in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Executive has responsibility within its jurisdiction. There are very similar Building Regulations in the Republic of Ireland. The Building Regulations 2010 have recently been updated by the Building Safety Act 2022.

Toy safety is the practice of ensuring that toys, especially those made for children, are safe, usually through the application of set safety standards. In many countries, commercial toys must be able to pass safety tests in order to be sold. In the U.S., some toys must meet national standards, while other toys may not have to meet a defined safety standard. In countries where standards exist, they exist in order to prevent accidents, but there have still been some high-profile product recalls after such problems have occurred. The danger is often not due to faulty design; usage and chance both play a role in injury and death incidents as well.

The Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive 1991 European Union directive concerning urban waste water "collection, treatment and discharge of urban waste water and the treatment and discharge of waste water from certain industrial sectors". It aims "to protect the environment from adverse effects of waste water discharges from cities and "certain industrial sectors". Council Directive 91/271/EEC on Urban Wastewater Treatment was adopted on 21 May 1991, amended by the Commission Directive 98/15/EC.
Premium efficiency, when used in reference to specific types of Electric Motors, is a class of motor efficiency.
The Ecodesign Directive of the European Union establishes a framework to set mandatory ecological requirements for energy-using and energy-related products sold in all 27 member states. Its scope currently covers more than 40 product groups, which are responsible for around 40% of all EU greenhouse gas emissions.

Construction Products Directive (Council Directive 89/106/EEC)(CPD) is a now repealed European Union Directive which aimed to remove technical barriers to trade in construction products between Member States in the European Union.

Regulation No. 305/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of the European Union is a regulation of 9 March 2011 which lays down harmonised conditions for the marketing of construction products and replaces Construction Products Directive (89/106/EEC). This EU regulation is designed to simplify and clarify the existing framework for the placing on the market of construction products. It replaced the earlier (1989) Construction Products Directive (89/106/EEC).
The Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 2006/95/EC is one of the oldest Single Market Directives adopted by the European Union before the "New" or "Global" Approach. The Directive provides common broad objectives for safety regulations, so that electrical equipment approved by any EU member country will be acceptable for use in all other EU countries. The Low Voltage Directive does not supply any specific technical standards that must be met, instead relying on IEC technical standards to guide designers to produce safe products. Products that conform to the general principles of the Low Voltage Directive and the relevant particular safety standards are marked with the CE marking to indicate compliance and acceptance throughout the EU. Conformance is asserted by the manufacturer based on its conformity assessment.

A high efficiency glandless circulating pump is a component of a heating and air conditioning system that allows the system to perform with increased efficiency while significantly reducing the system's electrical usage.
The Recreational Craft Directive, Directive 2013/53/EU, originally Directive 94/25/EC on recreational craft amended by Directive 2003/44/EC, is a European Union directive which sets out minimum technical, safety and environmental standards for boats, personal watercraft, marine engines and components in Europe. It covers boats between 2.5 and 24m, personal watercraft, engines and a number of components built since 1998. It ensures their suitability for sale and use in Europe.
Energy efficiency in agriculture refers to reducing the amount of energy required to provide agricultural products and services. The European Commission has policies related to energy efficiency, including in agriculture. The European Union has established measures to promote energy efficiency, including setting targets for energy savings, and requiring energy audits and management plans for large companies. The AGREE project conducted studies on energy efficiency in different agricultural production systems and proposed measures for improvement. The results of the project were summarized in reports that highlighted the opportunities and drawbacks for energy efficiency in agriculture in different European countries. Improving energy efficiency in agriculture contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.

The Energy Taxation Directive or ETD (2003/96/EC) is a European directive, which establishes the framework conditions of the European Union for the taxation of electricity, motor and aviation fuels and most heating fuels. The directive is part of European Union energy law; its core component is the setting of minimum tax rates for all Member States.

UK Conformity Assessed (UKCA) marking is a conformity mark that indicates conformity with the applicable requirements for products sold within Great Britain. Products with the CE mark are also acceptable in the UK market.







