Related Research Articles

Ashkenazi Jews, also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim, constitute a Jewish diaspora population that emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. They traditionally spoke Yiddish and largely migrated towards northern and eastern Europe during the late Middle Ages due to persecution. Hebrew was primarily used as a literary and sacred language until its 20th-century revival as a common language in Israel.
Y-chromosomal Aaron is the name given to the hypothesized most recent common ancestor of the patrilineal Jewish priestly caste known as Kohanim. According to the traditional understanding of the Hebrew Bible, this ancestor was Aaron, the brother of Moses.
Jewish ethnic divisions refer to many distinctive communities within the world's Jewish population. Although considered a self-identifying ethnicity, there are distinct ethnic subdivisions among Jews, most of which are primarily the result of geographic branching from an originating Israelite population, mixing with local communities, and subsequent independent evolutions.
The Genographic Project, launched on 13 April 2005 by the National Geographic Society and IBM, was a genetic anthropological study that aimed to map historical human migrations patterns by collecting and analyzing DNA samples. The final phase of the project was Geno 2.0 Next Generation. Upon retirement of the site, 1,006,542 participants in over 140 countries had joined the project.

The Thirteenth Tribe is a 1976 book by Arthur Koestler advocating the Khazar hypothesis of Ashkenazi ancestry, the thesis that Ashkenazi Jews are not descended from the historical Israelites of antiquity, but from Khazars, a Turkic people. Koestler hypothesized that the Khazars migrated westwards into Eastern Europe in the 12th and 13th centuries when the Khazar Empire was collapsing.

In population genetics, an ancestry-informative marker (AIM) is a single-nucleotide polymorphism that exhibits substantially different frequencies between different populations. A set of many AIMs can be used to estimate the proportion of ancestry of an individual derived from each population.
Haplogroup K, formerly Haplogroup UK, is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is defined by the HVR1 mutations 16224C and 16311C. It is now known that K is a subclade of U8.
Harry Ostrer is a medical geneticist who investigates the genetic basis of common and rare disorders. In the diagnostic laboratory, he translates the findings of genetic discoveries into tests that can be used to identify people's risks for disease prior to occurrence, or for predicting its outcome once it has occurred. He is also known for his study, writing and lectures on the origins of the Jewish people.

Shlomo Sand is an Israeli Emeritus Professor of History at Tel Aviv University.
Haplogroup H is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. The clade is believed to have originated in Southwest Asia, near present day Syria, around 20,000 to 25,000 years ago. Mitochondrial haplogroup H is today predominantly found in Europe, and is believed to have evolved before the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). It first expanded in the northern Near East and Southern Caucasus, and later migrations from Iberia suggest that the clade reached Europe before the Last Glacial Maximum. The haplogroup has also spread to parts of Africa, Siberia and Inner Asia. Today, around 40% of all maternal lineages in Europe belong to haplogroup H.
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup K1a1b1a is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.
The medical genetics of Jews have been studied to identify and prevent some rare genetic diseases that, while still rare, are more common than average among people of Jewish descent. There are several autosomal recessive genetic disorders that are more common than average in ethnically Jewish populations, particularly Ashkenazi Jews, because of relatively recent population bottlenecks and because of consanguineous marriage. These two phenomena reduce genetic diversity and raise the chance that two parents will carry a mutation in the same gene and pass on both mutations to a child.
Genetic studies of Jews are part of the population genetics discipline and are used to analyze the chronology of Jewish migration accompanied by research in other fields, such as history, linguistics, archaeology, and paleontology. These studies investigate the origins of various Jewish ethnic divisions. In particular, they examine whether there is a common genetic heritage among them. The medical genetics of Jews are studied for population-specific diseases.

The genetic history of Italy is greatly influenced by geography and history. The ancestors of Italians were mostly Indo-European speaking peoples and pre-Indo-European speakers. During the Roman empire, the Italian peninsula attracted people from various regions of the Mediterranean basin, including Southern Europe, North Africa and the Middle East. Based on DNA analysis, there is evidence of ancient regional genetic substructure and continuity within modern Italy dating to the pre-Roman and Roman periods.
