
Flavonoids are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.

In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of Heliconius butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body.
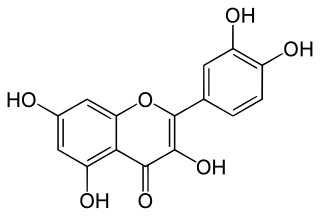
Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of quercetin. Quercetin has a bitter flavor and is used as an ingredient in dietary supplements, beverages, and foods.

Rutin, also called rutoside, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside and sophorin, is the glycoside combining the flavonol quercetin and the disaccharide rutinose. It is a citrus flavonoid found in a wide variety of plants including citrus.
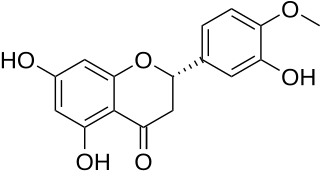
Hesperetin is the 4'-methoxy derivative of eriodictyol, a flavanone. Hesperetin's 7-O-glycoside, hesperidin, is a naturally occurring flavanon-glycoside, the main flavonoid in lemons and sweet oranges. Hesperetin are not found to a significant extent in Citrus spp.

Apigenin (4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone), found in many plants, is a natural product belonging to the flavone class that is the aglycone of several naturally occurring glycosides. It is a yellow crystalline solid that has been used to dye wool.

Erythrophleum is a genus of legume in the family Fabaceae. A partial list of species includes:
In enzymology, a dihydrokaempferol 4-reductase (EC 1.1.1.219) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott, the Japanese pagoda tree is a species of tree in the subfamily Faboideae of the pea family Fabaceae.

Alchornea cordifolia is a shrub or small tree distributed throughout tropical Africa, it can grow up to 8 metres tall. The plant is used in traditional African medicine. Common name is the Christmas bush.

The 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins and their glycosides are molecules with an anthocyanidins backbone lacking an hydroxyl group at position 3 on the C-ring. This nomenclature is the inverse of that which is commonly used in flavonoids, where the hydroxy-group is assumed absent if it is not specified, e. g. flavan-3-ol, flavan-4-ol, flavan-3,4-ol and flavonol.
E. africanum may refer to:

Herbacetin is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid.

Charaxes phaeus, the demon emperor or dusky charaxes, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in southern Africa.
Charaxes vansoni, the Van Son's emperor, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in southern Africa.
Charaxes fulgurata, the lightning charaxes, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in northern Angola, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, north-western Zimbabwe and Zambia.
Charaxes brainei, the Braine's charaxes, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in north-eastern Namibia, southern Angola and north-western Botswana.

Combretum paniculatum, the burning bush or forest flame-creeper, is a plant species in the genus Combretum found in Africa. The fruit is a samara, i.e. a winged seed.

Paullinia pinnata is a flowering plant species in the genus of Paullinia found in South America and Africa.

Eriocitrin is a flavanone-7-O-glycoside between the flavanone eriodictyol and the disaccharide rutinose. It is commonly found in lemons. It is colloquially called lemon flavonoid or a citrus flavonoid, one of the plant pigments that bring color to fruit and flowers. This antioxidant also predominates in Peppermint infusions.














