
The FTSE 250 Index, also called the FTSE 250, or, informally, the "Footsie 250", is a stock market index that measures the real strength of the economy of the United Kingdom and consists of the 101st to the 350th mid-cap blue chip companies listed on the London Stock Exchange.
An emerging market is a market that has some characteristics of a developed market, but does not fully meet its standards. This includes markets that may become developed markets in the future or were in the past. The term "frontier market" is used for developing countries with smaller, riskier, or more illiquid capital markets than "emerging". As of 2006, the economies of China and India are considered to be the largest emerging markets. According to The Economist, many people find the term outdated, but no new term has gained traction. Emerging market hedge fund capital reached a record new level in the first quarter of 2011 of $121 billion. Emerging market economies’ share of global PPP-adjusted GDP has risen from 27 percent in 1960 to around 53 percent by 2013. The ten largest emerging economies by nominal GDP are 4 of the 9 BRICS countries along with Mexico, South Korea, Indonesia, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and Poland. The inclusion of South Korea, Poland, and sometimes Taiwan are questionable given they are no longer considered emerging markets by the IMF and World Bank If we ignore those three, the top ten would include Argentina and Thailand.
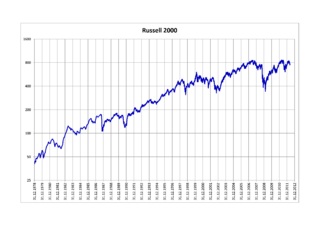
The Russell 2000 Index is a small-cap U.S. stock market index that makes up the smallest 2,000 stocks in the Russell Index. It was started by the Frank Russell Company in 1984. The index is maintained by FTSE Russell, a subsidiary of the London Stock Exchange Group (LSEG).
Russell indexes are a family of global stock market indices from FTSE Russell that allow investors to track the performance of distinct market segments worldwide. Many investors use mutual funds or exchange-traded funds based on the FTSE Russell Indexes as a way of gaining exposure to certain portions of the U.S. stock market. Additionally, many investment managers use the Russell Indexes as benchmarks to measure their own performance. Russell's index design has led to more assets benchmarked to its U.S. index family than all other U.S. equity indexes combined.

The Straits Times Index is a capitalisation-weighted measurement stock market index that is regarded as the benchmark index for the stock market in Singapore. It tracks the performance of the top 30 companies that are listed on the Singapore Exchange (SGX).

The MSCI World is a widely followed global stock market index that tracks the performance of around 1500 large and mid-cap companies across 23 developed countries. It is maintained by MSCI, formerly Morgan Stanley Capital International, and is used as a common benchmark for global stock funds intended to represent a broad cross-section of global markets.
In investing, a developed market is a country that is most developed in terms of its economy and capital markets. The country must be high income, but this also includes openness to foreign ownership, ease of capital movement, and efficiency of market institutions. This term is contrasted with developing market.

FTSE International Limited trading as FTSE Russell ( "Footsie") is a British provider of stock market indices and associated data services, wholly owned by the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and operating from premises in Canary Wharf. It operates the well known UK FTSE 100 Index as well as a number of other indices. FTSE stands for Financial Times Stock Exchange.
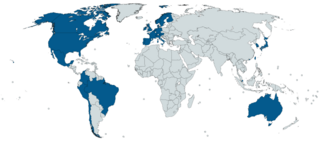
The S&P Global 1200 Index is a free-float weighted stock market index of global equities from Standard & Poor's. The index was launched on Sep 30, 1999 and covers 31 countries and approximately 70 percent of global stock market capitalization. It is composed of seven regional indices:
The S&P 100 Index is a stock market index of United States stocks maintained by Standard & Poor's.

The FTSE All-Share Index, originally known as the FTSE Actuaries All Share Index, is a capitalisation-weighted index, comprising around 600 of more than 2,000 companies traded on the London Stock Exchange (LSE). By weighting companies based on their market capitalisation, the index ensures that companies with larger market capitalisations have a greater influence on the index's performance. Since 29 December 2017 the constituents of this index totaled 641 companies. The FTSE All-Share is the aggregation of the FTSE 100 Index and the FTSE 250 Index, which are together known as the FTSE 350 Index, and the FTSE SmallCap Index. The index is maintained by FTSE Russell, a subsidiary of the London Stock Exchange Group. It aims to represent at least 98% of the full capital value of all UK companies that qualify as eligible for inclusion.
The FTSE Bursa Malaysia KLCI, also known as the FBM KLCI, is a capitalisation-weighted stock market index, composed of the 30 largest companies on the Bursa Malaysia by market capitalisation that meet the eligibility requirements of the FTSE Bursa Malaysia Index Ground Rules. The index is jointly operated by FTSE and Bursa Malaysia.
Fundamentally based indexes or fundamental indexes, also called fundamentally weighted indexes, are indexes in which stocks are weighted according to factors related to their fundamentals such as earnings, dividends and assets, commonly used when performing corporate valuations. Indexes that use a composite of several fundamental factors attempt to average out sector biases that may arise from relying on a single fundamental factor. A key belief behind the fundamental index methodology is that underlying corporate accounting/valuation figures are more accurate estimators of a company's intrinsic value, rather than the listed market value of the company, i.e. that one should buy and sell companies in line with their accounting figures rather than according to their current market prices. In this sense fundamental indexing is linked to so-called fundamental analysis.

The Swiss Performance Index (SPI) is a wide total-return index that tracks equity primarily listed on SIX Swiss Exchange with a free-float of at least 20%, and excluding investment companies. The index covers large, mid and small caps and is weighted by market capitalization. Most constituents, although not all, are domiciled in Switzerland or the Principality of Liechtenstein.
The MSCI KLD 400 Social Index was launched in 1990 and is designed to help socially conscious investors weigh social and environmental factors in their investment choices. It was founded by KLD's Amy Domini as the Domini 400 Social Index.
A frontier market is a term for a type of developing country's market economy which is more developed than a least developed country's, but too small, risky, or illiquid to be generally classified as an emerging market economy. The term is an economic term which was coined by International Finance Corporation’s Farida Khambata in 1992. The term is commonly used to describe the equity markets of the smaller and less accessible, but still "investable" countries of the developing world. The frontier, or pre-emerging equity markets are typically pursued by investors seeking high, long-run return potential as well as low correlations with other markets. Some frontier market countries were emerging markets in the past, but have regressed to frontier status.
The FTSE Developed Europe Index is an index of European stocks, part of the FTSE Global Equity Index Series. It is a subset of the FTSE Europe Index. The FTSE Eurobloc Index is a subset of it.

In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.
The Russell Microcap Index measures the performance of the microcap segment of the U.S. equity market. It makes up less than 3% of the U.S. equity market. It includes 1,000 of the smallest securities in the Russell 2000 Index based on a combination of their market cap and current index membership and it also includes up to the next 1,000 stocks. As of 31 December 2016, the weighted average market capitalization for a company in the index was $535 million; the median market cap was $228 million. The market cap of the largest company in the index was $3.6 billion.









