
The Great North Road is a major route in Zambia, running north from Lusaka through Kabwe, Kapiri Mposhi, Serenje, Mpika, Isoka and Nakonde to the border with Tanzania. The entire route is designated as the T2 road on Zambia's road network. It forms the Zambian section of the Tanzam Highway.

Independence Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium in Lusaka, Zambia. It was originally built in the mid-1960s for use in hosting the country's independence celebrations. It is currently used mostly for football matches. The stadium holds 30,000 people. It is located adjacent to the National Heroes Stadium.

Kenneth Kaunda International Airport is an international airport located in Chongwe District, off the Great East Road, approximately 27 kilometres (17 mi) northeast of the city centre of Lusaka, the capital and largest city of Zambia. The airport has a capacity of 6 million and is the largest in Zambia, serving as a hub for its region. The airport serves as a hub for Zambia Airways, Proflight Zambia, Royal Zambian Airlines, and Mahogany Air.

Hakainde Hichilema is a Zambian businessman, farmer, and politician who is the seventh and current president of Zambia since 24 August 2021. After having contested five previous elections in 2006, 2008, 2011, 2015 and 2016, he won the 2021 presidential election with 59.02% of the vote. He has led the United Party for National Development since 2006 following the death of the party founder Anderson Mazoka.

The Lusaka Securities Exchange is the principal stock exchange of Zambia. Founded in 1993, it is located in Lusaka. The LuSE is a member of the African Stock Exchanges Association.

Lusaka is the capital and largest city of Zambia. It is one of the fastest-developing cities in southern Africa. Lusaka is in the southern part of the central plateau at an elevation of about 1,279 metres (4,196 ft). As of 2019, the city's population was about 3.3 million, while the urban population is estimated at 2.5 million in 2018. Lusaka is the centre of both commerce and government in Zambia and connects to the country's four main highways heading north, south, east, and west. English is the official language of the city administration, while Bemba and Nyanja are the commonly spoken street languages.
Chishimba Kambwili is a former member of the National Assembly of Zambia for Roan Constituency in Luanshya District. He has also held several posts in the cabinet. He is the former leader of the National Democratic Congress.

Chalo Chatu translated as our world in the Zambian language is an English-language wiki-based free encyclopaedia project created by Jason Mulikita that is dedicated to documenting the Zambia and also try to preserve the history and pride of Zambia covering historical events and current events, notable public figures, companies, organizations, websites, national monuments and other notable key features of Zambia. The site uses MediaWiki software to maintain a user-created database of information. The site's content is under a Creative Commons license(CC BY-SA 3.0) which means that it is available free to the public, but cannot be used for commercial purposes and should not be modified by people who are not part of the community of the website. Chalo Chatu is a work-in-progress, with articles in various stages of completion.
The one hundred kwacha note of Zambia is a denomination of the Zambian currency. The current paper note, first issued in 2013, features the Freedom Statue in Lusaka, the issuing authority of legal tender currency in Zambia. In the middle there is the National Assembly; the face value of the banknote is shown in words in the lower left corner, and in numerals in the other three corners, and the new printer imprint of Giesecke & Devrient at the lower right corner. There is also a buffalo on the reverse. The obverse features the African fish eagle, which is considered as the primary recognition of the Zambian banknote, together with the country's coat of arms, the signature of the Bank of Zambia Governor and obligation to pay the sum indicated on the banknote, and the face value of the specified banknote and the baobab tree. It is the highest denomination of banknote issued by the Bank of Zambia since January, 2013 when the currency was redenominated, as described in the next section.

Mulenga Mpundu Kapwepwe is a distinguished Zambian author and social activist. Kapwepwe has garnered widespread recognition for her remarkable contributions in the field of women's history, having co-founded the Zambian Women's History Museum.

Cynthia Zukas is a South African-born Zambian painter; she received the Order of the British Empire in 2012.

The T2 is a trunk road in Zambia. The road runs from the Tunduma border with Tanzania via Mpika, Kabwe and Lusaka to the Chirundu border with Zimbabwe. The road is the longest route of the country, as it is approximately 1,155 kilometres (718 mi). The route from Mpika to Kafue is a toll road. The route from Tanzania to Lusaka is Zambia's Great North Road and is part of the Tanzam Highway.
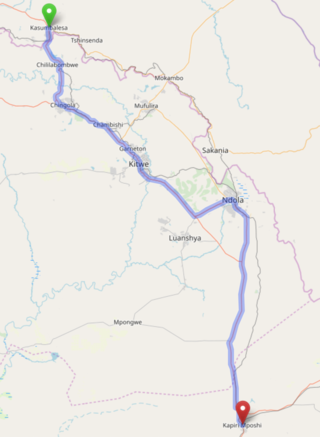
The T3 is a trunk road in Zambia. The road runs from Kapiri Mposhi via Ndola, Kitwe and Chingola to Kasumbalesa on the border with DR Congo. The entire route is a toll road.

Cassie Kabwita is a Zambian actress and film producer and rotarian. She is known for her works in the Zambian and Tanzanian film industries. Cassie is the Ambassador for The African Film Festival(TAFF) in Dallas
Sun Share Tower is a skyscraper in Lusaka, Zambia, and is the country's second tallest building, at 190 feet (58 m) tall. It is Lusaka's most modern skyscraper; construction ended in 2016. The Tower is owned by Sun Share Investment, a Chinese-affiliated company.
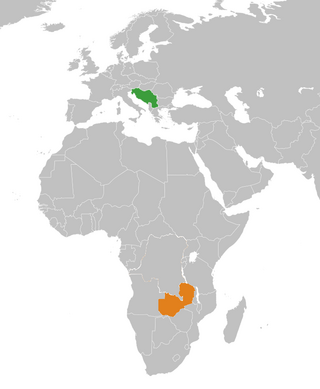
Yugoslavia–Zambia relations were historical foreign relations between now split-up Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and Zambia. Relations developed and were focused around shared membership and participation in the Non-Aligned Movement activities. Diplomatic relations between Yugoslavia and Zambia were established on 24 October 1964. They reached their peak before and during the 1970 3rd conference of Heads of State or Government of the Non-Aligned Countries in Lusaka when Yugoslavia provided major logistical and diplomatic support to the relatively recently decolonized Zambia.

Third Conference of the Non-Aligned Movement on 8–10 September 1970 in Lusaka, Zambia was the third conference of the Non-Aligned Movement. A preparatory meeting of Foreign Ministers drafted a number of resolutions which were considered by the Summit Conference. President of Zambia Kenneth Kaunda opened the conference by underlining non-alignment as "the natural choice at the time of increased hostility created by ideological conflicts in the bipolar world"
















