
How Green Was My Valley is a 1939 novel by Richard Llewellyn, narrated by Huw Morgan, the main character, about his Welsh family and the mining community in which they live. The author had claimed that he based the book on his own experiences but this was found to be untrue after his death; Llewellyn was English-born and spent little time in Wales, though he was of Welsh descent. Llewellyn gathered material for the novel from conversations with local mining families in Gilfach Goch.

The picaresque novel is a genre of prose fiction. It depicts the adventures of a roguish but "appealing hero", usually of low social class, who lives by his wits in a corrupt society. Picaresque novels typically adopt the form of "an episodic prose narrative" with a realistic style. There are often some elements of comedy and satire. Although the term "picaresque novel" was coined in 1810, the picaresque genre began with the Spanish novel Lazarillo de Tormes (1554), which was published anonymously during the Spanish Golden Age because of its anticlerical content. Literary works from Imperial Rome published during the 1st-2nd century AD, such as Satyricon by Petronius and The Golden Ass by Apuleius had a relevant influence on the picaresque genre and are considered predecessors. Other notable early Spanish contributors to the genre included Mateo Alemán's Guzmán de Alfarache (1599-1604) and Francisco de Quevedo's El Buscón (1626). Some other ancient influences of the picaresque genre include Roman playwrights such as Plautus and Terence. The Golden Ass by Apuleius nevertheless remains, according to different scholars such as F. W. Chandler, A. Marasso, T. Somerville and T. Bodenmüller, the primary antecedent influence for the picaresque genre. Subsequently, following the example of Spanish writers, the genre flourished throughout Europe for more than 200 years and it continues to have an influence on modern literature and fiction.
Acmeism, or the Guild of Poets, was a modernist transient poetic school, which emerged c. 1911 or in 1912 in Russia under the leadership of Nikolay Gumilev and Sergei Gorodetsky. Their ideals were compactness of form and clarity of expression. The term was coined after the Greek word ἀκμή (akmē), i.e., "the best age of man".

The Mabinogion are the earliest Welsh prose stories, and belong to the Matter of Britain. The stories were compiled in Middle Welsh in the 12th–13th centuries from earlier oral traditions. There are two main source manuscripts, created c. 1350–1410, as well as a few earlier fragments. The title covers a collection of eleven prose stories of widely different types, offering drama, philosophy, romance, tragedy, fantasy and humour, and created by various narrators over time. There is a classic hero quest, "Culhwch and Olwen"; a historic legend in "Lludd and Llefelys", complete with glimpses of a far off age; and other tales portray a very different King Arthur from the later popular versions. The highly sophisticated complexity of the Four Branches of the Mabinogi defies categorisation. The stories are so diverse that it has been argued that they are not even a true collection.
Literal and figurative language is a distinction that exists in all natural languages; it is studied within certain areas of language analysis, in particular stylistics, rhetoric, and semantics.
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1891.

Merriam-Webster, Incorporated is an American company that publishes reference books and is mostly known for its dictionaries. It is the oldest dictionary publisher in the United States.

The Red Book of Hergest, Oxford, Jesus College, MS 111, is a large vellum manuscript written shortly after 1382, which ranks as one of the most important medieval manuscripts written in the Welsh language. It preserves a collection of Welsh prose and poetry, notably the tales of the Mabinogion and Gogynfeirdd poetry. The manuscript derives its name from the colour of its leather binding and from its association with Hergest Court between the late 15th and early 17th century.

Edward Williams, better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg, was a Welsh antiquarian, poet and collector. He was seen as an expert collector of Medieval Welsh literature, but it emerged after his death that he had forged several manuscripts, notably some of the Third Series of Welsh Triads. Even so, he had a lasting impact on Welsh culture, notably in founding the secret society known as the Gorsedd, through which Iolo Morganwg successfully co-opted the 18th-century Eisteddfod revival. The philosophy he spread in his forgeries has had an enormous impact upon neo-Druidism. His bardic name is Welsh for "Iolo of Glamorgan".

Y Gododdin is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia at a place named Catraeth in about AD 600. It is traditionally ascribed to the bard Aneirin and survives only in one manuscript, the "Book of Aneirin".

