Related Research Articles

A mouth ulcer (aphtha) is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanisms, but usually there is no serious underlying cause. Rarely, a mouth ulcer that does not heal may be a sign of oral cancer. These ulcers may form individually or multiple ulcers may appear at once. Once formed, an ulcer may be maintained by inflammation and/or secondary infection.
The third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is the most posterior of the three molars in each quadrant of the human dentition. The age at which wisdom teeth come through (erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens and early twenties. Most adults have four wisdom teeth, one in each of the four quadrants, but it is possible to have none, fewer, or more, in which case the extras are called supernumerary teeth. Wisdom teeth may become stuck (impacted) against other teeth if there is not enough space for them to come through normally. Impacted wisdom teeth are still sometimes removed for orthodontic treatment, believing that they move the other teeth and cause crowding, though this is not held anymore as true.
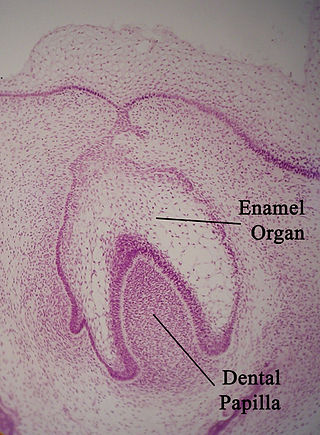
The enamel organ, also known as the dental organ, is a cellular aggregation seen in a developing tooth and it lies above the dental papilla. The enamel organ which is differentiated from the primitive oral epithelium lining the stomodeum. The enamel organ is responsible for the formation of enamel, initiation of dentine formation, establishment of the shape of a tooth's crown, and establishment of the dentoenamel junction.
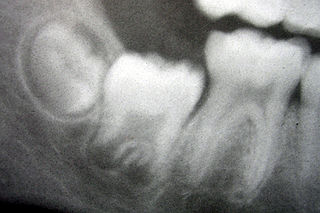
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stages of fetal development. Primary (baby) teeth start to form between the sixth and eighth week of prenatal development, and permanent teeth begin to form in the twentieth week. If teeth do not start to develop at or near these times, they will not develop at all, resulting in hypodontia or anodontia.

The dental follicle, also known as dental sac, is made up of mesenchymal cells and fibres surrounding the enamel organ and dental papilla of a developing tooth. It is a vascular fibrous sac containing the developing tooth and its odontogenic organ. The dental follicle (DF) differentiates into the periodontal ligament. In addition, it may be the precursor of other cells of the periodontium, including osteoblasts, cementoblasts and fibroblasts. They develop into the alveolar bone, the cementum with Sharpey's fibers and the periodontal ligament fibers respectively. Similar to dental papilla, the dental follicle provides nutrition to the enamel organ and dental papilla and also have an extremely rich blood supply.
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed lamina propria. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved.

Oral mucocele is a condition caused by two related phenomena - mucus extravasation phenomenon and mucous retention cyst.

Pericoronitis is inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth, including the gingiva (gums) and the dental follicle. The soft tissue covering a partially erupted tooth is known as an operculum, an area which can be difficult to access with normal oral hygiene methods. The hyponym operculitis technically refers to inflammation of the operculum alone.
An oral medicine or stomatology doctor/dentist has received additional specialized training and experience in the diagnosis and management of oral mucosal abnormalities including oral cancer, salivary gland disorders, temporomandibular disorders and facial pain, taste and smell disorders; and recognition of the oral manifestations of systemic and infectious diseases. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry. An oral medicine doctor is trained to diagnose and manage patients with disorders of the orofacial region, essentially as a "physician of the mouth".

A dentigerous cyst, also known as a follicular cyst, is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in the reduced enamel epithelium and encloses the crown of an unerupted tooth at the cemento-enamel junction. Fluid is accumulated between reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth.
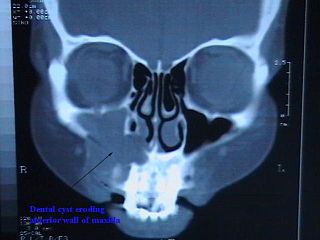
Commonly known as a dental cyst, the periapical cyst is the most common odontogenic cyst. It may develop rapidly from a periapical granuloma, as a consequence of untreated chronic periapical periodontitis.

