Related Research Articles

The Bachem Ba 349 Natter was a World War II German point-defence rocket-powered interceptor, which was to be used in a very similar way to a manned surface-to-air missile. After a vertical take-off, which eliminated the need for airfields, most of the flight to the Allied bombers was to be controlled by an autopilot. The primary role of the relatively untrained pilot was to aim the aircraft at its target bomber and fire its armament of rockets. The pilot and the fuselage containing the rocket motor would then land using separate parachutes, while the nose section was disposable.

The Heinkel He 162 Volksjäger was a German single-engine, jet-powered fighter aircraft fielded by the Luftwaffe in World War II. Developed under the Emergency Fighter Program, it was designed and built quickly and made primarily of wood as metals were in very short supply and prioritised for other aircraft. Volksjäger was the Reich Air Ministry's official name for the government design program competition won by the He 162 design. Other names given to the plane include Salamander, which was the codename of its wing-construction program, and Spatz ("Sparrow"), which was the name given to the plane by the Heinkel aviation firm.

Air Canada Flight 143, commonly known as the Gimli Glider, was a Canadian scheduled domestic passenger flight between Montreal and Edmonton that ran out of fuel on July 23, 1983, at an altitude of 41,000 feet (12,500 m), midway through the flight. The flight crew successfully glided the Boeing 767 to an emergency landing that resulted in no serious injuries to passengers or persons on the ground, at a former Royal Canadian Air Force base in Gimli, Manitoba, that had been converted to a motor racing track. This unusual aviation incident earned the aircraft the nickname "Gimli Glider". The accident is commonly blamed on mistaking pounds for kilograms, which resulted in the aircraft carrying only 45% of its required fuel load. However, the units error was the last in a series of failures that aligned in a Swiss cheese model to cause the accident.

The history of aviation extends for more than two thousand years, from the earliest forms of aviation such as kites and attempts at tower jumping to supersonic and hypersonic flight by powered, heavier-than-air jets.

Percy Sinclair Pilcher was a British inventor and pioneer aviator who was his country's foremost experimenter in unpowered flight near the end of the nineteenth century.
Alexander Schleicher GmbH & Co is a major manufacturer of sailplanes located in Poppenhausen, near Fulda in Germany.

The Blohm & Voss BV 40 was a German glider fighter designed to attack Allied bomber formations during the time of the bombing raids over Nazi Germany.
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1902:

Alan Derek Piggott was one of Britain's best known glider pilots and instructors. He had over 5,000 hours on over 153 types of powered aircraft and over 5,000 hours on over 184 types of glider. He was honoured for his work on the instruction and safety of glider pilots. In 1961 he became the first person to make an officially authenticated take-off and flight in a man-powered aircraft. He also worked as a stunt pilot in several feature films.

Gordon Gollob was an Austrian fighter pilot during World War II. A fighter ace, he was credited with 150 enemy aircraft shot down in over 340 combat missions. Gollob claimed the majority of his victories over the Eastern Front, and six over the Western Front.
An eel is a fish in the order of Anguilliformes.

An electric aircraft is an aircraft powered by electricity, almost always via one or more electric motors which drive propellers. Electricity may be supplied by a variety of methods, the most common being batteries.

Günther Radusch was a World War II German Luftwaffe pilot and wing commander. As a fighter ace, he claimed 65 enemy aircraft shot down in over 140 combat missions. He claimed one victory in the Spanish Civil War. During World War II, he was credited with 64 aerial victories in Defense of the Reich all of which claimed at night and includes the destruction of 57 four-engined bombers.
The US Aviation Cumulus is an American low-wing, single-seat, open cockpit motor glider that was designed by Dave Ekstrom and produced by US Aviation, supplied in kit form for amateur construction.

The EEL ULF 1 is a West German high-wing, single-seat, foot-launched, microlift glider that was designed by Dieter Reich. When it was available it was provided in the form of plans by Entwicklung und Erprobung von Leichtflugzeugen (EEL) for amateur construction. By the end of 2019 the company website had been take down and it is likely that the company has gone out of business.

The EEL ULF-2 is a German low-wing, conventional landing gear, single-seat motor glider that was designed by Dieter Reich and is provided in the form of plans by Entwicklung und Erprobung von Leichtflugzeugen for amateur construction.
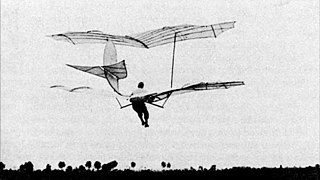
Otto Lilienthal's Large Biplane glider was designed and built in 1895 as an advanced stage of the Lilienthal Normalsegelapparat – a monoplane glider invented by Otto Lilienthal. The Normalsegelapparat, patented in 1893, was the first production aircraft in history. Like its preceding model, the Large Biplane is a hang glider which is controlled through weight-shift by the pilot, as hang gliders are to this day.
References
- 1 2 Bertrand, Noel; Rene Coulon; et al: World Directory of Leisure Aviation 2003-04, page 136. Pagefast Ltd, Lancaster OK, 2003. ISSN 1368-485X
- 1 2 Entwicklung und Erprobung von Leichtflugzeugen. "ULF 2 Description". Archived from the original on 9 September 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2015.
- ↑ Entwicklung und Erprobung von Leichtflugzeugen. "About Us". Archived from the original on 31 August 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2015.
- ↑ Entwicklung und Erprobung von Leichtflugzeuge. "ULF 1 Description". Archived from the original on 9 September 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2015.