
Kniphofia is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Asphodelaceae, first described as a genus in 1794. Species are native to Africa. Common names include tritoma, red hot poker, torch lily and poker plant.

Protea gaguedi is a species of tree which belongs to the genus Protea.

Eriosema is a genus of legume in the family Fabaceae. Accepted species number over 150. The genus is widespread in tropics.

Isoglossa woodii, commonly known as buckweed, is a monocarpic shrub of the family Acanthaceae, growing up to 4 m tall. It grows in colonies in coastal forest areas of KwaZulu-Natal and marginally into Eastern Cape, South Africa.

Croton sylvaticus is a tree in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is commonly known as the forest fever-berry. These trees are distributed in forests from the east coast of South Africa to Tropical Africa. It grows 7–13 metres (23–43 ft) in height, occasionally up to 30 metres (100 ft), in moist forests, thickets and forest edges at altitudes of 350–1,800 metres (1,100–5,900 ft).

Mimusops caffra is a species of tree in family Sapotaceae. This tree is found in coastal dune vegetation in Southern Africa from the Eastern Cape, through KwaZulu-Natal to southern Mozambique.

Deinbollia oblongifolia is a shrub or small tree in the family Sapindaceae. It is commonly known as the dune soap-berry and is found in coastal vegetation from the Eastern Cape of South Africa, through KwaZulu-Natal to southern Mozambique and Eswatini. It is named after Peter Vogelius Deinboll (1783-1876), a Danish botanist and plant collector.
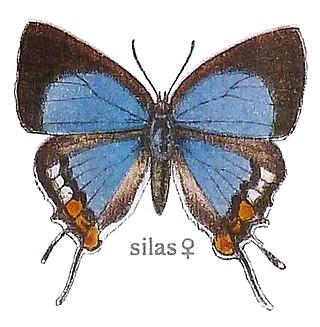
Iolaus silas, the southern sapphire, is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae which is endemic to South Africa.

Iolaus silarus, the straight-line sapphire, is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. The species was first described by Hamilton Herbert Druce in 1885. It is found in Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Namibia, Malawi, Zambia, southern Zaire, Tanzania, south-western Kenya and South Africa. In South Africa it is found in wooded savannah in northern KwaZulu-Natal and in savannah from Eswatini to Mpumalanga, Limpopo and North West. It is also present in Afromontane forest on the Wolkberg and the northern Drakensberg.

Capparis tomentosa, the woolly caper bush or African caper, is a plant in the Capparaceae family and is native to Africa.

Capparis fascicularis, the zigzag caper-bush, is a plant in the Capparaceae family and is native to Africa.

Dalbergia obovata is a robust shrub or climber in the family Fabaceae, and is native to Southern Africa.

Pereskia aculeata is a scrambling shrub in the family Cactaceae. Common names include Barbados gooseberry, blade-apple cactus, leaf cactus, rose cactus, and lemonvine. It is native to tropical America. The leaves and fruits are edible, containing high quantities of protein, iron and other nutrients, and it is a popular vegetable in parts of the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais under the name of ora-pro-nóbis.

Tragia durbanensis, the stinging nettle creeper, is a twining herb in the family Euphorbiaceae, with a restricted distribution in southern Africa. There are some 150 species in the genus Tragia.

Mikania natalensis, the Natal mikania, is a plant in the family Asteraceae, and is native to Africa.

Dalbergia armata is a scrambling, deciduous species of legume that is native to subtropical to temperate regions of southeastern Africa. The robust, woody liana or small tree is armed with strong spines on the main stem and branches. It occurs sparsely or commonly in forest, bush, riparian fringes and in wooded ravines. It is sometimes employed as a bonsai subject, and it can be propagated from either seed or cuttings.

Boscia foetida, commonly known as the stink shepherd's tree and the smelly shepherd's bush, is an evergreen shrub or tree that is native to the warmer and drier parts southern Africa. It is found in semi-desert and arid bushveld, and in the west it occurs commonly in areas which are otherwise sparsely wooded. It is known for the particularly unpleasant smell of its flowers which appear during early spring, to which its specific name foetida alludes. Its freshly cut wood likewise has an unpleasant smell, and has traditional medicinal and magical uses, for instance as a protection against lightning. In central Botswana the village of Mopipi is named after this species.

Cola greenwayi, commonly known as hairy cola or Zulu coshwood, is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae. It was first described in 1956 by the British botanist John Patrick Micklethwait Brenan. It is native to southeastern Africa.
Drypetes gerrardii is a species of small tree or large shrub in the family Putranjivaceae. Common names include forest ironplum, bastard white ironwood, and forest ironwood. It is native to tropical and subtropical central and eastern Africa. It was first described in 1920 by the English botanist John Hutchinson, who named it after the English botanist William Tyrer Gerrard who collected plants and seeds in southern Africa in the 1860s.




