An odontogenic keratocyst is a rare and benign but locally aggressive developmental cyst. It most often affects the posterior mandible and most commonly presents in the third decade of life. Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19% of jaw cysts.

Calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC) is a rare developmental lesion that comes from odontogenic epithelium. It is also known as a calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor, which is a proliferation of odontogenic epithelium and scattered nest of ghost cells and calcifications that may form the lining of a cyst, or present as a solid mass.
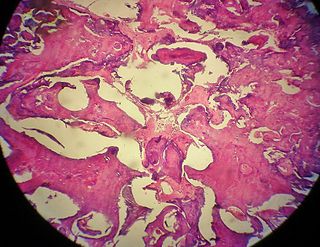
An odontoma, also known as an odontome, is a benign tumour linked to tooth development. Specifically, it is a dental hamartoma, meaning that it is composed of normal dental tissue that has grown in an irregular way. It includes both odontogenic hard and soft tissues. As with normal tooth development, odontomas stop growing once mature which makes them benign.
The junctional epithelium (JE) is that epithelium which lies at, and in health also defines, the base of the gingival sulcus. The probing depth of the gingival sulcus is measured by a calibrated periodontal probe. In a healthy-case scenario, the probe is gently inserted, slides by the sulcular epithelium (SE), and is stopped by the epithelial attachment (EA). However, the probing depth of the gingival sulcus may be considerably different from the true histological gingival sulcus depth.

An impacted tooth is one that fails to erupt into the dental arch within the expected developmental window. Because impacted teeth do not erupt, they are retained throughout the individual's lifetime unless extracted or exposed surgically. Teeth may become impacted because of adjacent teeth, dense overlying bone, excessive soft tissue or a genetic abnormality. Most often, the cause of impaction is inadequate arch length and space in which to erupt. That is the total length of the alveolar arch is smaller than the tooth arch. The wisdom teeth are frequently impacted because they are the last teeth to erupt in the oral cavity. Mandibular third molars are more commonly impacted than their maxillary counterparts.
Epulis is any tumor like enlargement situated on the gingival or alveolar mucosa. The word literally means "(growth) on the gingiva", and describes only the location of the mass and has no further implications on the nature of the lesion. There are three types: fibromatous, ossifying and acanthomatous. The related term parulis refers to a mass of inflamed granulation tissue at the opening of a draining sinus on the alveolus over the root of an infected tooth. Another closely related term is gingival enlargement, which tends to be used where the enlargement is more generalized over the whole gingiva rather than a localized mass.
Odontogenic cyst are a group of jaw cysts that are formed from tissues involved in odontogenesis. Odontogenic cysts are closed sacs, and have a distinct membrane derived from rests of odontogenic epithelium. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. Intra-bony cysts are most common in the jaws, because the mandible and maxilla are the only bones with epithelial components. That odontogenic epithelium is critical in normal tooth development. However, epithelial rests may be the origin for the cyst lining later. Not all oral cysts are odontogenic cysts. For example, mucous cyst of the oral mucosa and nasolabial duct cyst are not of odontogenic origin.
A cyst is a pathological epithelial lined cavity that fills with fluid or soft material and usually grows from internal pressure generated by fluid being drawn into the cavity from osmosis. The bones of the jaws, the mandible and maxilla, are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body. This is due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm, and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during odontogenesis. The bones of the jaws develop from embryologic processes which fuse, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammation is thought to be a major factor. The high prevalence of tooth impactions and dental infections that occur in the bones of the jaws is also significant to explain why cysts are more common at these sites.

Gingival cyst, also known as Epstein's pearl, is a type of cysts of the jaws that originates from the dental lamina and is found in the mouth parts. It is a superficial cyst in the alveolar mucosa. It can be seen inside the mouth as small and whitish bulge. Depending on the ages in which they develop, the cysts are classified into gingival cyst of newborn and gingival cyst of adult. Structurally, the cyst is lined by thin epithelium and shows a lumen usually filled with desquamated keratin, occasionally containing inflammatory cells. The nodes are formed as a result of cystic degeneration of epithelial rests of the dental lamina.
References
- ↑ ESSENTIALS OF ORAL PATHOLOGY BY MEMBERS OF ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT. FACULTY OF DENTISTRY, ALEXANDRIA UNIVERSITY