
Euphorbia is a very large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the family Euphorbiaceae. "Euphorbia" is sometimes used in ordinary English to collectively refer to all members of Euphorbiaceae, not just to members of the genus.
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists.
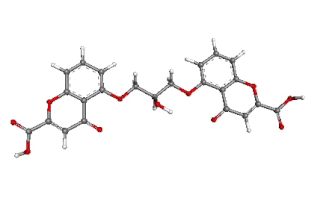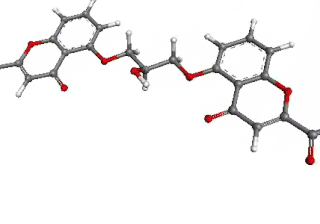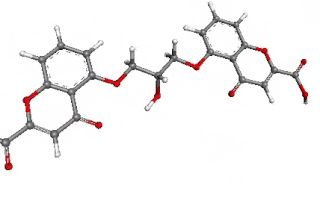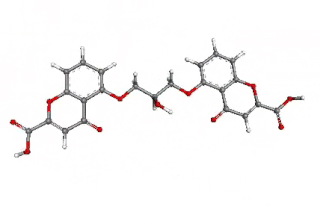
Cromoglicic acid (INN)—also referred to as cromolyn (USAN), cromoglycate, or cromoglicate—is traditionally described as a mast cell stabilizer, and is commonly marketed as the sodium salt sodium cromoglicate or cromolyn sodium. This drug prevents the release of inflammatory chemicals such as histamine from mast cells.

Hydrangea macrophylla is a species of flowering plant in the family Hydrangeaceae, native to Japan. It is a deciduous shrub growing to 2 m (7 ft) tall by 2.5 m (8 ft) broad with large heads of pink or blue flowers in summer and autumn. Common names include bigleaf hydrangea, French hydrangea, lacecap hydrangea, mophead hydrangea, and hortensia. It is widely cultivated in many parts of the world in many climates. It is not to be confused with H. aspera 'Macrophylla'.

Resiniferatoxin (RTX) is a naturally occurring chemical found in resin spurge, a cactus-like plant commonly found in Morocco, and in Euphorbia poissonii found in northern Nigeria. It is a potent functional analog of capsaicin, the active ingredient in chili peppers.

Phorbol is a natural, plant-derived organic compound. It is a member of the tigliane family of diterpenes. Phorbol was first isolated in 1934 as the hydrolysis product of croton oil, which is derived from the seeds of the purging croton, Croton tiglium. The structure of phorbol was determined in 1967. Various esters of phorbol have important biological properties, the most notable of which is the capacity to act as tumor promoters through activation of protein kinase C. They mimic diacylglycerols, glycerol derivatives in which two hydroxyl groups have reacted with fatty acids to form esters. The most common and potent phorbol ester is 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), also called phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), which is used as a biomedical research tool in contexts such as models of carcinogenesis.

Euphorbia peplus, is a species of Euphorbia, native to most of Europe, northern Africa and western Asia, where it typically grows in cultivated arable land, gardens and other disturbed land.

Bifurcaria is a genus of brown algae seaweeds found on rocky North American and European shores and tidepools of the Atlantic Ocean. One species is also found on the shores of the Galapagos Islands in the Pacific Ocean.

Euphorbiaceae, the spurge family, is a large family of flowering plants. In English, they are also commonly called euphorbias, which is also the name of the type genus of the family. Most spurges, such as Euphorbia paralias, are herbs, but some, especially in the tropics, are shrubs or trees, such as Hevea brasiliensis. Some, such as Euphorbia canariensis, are succulent and resemble cacti because of convergent evolution. This family has a cosmopolitan global distribution. The greatest diversity of species is in the tropics; however, the Euphorbiaceae also have many species in nontropical areas of all continents except Antarctica.
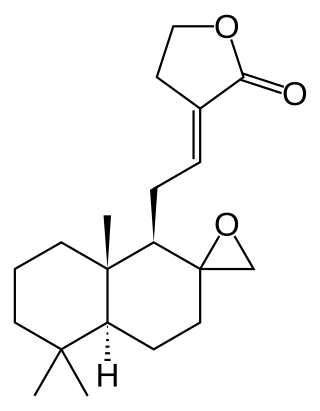
Galanolactone is a diterpenoid lactone first isolated from ginger. It is present in acetone extracts of ginger, and appears to be an antagonist at 5-HT3 receptors.

Taxodone is a naturally occurring diterpenoid found in Taxodium distichum, Rosmarinus officinalis (rosemary), several salvia species and other plants, along with its oxidized rearrangement product, taxodione. Taxodone and taxodione exhibit anticancer, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal, insecticide, and antifeedant activities.

A quinone methide is a type of conjugated organic compound that contain a cyclohexadiene with a carbonyl and an exocyclic methylidene or extended alkene unit. It is analogous to a quinone, but having one of the double bonded oxygens replaced with a carbon. The carbonyl and methylidene are usually oriented either ortho or para to each other. There are some examples of transient synthetic meta quinone methides.

Ingenol mebutate, sold under the brand name Picato, is a substance that is found in the sap of the plant Euphorbia peplus, commonly known as petty spurge, and is an inducer of cell death. This compound was isolated first from this plant in 2000. A gel formulation of the drug has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the topical treatment of actinic keratosis. Two different strengths of the gel have been approved for use on either the face and scalp (0.015%) or the trunk and extremities (0.05%), respectively. In 2020 the drug was withdrawn from the market in the EU.

Punigluconin is an ellagitannin, a polyphenol compound. It is found in the bark of Punica granatum (pomegranate) and in Emblica officinalis. It is a molecule having a hexahydroxydiphenic acid group and two gallic acids attached to a gluconic acid core.
Ecklonia kurome is a brown alga species in the genus Ecklonia found in the Sea of Japan.

Mallotus japonicus, also known as East Asian mallotus, the food wrapper plant or "Akamegashiwa" in Japanese, is a plant species in the genus Mallotus native to China. It is also found in Japan and Korea. This species was first described in 1865, its name was verified by AAS Systematic Botanists on October 2, 2015.

Mallotusinic acid is a hydrolysable tannin found in the bark of Mallotus japonicus. It is more generally present in Geraniales.

Mallojaponin is a hydrolysable tannin found in the bark of Mallotus japonicus. This compound contains the moiety elaeocarpusinic acid, an oxidized hexahydroxydiphenic acid group which reacted with a dehydroascorbic acid molecule. It also contains a valoneic acid and a gallic acid moieties linked to a glucose molecule.
Plaunotol (18-hydroxygeranylgeraniol) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C20H34O2. It is a diterpene that was first isolated from Croton sublyratus.
