Daniel Owen was a Welsh novelist. He is generally regarded as the foremost Welsh-language novelist of the 19th century and the first significant novelist to write in Welsh.
This article is about the particular significance of the year 1970 to Wales and its people.
The Tir na n-Og Awards are a set of annual children's literary awards in Wales from 1976. They are presented by the Books Council of Wales to the best books published during the preceding calendar year in each of three awards categories, one English-language and two Welsh-language. Their purpose is "[to raise] the standard of children's and young people's books and to encourage the buying and reading of good books." There is no restriction to fiction or prose. Each prize is £1,000.
This article is about the particular significance of the year 1891 to Wales and its people.

Owen Glendower: An Historical Novel by John Cowper Powys was first published in America in January 1941, and in the UK in February 1942. Powys returned to Britain from the United States in 1934, with his lover Phyllis Playter, living first in Dorchester, where he began work on his novel Maiden Castle. However, in July, 1935, they moved to the village of Corwen, Denbighshire, North Wales, historically part of Edeirnion or Edeyrnion, an ancient commote of medieval Wales that was once part of the Kingdom of Powys; it was at Corwen that he completed Maiden Castle (1936). This move to the land of his ancestors led Powys to write Owen Glendower the first of two historical novels set in this region of Wales; the other was Porius (1951). Owen, Powys's ninth novel, reflects "his increasing sense of what he thought of as his bardic heritage."

Welsh-language literature has been produced continuously since the emergence of Welsh from Brythonic as a distinct language in around the 5th century AD. The earliest Welsh literature was poetry, which was extremely intricate in form from its earliest known examples, a tradition sustained today. Poetry was followed by the first British prose literature in the 11th century. Welsh-language literature has repeatedly played a major part in the self-assertion of Wales and its people. It continues to be held in the highest regard, as evidenced by the size and enthusiasm of the audiences attending the annual National Eisteddfod of Wales, probably the largest amateur arts festival in Europe, which crowns the literary prize winners in a dignified ceremony.
Huw Ceredig Jones was a Welsh actor, best known for portraying Reg Harries in the Welsh-language soap opera Pobol y Cwm.
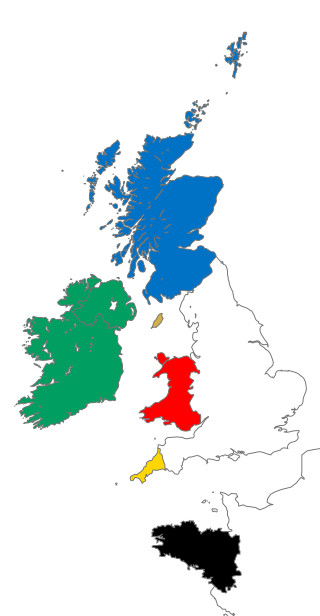
In addition to English, literature has been written in a wide variety of other languages in Britain, that is the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. This includes literature in Scottish Gaelic, Welsh, Latin, Cornish, Anglo-Norman, Guernésiais, Jèrriais, Manx, and Irish. Literature in Anglo-Saxon is treated as English literature and literature in Scots as Scottish literature.
The comedy of intrigue, also known as the comedy of situation, is a genre of comedy in which dramatic action is prioritised over the development of character, complicated strategems and conspiracies drive the plot, and farcical humour and contrived or ridiculous dramatic situations are often employed. Characterisation tends to be defined only vaguely and the plot gives the illusion of dynamic, constant movement. The German philosopher Hegel argued that characters pursue their aims in such comedies via the use of deception. The genre was first developed in the theatre of classical Rome by Plautus and Terence. Examples of comedies of intrigue include Niccolò Machiavelli's The Mandrake (1524), the anonymous Italian play The Deceived Ones (1531), Shakespeare's The Merchant of Venice and "Much Ado About Nothing", Thomas Heywood's The Wise Woman of Hoxton, Molière's Scapin the Schemer (1671), and the plays of Aphra Behn and Thomas D'Urfey.
John Gwilym Jones was a Welsh dramatist, novelist, short-story writer, drama director, academic and critic, considered a pre-eminent figure in those fields. In particular, he is widely acknowledged to be one of the two greatest 20th-century Welsh playwrights, along with Saunders Lewis; of his many plays, Hanes Rhyw Gymro (1964), Ac Eto Nid Myfi (1976) and Yr Adduned (1979) are considered masterpieces. Almost all of his work was written in the Welsh language. A writer in the modernist tradition, he is credited with introducing Brechtian techniques, stream-of-consciousness narrative and Freudianism to Welsh literature. Creative writers such as Kate Roberts and John Rowlands owed him a profound debt, and a whole generation of critics were influenced by his work as a teacher of Welsh literature.












