Related Research Articles

Amber is fossilized tree resin, which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects. Amber is used in jewelry. It has also been used as a healing agent in folk medicine.

Hashish, or hash, is a drug made from the resin of the cannabis plant. It is consumed by inhaling from a small piece, typically in a pipe, bong, vaporizer or joint, or via oral ingestion. As pure hashish will not burn if rolled alone in a joint, it is typically mixed with herbal cannabis, tobacco or another type of herb for this method of consumption. Depending on region or country, multiple synonyms and alternative names exist.

Waxes are a diverse class of organic compounds that are lipophilic, malleable solids near ambient temperatures. They include higher alkanes and lipids, typically with melting points above about 40 °C (104 °F), melting to give low viscosity liquids. Waxes are insoluble in water but soluble in organic, nonpolar solvents. Natural waxes of different types are produced by plants and animals and occur in petroleum.

In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on naturally occurring resins.

Euphorbia is a very large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae). "Euphorbia" is sometimes used in ordinary English to collectively refer to all members of Euphorbiaceae, not just to members of the genus. Some euphorbias are commercially widely available, such as poinsettias at Christmas. Some are commonly cultivated as ornamentals, or collected and highly valued for the aesthetic appearance of their unique floral structures, such as the crown of thorns plant. Euphorbias from the deserts of Southern Africa and Madagascar have evolved physical characteristics and forms similar to cacti of North and South America, so they are often incorrectly referred to as cacti. Some are used as ornamentals in landscaping, because of beautiful or striking overall forms, and drought and heat tolerance.
Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3 (also represented by the pseudoelement symbols PhAc or BzMe). It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances.

Robert Bentley was an English botanist. He is perhaps best remembered today for the four-volume Medicinal Plants, published in 1880 with Henry Trimen and containing over three hundred hand-colored plates by botanist David Blair.

An eschar is a slough or piece of dead tissue that is cast off from the surface of the skin, particularly after a burn injury, but also seen in gangrene, ulcer, fungal infections, necrotizing spider bite wounds, tick bites associated with spotted fevers, and exposure to cutaneous anthrax. The term "eschar" is not interchangeable with "scab". An eschar contains necrotic tissue, whereas a scab is composed of dried blood and exudate.

Labdanum, also called ladanum, ladan or ladanon, is a sticky brown resin obtained from the shrubs Cistus ladanifer and Cistus creticus, species of rockrose. It was historically used in herbal medicine and is still used in the preparation of some perfumes and vermouths.

Calophyllum is a genus of tropical flowering plants in the family Calophyllaceae. They are mainly distributed in Asia, with some species in Africa, the Americas, Australasia, and the Pacific Islands.
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia and is also the smell of the hawthorn plant. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed, usually as a base, in organic synthesis.
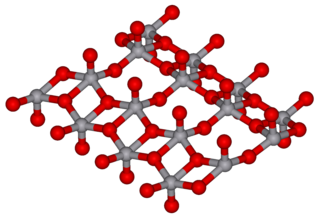
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.
Copaline, also termed fossil resin or Highgate resin, is a naturally occurring organic substance found as irregular pieces of a pale yellow colour, for example in the London Clay at Highgate Hill. It has a resinous aromatic odour when freshly broken, volatilizes at a moderate temperature, and burns readily with a yellow, smoky flame, leaving scarcely any ash.
Ammoniacum, or gum ammoniac, is a gum-resin exuded from the stem of the perennial herb Dorema ammoniacum of the umbel family (Apiaceae). The plant grows to the height of 2½ or 3 meters and its whole stem is pervaded with a milky juice, which oozes out on an incision being made at any part. This juice quickly hardens into round tears, forming the "tear ammoniacum" of commerce. "Lump ammoniacum", the other form of the substance, consists of aggregations of tears, frequently incorporating fragments of the plant itself, as well as other foreign bodies.

Galbanum is an aromatic gum resin and a product of certain umbelliferous Persian plant species in the genus Ferula, chiefly Ferula gummosa and Ferula rubricaulis. Galbanum-yielding plants grow plentifully on the slopes of the mountain ranges of northern Iran. It occurs usually in hard or soft, irregular, more or less translucent and shining lumps, or occasionally in separate tears, of a light-brown, yellowish or greenish-yellow colour, and has a disagreeable, bitter taste, a peculiar, somewhat musky odour, an intense green scent, and a specific gravity of 1.212. It contains about 8% terpenes; about 65% of a resin which contains sulfur; about 20% gum; and a very small quantity of the colorless crystalline substance umbelliferone. It also contains α-pinene, β-pinene, limonene, cadinene, 3-carene, and ocimene.

Resiniferatoxin (RTX) is a naturally occurring chemical found in resin spurge, a cactus-like plant commonly found in Morocco, and in Euphorbia poissonii found in northern Nigeria. It is a potent functional analog of capsaicin, the active ingredient in chili peppers.

Euphorbia resinifera, the resin spurge, is a species of spurge native to Morocco, where it occurs on the slopes of the Atlas Mountains. The dried latex of the plant was used in ancient medicine. It contains resiniferatoxin, a capsaicin analog tested as an analgesic since 1997.

The African olive pigeon or Rameron pigeon is a pigeon which is a resident breeding bird in much of eastern and southern Africa from Ethiopia to the Cape. Populations also are found in western Angola, southwestern Saudi Arabia and northern Yemen. It is locally common, although sizeable gaps in its distribution occur due to its habitat requirements.

Euphorbia royleana is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is also known as Sullu spurge, and Royle's spurge. It is a succulent and almost cactus like in appearance although unrelated. It grows right across the Himalaya mountains from Pakistan, India, Bhutan, Myanmar, Nepal to western China, It prefers dry and rocky slopes between 1000 and 1500 meters, but has been found up to 2000 meters. Flowering and fruiting is in spring to early summer (March–July) and seeding is in June–October. It is used as a hedging plant in northern India and has medicinal uses.
References
- ↑

- ↑ Bentley, Robert (1887). "Euphorbium". A Text-book of Organic Materia Medica. pp. 304–305.
- ↑ Appendino, Giovanni; Szallasi, Arpad (31 January 1997). "Euphorbium: modern research on its active principle, resiniferatoxin, revives an ancient medicine". Life Sciences. 60 (10): 681–696. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(96)00567-X. PMID 9064473.