Listed here are notable ethnic groups and populations from Western Asia, Egypt and South Caucasus by human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups based on relevant studies. The samples are taken from individuals identified with the ethnic and linguistic designations in the first two columns, the third column gives the sample size studied, and the other columns give the percentage of the particular haplogroup. Some old studies conducted in the early 2000s regarded several haplogroups as one haplogroup, e.g. I, G and sometimes J were haplogroup 2, so conversion sometimes may lead to unsubstantial frequencies below.

The Invention of the Jewish People is a study of Jewish historiography by Shlomo Sand, Professor of History at Tel Aviv University. It has generated a heated controversy. The book was on the best-seller list in Israel for nineteen weeks.
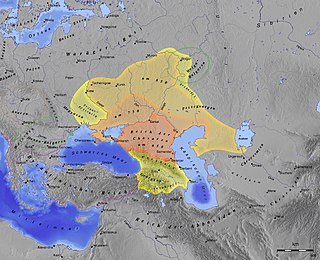
The Khazar hypothesis of Ashkenazi ancestry, often called the Khazar myth by its critics, is a largely abandoned historical hypothesis that postulated that Ashkenazi Jews were primarily, or to a large extent, descended from Khazars, a multi-ethnic conglomerate of mostly Turkic peoples who formed a semi-nomadic khanate in and around the northern and central Caucasus and the Pontic–Caspian steppe. The hypothesis also postulated that after collapse of the Khazar empire, the Khazars fled to Eastern Europe and made up a large part of the Jews there. The hypothesis draws on medieval sources such as the Khazar Correspondence, according to which at some point in the 8th–9th centuries, a small number of Khazars were said by Judah Halevi and Abraham ibn Daud to have converted to Rabbinic Judaism. The scope of the conversion within the Khazar Khanate remains uncertain, but the evidence used to tie the subsequent Ashkenazi communities to the Khazars is meager and subject to conflicting interpretations.
Paul Wexler is an American-born Israeli linguist, and Professor Emeritus of linguistics at Tel Aviv University. His research fields include historical linguistics, bilingualism, Slavic linguistics, creole linguistics, Romani and Jewish languages.
Itsik Pe'er is a computational biologist and a Full Professor in the Department of Computer Science at Columbia University.
In the late 19th century, amid attempts to apply science to notions of race, some advocates of Zionism sought to reformulate conceptions of Jewishness in terms of racial identity and the "race science" of the time. They believed that this concept would allow them to build a new framework for collective Jewish identity, and thought that biology might provide "proof" for the "ethnonational myth of common descent" from the biblical land of Israel. Countering antisemitic claims that Jews were both aliens and a racially inferior people who needed to be segregated or expelled, these Zionists drew on and appropriated elements from various race theories, to argue that only a Jewish national home could enable the physical regeneration of the Jewish people and a renaissance of pride in their ancient cultural traditions.
References
- ↑ About Ancient DNA Origins, 2020
- ↑ Christine Kenneally, The Invisible History of the Human Race: How DNA and History Shape Our Identities and Our Futures, Penguin Books, 2014 ISBN 978-0-698-17629-4:'In 2011 Eran Elhaik was hired to solve one of the biggest jigsaw puzzles in the history of the human race. ‘Following the failed Human Genome Diversity Project, National Geographic launched the Genographic Project in 2005 to develop a way of reading people's Y chromosome and mttDNA). In 2011 Genographic decided to include all the chromosomes and analyse autosomal DNA as well. Elhaik was asked to design a method that would extract the most information from a sample but at the same time extract only historical information and not anything to do with an individual's health or features.'
- ↑ "Dr Eran Elhaik". University of Sheffield.
- ↑ Eran Elhaik, Lund University
- ↑ "Eran Elhaik – new senior lecturer". Biologibloggen. 7 November 2019.
- ↑ Elhaik, Eran; Graur, Dan; Josić, Krešimir; Landan, Giddy (2010). "Identifying compositionally homogeneous and nonhomogeneous domains within the human genome using a novel segmentation algorithm". Nucleic Acids Research. 38 (15): e158. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq532. PMC 2926622 . PMID 20571085.
- ↑ Elhaik, Eran; Zandi, Peter (2015). "Dysregulation of the NF-κB pathway as a potential inducer of bipolar disorder". Journal of Psychiatric Research. 70: 18–27. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.08.009. PMID 26424419.
