
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage (NEP). The various islands of the archipelago are separated from one another and from Mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters.

The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and the Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named after Vitus Bering, a Danish navigator in Russian service, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean.

Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of 1,230,000 km2 (470,000 sq mi). It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. It is an inland marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It drains a very large area, about 3,861,400 km2 (1,490,900 sq mi), that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay.

Baffin Island, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is 507,451 km2 (195,928 sq mi) with a population density of 0.03/km²; the population was 13,039 according to the 2021 Canadian census; and it is located at 68°N70°W. It also contains the city of Iqaluit, which is the capital of Nunavut.

The ringed seal is an earless seal inhabiting the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. The ringed seal is a relatively small seal, rarely greater than 1.5 m in length, with a distinctive patterning of dark spots surrounded by light gray rings, hence its common name. It is the most abundant and wide-ranging ice seal in the Northern Hemisphere, ranging throughout the Arctic Ocean, into the Bering Sea and Okhotsk Sea as far south as the northern coast of Japan in the Pacific and throughout the North Atlantic coasts of Greenland and Scandinavia as far south as Newfoundland, and including two freshwater subspecies in northern Europe. Ringed seals are one of the primary prey of polar bears and killer whales, and have long been a component of the diet of indigenous people of the Arctic.
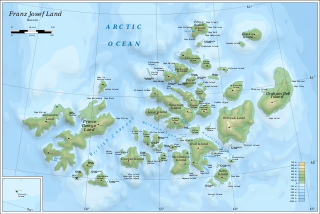
Franz Josef Land is a Russian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. It is inhabited only by military personnel. It constitutes the northernmost part of Arkhangelsk Oblast and consists of 192 islands, which cover an area of 16,134 square kilometers (6,229 sq mi), stretching 375 kilometers (233 mi) from east to west and 234 kilometers (145 mi) from north to south. The islands are categorized in three groups separated by the British Channel and the Austrian Strait. The central group is further divided into a northern and southern section by the Markham Sound. The largest island is Prince George Land, which measures 2,741 square kilometers (1,058 sq mi), followed by Wilczek Land, Graham Bell Island and Alexandra Land.

The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east.

Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.

Severnaya Zemlya is a 37,000 km2 (14,000 sq mi) archipelago in the Russian high Arctic. It lies off Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula, separated from the mainland by the Vilkitsky Strait. This archipelago separates two marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, the Kara Sea in the west and the Laptev Sea in the east.

The Cyclopteridae are a family of marine fishes, commonly known as lumpsuckers or lumpfish, in the order Scorpaeniformes. They are found in the cold waters of the Arctic, North Atlantic, and North Pacific oceans. The greatest number of species are found in the North Pacific. The family name Cyclopteridae derives from the Greek words κύκλος (kyklos), meaning "circle", and πτέρυξ (pteryx), meaning "wing" or "fin", in reference to the circle-shaped pectoral fins of most of the fish in this family.

Sirmilik National Park is a national park located in Qikiqtaaluk, Nunavut, Canada, established in 1999. Situated within the Arctic Cordillera, the park is composed of three areas: most of Bylot Island with the exception for a few areas that are Inuit-owned lands, Kangiqłuruluk, and Baffin Island's Borden Peninsula. Much of the park is bordered by water.

The Pechora Sea is an Arctic sea to the north-west of European Russia, forming the south-eastern portion of the Barents Sea. It is bordered to the west by Kolguyev Island; to the east by Vaygach Island's western coasts and the Yugorsky Peninsula; and to the north by the southern end of Novaya Zemlya.

The bowhead whale is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and is the only living representative of the genus Balaena. It is the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, and is named after its characteristic massive triangular skull, which it uses to break through Arctic ice. Other common names of the species included the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, steeple-top, and polar whale.

Eumicrotremus is a genus of lumpfishes native to the northern oceans. The name for this genus comes from the Greek roots eu meaning "good", mikros meaning "small" or "little", and trema meaning "hole".

Lethotremus is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cyclopteridae, the lumpfishes or lumpsuckers. This genus is found in the northern Pacific Ocean. Following a 2017 taxonomic review by Lee et al., the species Lethotremus awae was reclassified as a species of Eumicrotremus, leaving the genus monotypic with Lethotremus muticus as its only species. Also known as the docked snailfish, is a species of lumpfish native to the Northeast Pacific. It is known from the Bering Sea and the Aleutian Islands, where its range extends to Unimak Pass, and it occurs at a depth range of 58 to 330 m. It is a benthic species that reaches 11.5 cm in total length. It can be found on substrates of mud, rock, or gravel, and it is currently the only known species of Lethotremus, following a reclassification of the second described species in the genus as Eumicrotremus awae.

The Pacific spiny lumpsucker is a species of bony fish in the family Cyclopteridae.
Eumicrotremus andriashevi, also known as the pimpled lumpsucker, is a species of lumpfish native to the Arctic and North Pacific. In addition to the Arctic Ocean, it may be found in the Chukchi and Bering Seas, where it occurs at a depth range of 20 to 83 m. It is a small bottom-dwelling fish that reaches 4.8 cm in standard length.

Eumicrotremus spinosus, commonly known as the Atlantic spiny lumpsucker, is a species of lumpfish native to the Arctic and North Atlantic.
Eumicrotremus jindoensis is a species of lumpfish native to the Northwest Pacific, where it may be found off the coast of the Korean Peninsula and in the Yellow Sea. It occurs at a depth range of 20 to 30 metres, and it reaches 2.5 centimetres (1 in) SL. This species was described in 2017 as part of a review of "dwarf" species of Eumicrotremus, which reclassified the species then known as Lethotremus awae as a member of Eumicrotremus in addition to describing another similarly small new species, known as Eumicrotremus uenoi.
Eumicrotremus tartaricus is a species of lumpfish native to the Northwest Pacific. It is known from the Sea of Japan, the Sea of Okhotsk, Peter the Great Bay, and the Pacific coast of the Kuril Islands, where it may be found at a depth range of 20 to 30 m. It has sometimes been considered a subspecies of the Pacific spiny lumpsucker, but it is generally agreed upon that E. tartaricus represents its own distinct species.
















