Related Research Articles

The European patent with unitary effect, more commonly known as the unitary patent, is a new type of European patent in advanced stage of adoption which would be valid in participating member states of the European Union. Unitary effect can be registered for a European patent upon grant, replacing validation of the European patent in the individual countries concerned. The unitary effect means a single renewal fee, a single ownership, a single object of property, a single court and uniform protection—which means that revocation as well as infringement proceedings are to be decided for the unitary patent as a whole rather than for each country individually. Licensing is however to remain possible for part of the unitary territory.
The patentability of software, computer programs and computer-implemented inventions under the European Patent Convention (EPC) is the extent to which subject matter in these fields is patentable under the Convention on the Grant of European Patents of October 5, 1973. The subject also includes the question of whether European patents granted by the European Patent Office (EPO) in these fields are regarded as valid by national courts.
The Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council on the patentability of computer-implemented inventions, procedure number 2002/0047 (COD) was a proposal for a European Union (EU) directive aimed to harmonise national patent laws and practices concerning the granting of patents for computer-implemented inventions, provided they meet certain criteria.
The European Patent Organisation is a public international organisation created in 1977 by its contracting states to grant patents in Europe under the European Patent Convention (EPC) of 1973. The European Patent Organisation has its seat at Munich, Germany, and has administrative and financial autonomy. The European Patent Organisation is not legally bound to the European Union (EU) and has several members which are not themselves EU states.

The European Patent Convention (EPC), also known as the Convention on the Grant of European Patents of 5 October 1973, is a multilateral treaty instituting the European Patent Organisation and providing an autonomous legal system according to which European patents are granted. The term European patent is used to refer to patents granted under the European Patent Convention. However, a European patent is not a unitary right, but a group of essentially independent nationally enforceable, nationally revocable patents, subject to central revocation or narrowing as a group pursuant to two types of unified, post-grant procedures: a time-limited opposition procedure, which can be initiated by any person except the patent proprietor, and limitation and revocation procedures, which can be initiated by the patent proprietor only.
Prior art, in most systems of patent law, is constituted by all information that has been made available to the public in any form before a given date that might be relevant to a patent's claims of originality. If an invention has been described in the prior art or would have been obvious from what has been described in the prior art, a patent on that invention is not valid.
The Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property, signed in Paris, France, on 20 March 1883, was one of the first intellectual property treaties. It established a Union for the protection of industrial property. The Convention is currently still in force. The substantive provisions of the Convention fall into three main categories: national treatment, priority right and common rules.
In patent, industrial design rights and trademark laws, a priority right or right of priority is a time-limited right, triggered by the first filing of an application for a patent, an industrial design or a trademark respectively. The priority right allows the claimant to file a subsequent application in another country for the same invention, design, or trademark effective as of the date of filing the first application. When filing the subsequent application, the applicant must claim the priority of the first application in order to make use of the right of priority. The right of priority belongs to the applicant or his successor in title.
The WTO's Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS), particularly Article 27, is occasionally referenced in the political debate on the international legal framework for the patentability of software, and on whether software and computer-implemented inventions should be considered as a field of technology.
The EPC 2000 or European Patent Convention 2000 is the version of the European Patent Convention (EPC) as revised by the Act Revising the Convention on the Grant of European Patents signed in Munich on November 29, 2000. On June 28, 2001, the Administrative Council of the European Patent Organisation adopted the final new text of the EPC 2000. The EPC 2000 entered into force on December 13, 2007.
The Convention on the Unification of Certain Points of Substantive Law on Patents for Invention, also called Strasbourg Convention or Strasbourg Patent Convention, is a multilateral treaty signed by Member States of the Council of Europe on November 27, 1963 in Strasbourg, France. It entered into force on August 1, 1980 and led to a significant harmonization of patent laws across European countries.
Espacenet is a free online service for searching patents and patent applications. Espacenet was developed by the European Patent Office (EPO) together with the member states of the European Patent Organisation. Most member states have an Espacenet service in their national language, and access to the EPO's worldwide database, most of which is in English. In 2015, the Espacenet worldwide service claimed to have records on more than 90 million patent publications.
The International Patent Classification (IPC) is a hierarchical patent classification system used in over 100 countries to classify the content of patents in a uniform manner. It was created under the Strasbourg Agreement (1971), one of a number of treaties administered by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). The classification is updated on a regular basis by a Committee of Experts, consisting of representatives of the Contracting States of that Agreement with observers from other organisations, such as the European Patent Office.
Intellectual property law in Romania has developed significantly in the period since the Romanian Revolution of 1989 because of the need to enforce various regional and international treaties and agreements, such as the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS), the European Directives on Biotechnological Inventions, on Trademarks and Geographical Indications, and on Supplementary protection certificates, the Trademark Law Treaty, the Patent Law Treaty, and the European Union regulation on the Community Trademark, and the need to harmonize domestic patent law with the European Patent Convention (EPC) and with the European Union.
The Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) is an Indian digital knowledge repository of the traditional knowledge, especially about medicinal plants and formulations used in Indian systems of medicine.
The Strasbourg Agreement Concerning the International Patent Classification, also known as the IPC Agreement, is an international treaty that established a common classification for patents for invention, inventors' certificates, utility models and utility certificates, known as the "International Patent Classification" (IPC). The treaty was signed in Strasbourg, France, on March 24, 1971, it entered into force on October 7, 1975, and was amended on September 28, 1979.
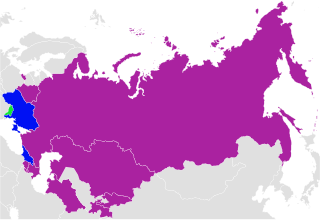
The Eurasian Patent Convention is an international patent law treaty instituting both the Eurasian Patent Organization (EAPO) and the legal system pursuant to which Eurasian patents are granted. It was signed on 9 September 1994 in Moscow, Russia, and entered into force on 12 August 1995.
The European Convention relating to the formalities required for patent applications was signed at Paris on December 11, 1953. Its aim was to "simplify and unify, as far as it is possible, the formalities required by the various national legislations for patent applications". It was open to the signature of the members of the Council of Europe, came into force on June 1, 1955, and, after it came into force, became open to accession by all States which are members of the International Union for the Protection of Industrial Property. There were 21 ratifications or accessions to the Convention, including Israel and South Africa. Since then, all but five of the states parties have denounced the Convention.
During the grant procedure before the European Patent Office (EPO), divisional applications can be filed under Article 76 EPC out of pending earlier European patent applications. A divisional application, sometimes called European divisional application, is a new patent application which is separate and independent from the earlier application, unless specific provisions in the European Patent Convention (EPC) require something different. A divisional application, which is divided from an earlier application, cannot be broader than the earlier application, neither in terms of subject-matter nor in terms of geographical cover.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to patents:
References
- ↑ G. W. Tookey, Patents in the European Field in Council of Europe, Council of Europe staff, European Yearbook 1969, Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, 1971, pages 76-97 (especially page 81), ISBN 90-247-1218-1.