Related Research Articles

Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests at present. This is one-third less than the forest cover before the expansion of agriculture, a half of that loss occurring in the last century. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Bangladesh, are destroyed every year. On average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute.

Resource depletion is the consumption of a resource faster than it can be replenished. Natural resources are commonly divided between renewable resources and non-renewable resources. Use of either of these forms of resources beyond their rate of replacement is considered to be resource depletion. The value of a resource is a direct result of its availability in nature and the cost of extracting the resource, the more a resource is depleted the more the value of the resource increases. There are several types of resource depletion, the most known being: Aquifer depletion, deforestation, mining for fossil fuels and minerals, pollution or contamination of resources, slash-and-burn agricultural practices, soil erosion, and overconsumption, excessive or unnecessary use of resources.

Environmental issues in Mali include desertification, deforestation, soil erosion, drought, and inadequate supplies of potable water. Deforestation is an especially serious and growing problem. According to the Ministry of the Environment, Mali’s population consumes 6 million tons of wood per year for timber and fuel. To meet this demand, 4,000 square kilometers of tree cover are lost annually, virtually ensuring destruction of the country’s savanna woodlands.

Environmental issues in Haiti include a historical deforestation problem, overpopulation, a lack of sanitation, natural disasters, and food insecurity. The major reasons for these environmental issues are corruption, foreign intervention by the U.S and human exploitation, and the embezzlement of taxpayers' funds for personal gains. In addition, there is not sufficient protection or management of the country's natural resources. Other environmental issues, such as decreases in precipitation and more severe natural disasters, will likely arise in Haiti as a result of climate change. Experts agree that Haiti needs to adopt new policies to address both the issues that already exist and to prepare for the effects of climate change.
Environmental issues in Paraguay include deforestation.

Environmental issues can be defined as the harmful effects of any human activity on the environment. African environmental issues are caused by anthropogenic effects on the African natural environment and have major impacts on humans and nearly all forms of endemic life. Issues include for example deforestation, soil degradation, air pollution, water pollution, garbage pollution climate change and water scarcity. Nearly all of Africa's environmental problems are geographically variable and human induced.

The Indian wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf that ranges from Southwest Asia to the Indian Subcontinent. It is intermediate in size between the Himalayan wolf and the Arabian wolf, and lacks the former's luxuriant winter coat due to it living in warmer conditions. Within this subspecies, the "Indian plains wolf" is genetically basal to all other extant Canis lupus apart from the older-lineage Himalayan wolf, with both proposed as separate species. The Indian wolf travels in smaller packs and is less vocal than other variants of the gray wolf, and has a reputation for being cunning. The Indian wolf is one of the most endangered populations of gray wolf in the world.

The Himalayan wolf is a canine of debated taxonomy. It is distinguished by its genetic markers, with mitochondrial DNA indicating that it is genetically basal to the Holarctic gray wolf, genetically the same wolf as the Tibetan and Mongolian wolf, and has an association with the African wolf. No striking morphological differences are seen between the wolves from the Himalayas and those from Tibet. The Himalayan wolf lineage can be found living in Ladakh in the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, and the mountains of Central Asia predominantly above 4,000 m (13,000 ft) in elevation because it has adapted to a low-oxygen environment, compared with other wolves that are found only at lower elevations.
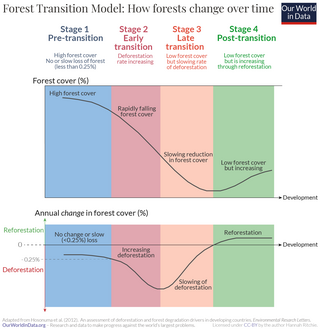
Forest transition refers to a geographic theory describing a reversal or turnaround in land-use trends for a given territory from a period of net forest area loss to a period of net forest area gain. The term "landscape turnaround" has also been used to represent a more general recovery of natural areas that is independent of biome type.

The composition of Madagascar's wildlife reflects the fact that the island has been isolated for about 88 million years. The prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana separated the Madagascar-Antarctica-India landmass from the Africa-South America landmass around 135 million years ago. Madagascar later split from India about 88 million years ago, allowing plants and animals on the island to evolve in relative isolation.

Deforestation in Ethiopia is due to locals clearing forests for their personal needs, such as for fuel, hunting, agriculture, and sometimes religious reasons. The main causes of deforestation in Ethiopia are shifting agriculture, livestock production and fuel in drier areas. Deforestation is the process of removing the forest ecosystem by cutting the trees and changing the shape of the land to suit different uses.

Malaysia faces several environmental issues. Malaysia's environment possesses megadiverse biological diversity, with globally significant endemism and biodiversity, but is threatened by several issues. Deforestation is a major issue in the country that has led to many species becoming threatened with extinction. As a major economic sector, palm oil production has had a substantial environmental impact. Air pollution is also a major issue, with the country one of the most affected countries by seasonal Southeast Asian haze. The country is also affected by climate change.