- ↑ Elhaik, Eran (2016). "A 'Wear and Tear' Hypothesis to Explain Sudden Infant Death Syndrome". Frontiers in Neurology. 7: 180. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00180 . PMC 5083856 . PMID 27840622.
- ↑ "Genome Biology and Evolution | Oxford Academic".
- ↑ Chanda, P; Elhaik, E; Bader, JS (27 July 2012). "HapZipper: sharing HapMap populations just got easier". Nucleic Acids Research . 40 (20): e159. doi:10.1093/nar/gks709. PMC 3488212 . PMID 22844100.
- ↑ Conversations with Eran Elhaik: Tracking ancient migrations Scientific Inquirer 6 July 2017
- ↑ Elhaik, E (1 January 2013). "The missing link of Jewish European ancestry: Contrasting the Rhineland and the Khazarian hypotheses". Genome Biology and Evolution . 5 (1): 61–74. doi:10.1093/gbe/evs119. PMC 3595026 . PMID 23241444.
- ↑ Das, R (19 April 2016). "Localizing Ashkenazic Jews to Primeval Villages in the Ancient Iranian Lands of Ashkenaz". Genome Biology and Evolution . 8 (7): 1132–49. doi:10.1093/gbe/evw046. PMC 4860683 . PMID 26941229.
- ↑ Elhaik, E (5 August 2016). "In search of the jüdische Typus: A Proposed Benchmark to Test the Genetic Basis of Jewishness Challenges Notions of "Jewish Biomarkers"". frontiers in Genetics . 7 (141): 141. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00141 . PMC 4974603 . PMID 27547215.
- ↑ Elhaik, E (1 January 2013). "The missing link of Jewish European ancestry: Contrasting the Rhineland and the Khazarian hypotheses". Genome Biology and Evolution . 5 (1): 61–74. doi:10.1093/gbe/evs119. PMC 3595026 . PMID 23241444.
- ↑ Marshall, S (16 November 2016). "Reconstructing Druze population history". Scientific Reports . 6 (35837): 35837. Bibcode:2016NatSR...635837M. doi:10.1038/srep35837. PMC 5111078 . PMID 27848937.
- ↑ Keys, David (20 April 2016). "Scientists reveal Jewish history's forgotten Turkish roots". The Independent .
- ↑ Ranajit Das, Paul Wexler, Mehdi Pirooznia and Eran Elhaik,'The Origins of Ashkenaz, Ashkenazic Jews, and Yiddish,' Frontiers in Genetics 21 June 2017
- ↑ Elhaik, Eran; Tatarinova, Tatiana; Chebotarev, Dmitri; Piras, Ignazio S; Calò, Carla Maria; De Montis, Antonella; Atzori, Manuela; Marini, Monica; Tofanelli, Sergio; Francalacci, Paolo; Pagani, Luca; Tyler-Smith, Chris; Xue, Yali; Cucca, Francesco; Schurr, Theodore G.; Gaieski, Jill B.; Melendez, Carlalynne; Vilar, Miguel G.; Owings, Amanda C.; Gómez, Rocío; Fujita, Ricardo; Santos, Fabrício R.; Comas, David; Balanovsky, Oleg; Balanovska, Elena; Zalloua, Pierre; Soodyall, Himla; Pitchappan, Ramasamy; GaneshPrasad, ArunKumar; Hammer, Michael; Matisoo-Smith, Lisa; Wells, Spencer R.; The Genographic Consortium (2014). "Geographic population structure analysis of worldwide human populations infers their biogeographical origins". Nature Communications. 5: 3513. Bibcode:2014NatCo...5.3513.. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4513 . PMC 4007635 . PMID 24781250.
- 1 2 3 Rubin, Rita (7 May 2013). "'Jews a Race' Genetic Theory Comes Under Fierce Attack by DNA Expert".
