
Sergei Uasyl-ipa Bagapsh was an Abkhaz politician who served as the second President of Abkhazia from 12 February 2005 until his death on 29 May 2011. He previously served as Prime Minister of Abkhazia from 1997 to 1999. He was re-elected in the 2009 presidential election. Bagapsh's term as prime minister included the 1998 war with Georgia, while he oversaw both the recognition of Abkhazia by Russia and the Russo-Georgian War during his presidency.

Politics in Abkhazia is dominated by its conflict with Georgia. Abkhazia became de facto independent from Georgia after the 1992–1993 war, but its de jure independence has only been recognised by a few other countries. Abkhazia is a presidential representative democratic republic with a multi-party system, wherein the President is both head of state and head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government of the Republic of Abkhazia. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the People's Assembly of Abkhazia.

The Abkhazians or Abkhazes are a Northwest Caucasian ethnic group, mainly living in Abkhazia, a disputed region on the northeastern coast of the Black Sea. A large Abkhaz diaspora population resides in Turkey, the origins of which lie in the Caucasian War in the late 19th century. Many Abkhaz also live in other parts of the former Soviet Union, particularly in Russia and Ukraine.

Sukhumi is a city in a wide bay on the Black Sea's eastern coast. It is both the capital and largest city of the Republic of Abkhazia, a partially recognised state that most countries consider a part of Georgia. The city has been controlled by Abkhazia since the Abkhazian war in 1992–93. The city, which has an airport, is a port, major rail junction and a holiday resort because of its beaches, sanatoriums, mineral-water spas and semitropical climate. It is also a member of the International Black Sea Club.

The history of Abkhazia, a region in the South Caucasus, spans more than 5,000 years from its settlement by the lower-paleolithic hunter-gatherers to its present status as a partially recognized state.

Nestor Apollonovich Lakoba was an Abkhaz communist leader. Lakoba helped establish Bolshevik power in Abkhazia in the aftermath of the Russian Revolution, and served as the head of Abkhazia after its conquest by the Bolshevik Red Army in 1921. While in power, Lakoba saw that Abkhazia was initially given autonomy within the USSR as the Socialist Soviet Republic of Abkhazia. Though nominally a part of the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic with a special status of "union republic," the Abkhaz SSR was effectively a separate republic, made possible by Lakoba's close relationship with Joseph Stalin. Lakoba successfully opposed the extension of collectivization of Abkhazia, though in return Lakoba was forced to accept a downgrade of Abkhazia's status to that of an autonomous republic within the Georgian SSR.

The Socialist Soviet Republic of Abkhazia was a short-lived republic within the Caucasus region of the Soviet Union that covered the territory of Abkhazia, and existed from 31 March 1921 to 19 February 1931. Formed in the aftermath of the Red Army invasion of Georgia in 1921, it was independent until 16 December 1921 when it agreed to a treaty that united it with the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic. The SSR Abkhazia was similar to an autonomous Soviet republic, though it retained nominal independence from Georgia and was given certain features only full union republics had, like its own military units. Through its status as a "treaty republic" with Georgia, Abkhazia joined the Transcaucasian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, which united Armenian, Azerbaijani, and Georgian SSRs into one federal unit when the latter was formed in 1922. The SSR Abkhazia was abolished in 1931 and replaced with the Abkhaz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic within the Georgian SSR.
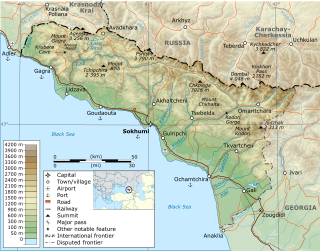
The War in Abkhazia was fought between Georgian government forces for the most part and Abkhaz separatist forces, Russian government armed forces and North Caucasian militants between 1992 and 1993. Ethnic Georgians who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population largely supported the Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists received support from thousands of North Caucasus and Cossack militants and from the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.

The history of the Jews in Abkhazia dates back to the early 19th century. The Jewish population of Abkhazia consisted of Ashkenazi, Georgian and other Jews. It grew after the incorporation of Abkhazia into the Russian Empire in the middle of the 19th century. Most of the Jews left or were evacuated from Abkhazia as a result of the Georgian-Abkhazian conflict of 1992–1993.
Many inhabitants of Abkhazia are Orthodox Christians, With significant minorities adhering to Islam and the Abkhaz neopaganism, or the "Abkhazian traditional religion". The influence of this last has always remained strong and has been experiencing a revival through the 1990s and 2000s.

The economy of Abkhazia is heavily integrated with the economy of Russia and uses the Russian ruble as its currency.

Abkhazia officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state, in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It covers 8,665 square kilometres (3,346 sq mi) and has a population of around 245,000. Its capital and largest city is Sukhumi.
The Armenians in Abkhazia form the second largest ethnic group in Abkhazia after the native Abkhazians. Armenians settled in Abkhazia in late 19th and the early 20th centuries and are now the largest ethnic group in Sukhumi, Gulripsh and Gagra Districts forming 20% of the Abkhazian population with approximately 42,000 out of a total of 242,862.

The Abkhazian Orthodox Church is an Eastern Orthodox church outside the official Eastern Orthodox ecclesiastical hierarchy. It came into existence when the Sukhumi-Abkhazian Eparchy declared on 15 September 2009 that it no longer considered itself part of the Georgian Orthodox Church and that it was "re-establishing the Catholicate of Abkhazia disbanded in 1795". Vissarion Aplaa is the Primate of the Abkhazian Orthodox Church since 2009 and is the self-proclaimed catholicos of the Church. It has two eparchies (dioceses) in Pitsunda and Sukhumi and is organized in 9 parishes.

The Catholic Church in Abkhazia is the third largest Christian denomination in the territory of the Republic of Abkhazia, which is part of the worldwide Catholic Church in communion with the Pope. Most Christians in Abkhazia are Orthodox, see Religion in Abkhazia. Due to Abkhazia's partial recognition, administration of Catholics comes from Catholic dioceses in Russia. The Catholic Church in Abkhazia mainly consists of Armenians, Poles, and expatriates living in Abkhazia. The Holy See does not have diplomatic relations with Abkhazia, but has enjoyed two high level visits from the apostolic nuncio.
The War in Abkhazia from 1992 to 1993 was waged chiefly between Georgian government forces on one side, Russian military forces on other side supporting separatist forces demanding independence of Abkhazia from Georgia. http://www.historyorb.com/russia/georgia.php Ethnic Georgians, who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population, largely supported Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists were supported by thousands of the North Caucasus and Cossack militants and by the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.

Sulevi is a village in Abkhazia, Georgia.

Alam-Linda, meaning 'Upper-Linda' or Kummi küla is a village in Abkhazia, Georgia.
Linda or Ülem-Linda is a village in Abkhazia, Georgia.

Siberian Ingrian Finnish is a Lower Luga Ingrian Finnish – Lower Luga Ingrian (Izhorian) mixed language. The ancestors of the speakers of this language migrated from the Rosona River area to Siberia in 1803–1804. Most native speakers of this language live in Ryzhkovo or nearby, as well as in Omsk and Tallinn (Estonia).