Rates and causes of deforestation vary from region to region around the world. In 2009, two-thirds of the world's forests were located in just 10 countries: Russia, Brazil, Canada, The United States, China, Australia, The Democratic Republic of the Congo, Indonesia, India, and Peru.
Like other island nations, Antigua and Barbuda faces unique environmental issues created by its proximity to the ocean, and small size. These include pressures on water resources, natural ecosystems, and deforestation more generally.
The principal environmental issues in Peru are water pollution, soil erosion, pollution and deforestation. Although these issues are problematic and equally destructive, the Peruvian Environmental ministry has been developing regulation and laws to decrease the amount of pollution created in major cities and have been making policies in order to decrease the present deforestation rate in Peru.
Cuba has an environment which includes very wide variety of different natural habitats and is home to large number of species, many of them endangered. Since the arrival of European settlers Cuba has suffered from deforestation as a result of more and more forest area being taken over by humans to use them for agricultural production. Cutting down trees for firewood and to obtain materials for building has contributed to the loss of forests and extinction of some species. Environmental awareness has since increased in Cuba and in the late 1990s and in the 2000s Cuban government has started new programs to protect the environment and to increase forest coverage.

William F. Laurance, also known as Bill Laurance, is Distinguished Research Professor at James Cook University, Australia and has been elected as a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Science. He has received an Australian Laureate Fellowship from the Australian Research Council. He held the Prince Bernhard Chair for International Nature Conservation at Utrecht University, Netherlands from 2010 to 2014.

The environment of North Korea comprises the diverse ecosystems of the part of the Korean peninsula controlled by the Democratic People's Republic of Korea. This includes alpine, forest, farmland, freshwater, and marine ecosystems.
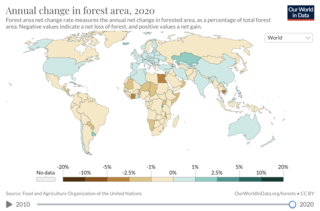
Deforestation is a primary contributor to climate change. Land use changes, especially in the form of deforestation, are the second largest anthropogenic source of atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions, after fossil fuel combustion. Greenhouse gases are emitted during combustion of forest biomass and decomposition of remaining plant material and soil carbon. Global models and national greenhouse gas inventories give similar results for deforestation emissions. As of 2019, deforestation is responsible for about 11% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon emissions from tropical deforestation are accelerating. Growing forests are a carbon sink with additional potential to mitigate the effects of climate change. Some of the effects of climate change, such as more wildfires, may increase deforestation. Deforestation comes in many forms: wildfire, agricultural clearcutting, livestock ranching, and logging for timber, among others. The vast majority of agricultural activity resulting in deforestation is subsidized by government tax revenue. Forests cover 31% of the land area on Earth and annually 75,700 square kilometers of the forest is lost. According to the World Resources Institute, there was a 12% increase in the loss of primary tropical forests from 2019 to 2020. Mass deforestation continues to threaten tropical forests, their biodiversity, and the ecosystem services they provide. The main area of concern of deforestation is in tropical rain forests since they are home to the majority of the planet's biodiversity.
Senegal's environmental issues are varied. According to the CIA world factbook pressing problems exist with: diminishing wildlife populations which are threatened by poaching, deforestation, overgrazing, soil erosion, desertification, and overfishing.
References
This article needs additional citations for verification .(April 2009) |
- ↑ Amber Henshaw, "Rare zoo lion cubs poisoned", BBC News website, originally published 22 November 2006 (accessed 8 January 2010)
- ↑ Grantham, H. S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T. D.; Jones, K. R.; Beyer, H. L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J. C.; Robinson, J. G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H. M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P. R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P.; Goldman, E.; Goetz, S.; Hansen, A.; Hofsvang, E.; Jantz, P.; Jupiter, S.; Kang, A.; Langhammer, P.; Laurance, W. F.; Lieberman, S.; Linkie, M.; Malhi, Y.; Maxwell, S.; Mendez, M.; Mittermeier, R.; Murray, N. J.; Possingham, H.; Radachowsky, J.; Saatchi, S.; Samper, C.; Silverman, J.; Shapiro, A.; Strassburg, B.; Stevens, T.; Stokes, E.; Taylor, R.; Tear, T.; Tizard, R.; Venter, O.; Visconti, P.; Wang, S.; Watson, J. E. M. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity - Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3 . ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057 . PMID 33293507.
- Haileselassie, A. (2004) “Ethiopia’s struggle over land reform,” World Press Review 51.4, 32(2). Expanded Academic ASAP.
- Hillstrom, K. & Hillstrom, C. (2003). Africa and the Middle east; a continental Overview of Environmental Issues. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO.
- Maddox, G.H. (2006). Sub-Saharan Africa: An environmental history. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO.
- McCann.J.C.(1990). "A Great Agrarian cycle? Productivity in Highland Ethiopia, 1900–1987," Journal of Interdisciplinary History, 20:3, pp. 389–416. (Retrieved November 18, 2006 from JSTOR database)
- McCann, J.C. (1999). Green land, Brown land, Black land: An environmental history of Africa 1800–1990. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann.
- Mongabay.com "Ethiopia statistics." (Retrieved November 18, 2006)
- Parry, J (2003). "Tree choppers become tree planters," Appropriate Technology, 30(4), 38–39. Retrieved November 22, 2006, from ABI/INFORM Global database. (Document ID: 538367341)
- Parry, K (2003) "Perceptions of forest cover and tree planting and ownership in Jimma Zone, Ethiopia” unasylva, vol 54 Iss: 213 (2003), pp. 18(2).
- Sucoff, E. (2003). "Deforestation", Environmental Encyclopedia, at pp. 358–359. Detroit: Gale.
- Williams, M. (2006). Deforesting the earth: From prehistory to global crisis: An Abridgment. Chicago: University Press.