- ↑ Umberto Esposito, Ranajit Das, Syakir Syed, Mehdi Pirooznia, and Eran Elhaik, 'Ancient Ancestry Informative Markers for Identifying Fine-Scale Ancient Population Structure in Eurasians,' Genes (Basel) 9 December 2018 vol. 9 (12): 625
- ↑ Sara Behnamian, Umberto Esposito, Grace Holland, Mehdi Pirooznia, Conrad Brimacombe, Eran Elhaik, 'Temporal population structure, a genetic dating method for ancient Eurasian genomes from the past 10,000 years,' Cell Reports Methods, Vol. 2, Issue 8, August 2022
- ↑ Elhaik, Eran (2022). "Principal Component Analyses (PCA)‑based findings in population genetic studies are highly biased and must be". Scientific Reports . 12 (1). 14683. Bibcode:2022NatSR..1214683E. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14395-4 . PMC 9424212 . PMID 36038559.
- ↑ Scientific Reports in 2022, Scientific Reports 2023
- ↑ Behar, Doron M.; Mespalu, Mait; Baran, Yael; Kopelman, Naama M. S; Yunusbayev, Bayazit; Gladstein, Ariella; Tzur, Shay; Sahakyan, Hovhannes; Bahmanimehr, Ardeshir; Yepiskoposyan, Levon; Tambets, Kristiina; Khusnutdinova, Elza K.; Kushiniarevich, Alena; Balanovsky, Oleg; Balanovsky, Elena; Kovacevic, Lejla; Marjanovic, Damir; Mihailov, Evelin; Kouvasti, Anastasia; Triantaphylldis, Costas; King, Roy J.; Semino, Ornella; Torroni, Antonio; Hammer, Michael F.; Metspalu, Ene; Skorecki, Karl; Rosset, Saharon; Halperin, Eran; Willems, Richard; Rosenberg, Noah A. (2013). "No Evidence from Genome-Wide Data of a Khazar Origin for the Ashkenazi Jews". Human Biology. 85 (6): 859–900. doi:10.3378/027.085.0604. PMID 25079123. S2CID 2173604.
- ↑ Flegontov, Pavel; Kassian, Alexei; Thomas, Mark G.; Fedchenko, Valentina; Changmai, Piya; Starostin, George (2016). "Pitfalls of the Geographic Population Structure (GPS) Approach Applied to Human Genetic History: A Case Study of Ashkenazi Jews". Genome Biology and Evolution. 8 (7): 2259–2265. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw162 . PMC 4987117 . PMID 27389685.
- ↑ Aptroot, Marion (2016). "Yiddish Language and Ashkenazic Jews: A Perspective from Culture, Language, and Literature". Genome Biology and Evolution. 8 (6): 1948–1949. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw131 . PMC 4943202 . PMID 27289098.
- ↑ Kutzik, Jordan (28 April 2016). "Don't Buy the Junk Science That Says Yiddish Originated in Turkey". The Forward . Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ↑ Thomas, Matthew (12 May 2014). "So many genes, so close to home". BioNews (Issue 753). Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ↑ Liphshiz, Cnaan (3 May 2016). "Scholars dismiss theory tracing Ashkenazi Jews to Turkey". The Canadian Jewish News . Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ↑ Ostrer, Harry (11 September 2017). "How 23andMe Fell For Anti-Semitic 'Khazar' Canard". The Forward. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ↑ Beider, Alexander (25 September 2017). "Ashkenazi Jews Are Not Khazars.Here's The Proof". The Forward . Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ↑ Yardumian, Aram; Schurr, Theodore G. (June 2019). "The Geography of Jewish Ethnogenesis". Journal of Anthropological Research. 75 (2): 206–234. doi:10.1086/702709. S2CID 167051866.
- ↑ Elhaik, Eran (2017). "Editorial: Population Genetics of Worldwide Jewish People". Frontiers in Genetics. 8: 101. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00101 . PMC 5532521 . PMID 28804494.
- ↑ Elhaik, Eran (29 August 2022). "Principal Component Analyses (PCA)-based findings in population genetic studies are highly biased and must be reevaluated". Scientific Reports. 12 (1). Bibcode:2022NatSR..1214683E. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-14395-4. PMC 9424212 .
- ↑ Falk, Raphael (21 January 2015). "Genetic markers cannot determine Jewish descent". Frontiers in Genetics. 5. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00462 . PMC 4301023 .
- ↑ Falk, Raphael (21 January 2015). "Genetic markers cannot determine Jewish descent". Frontiers in Genetics. 5. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00462 . PMC 4301023 .