
Ching-Te is a small lunar impact crater located in a mountainous area to the east of the Mare Serenitatis. It is a circular, bowl-shaped formation with no distinguishing features.
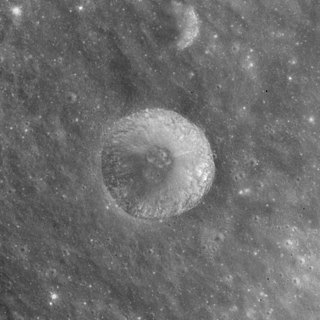
Acosta is a small lunar impact crater located just to the north of the prominent crater Langrenus, near the east edge of Mare Fecunditatis. To the west are the trio of Atwood, Naonobu, and Bilharz. Acosta is named after the Portuguese naturalist Cristóvão da Costa.

Beketov is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the northern reaches of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It is named after Russian chemist Nikolay Beketov. To the south is the ghost crater Jansen R. Northeast of Beketov, along the edge of the mare, is the crater Vitruvius. Beketov was previously designated Jansen C before being named by the IAU. The flooded crater Jansen itself lies to the south.

Chladni is a small lunar impact crater that lies near the northwest edge of Sinus Medii, in the central part of the Moon. The crater is named for German physicist and musician Ernst Chladni who, in 1794, wrote the first book on meteorites. The rim of the crater is roughly circular, and there is a small central floor at the midpoint of the sloping inner walls. This feature has a higher albedo than the surrounding terrain. It is connected by a low ridge to the rim of the crater Murchison, which lies to the northwest. Due east of Chladni is the larger Triesnecker.

Vitruvius is a small lunar impact crater that lies on the northern edge of the Mare Tranquillitatis. To the east is the crater Gardner, and to the northeast is Fabbroni. To the north-northwest is the elongated Mons Vitruvius mountain, and beyond is the valley where the Apollo 17 mission landed.

Bellot is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the southwest edge of Mare Fecunditatis. It lies between the craters Goclenius to the northwest and Crozier to the southeast. To the southwest is Colombo, and to the west is Magelhaens.

Peek is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the northern part of the Mare Smythii near the eastern limb of the Moon. This part of the lunar surface is subject to the effects of libration, and the crater can be hidden from sight during an unfavorable libration. Even when visible, however, the crater is seen almost edge-on, making it difficult to see much detail from the Earth. Due to foreshortening the crater appears close to Schubert, even though the two are about 60 km apart. It lies to the south-southeast of the large crater Neper.

Black is a small lunar impact crater that lies just to the southeast of the walled basin Kästner. To the south-southwest is the crater Ansgarius, and to the east is the small Dale. It is located near the eastern limb of the Moon, just to the southwest of the Mare Smythii.

C. Mayer is a lunar impact crater that is located at the northern edge of the Mare Frigoris, due north of the prominent crater Aristoteles. Also to the south, but only a third as distant, is the smaller crater Sheepshanks. Due east of C. Mayer is the flooded crater Kane.
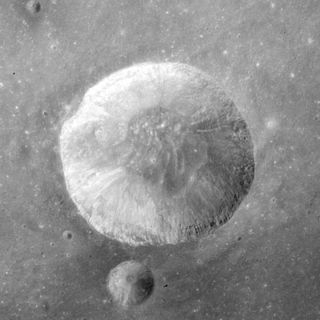
Carmichael is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern edge of the Sinus Amoris, in the northeastern quadrant of the Moon's near side. Its diameter is 20 km. It was named after American psychologist Leonard Carmichael. It lies within a couple of crater diameters south-southwest of the smaller crater Hill. Further to the east-northeast is the prominent crater Macrobius. Carmichael was designated Macrobius A before being given its current name by the IAU.

Drude is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon, in the rugged Montes Cordillera range that forms the outer ring around the Mare Orientale impact basin. It is located just behind the west-southwest limb, and this area is sometimes brought into sight from Earth during favorable librations. However, even at such times, the crater is viewed from the edge and little detail can be seen.
Kramarov is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies just beyond the western limb, at the far edge of the region that is brought into view during favorable librations. The crater is situated in the northern part of the Montes Cordillera, the outer ring of the mountains that surround Mare Orientale.

Gardner is a small lunar impact crater in the northeast part of the Moon and is named after an American physicist Irvine Clifton Gardner. It lies due east of the crater Vitruvius, in a section of rough terrain north of the Mare Tranquillitatis. Gardner was previously designated Vitruvius A before being given its present name by the IAU. To the northeast of Gardner is the larger crater Maraldi.

Feuillée is a small lunar impact crater in the eastern part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after French natural scientist Louis Feuillée. It lies less than a half crater diameter to the northwest of Beer, and the two formations form a nearly matched pair. To the west is the small but prominent crater Timocharis.

Chant is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, behind the southwest limb as seen from the Earth. It lies within the southwestern part of the blanket of ejecta surrounding the Mare Orientale, beyond the Montes Cordillera mountain ring. To the west-northwest is the large walled plain Blackett. Southward is the crater Mendel.

Chadwick is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon's surface, just beyond the southwestern limb. It is located to the northwest of the crater De Roy, and was previously designated De Roy X before being given its current name by the IAU. This region of the lunar surface lies at the southern end of the ejecta blanket that surrounds the Mare Orientale impact basin.

Foucault is a small lunar impact crater that lies along the southern edge of Mare Frigoris, to the southeast of the crater Harpalus. In the rugged terrain to the south of Foucault is Sharp. The outer perimeter of Foucault forms a somewhat irregular circle, with slight outward bulges to the south and northeast. The inner wall of the rim is not notably terraced, and slopes down directly to the uneven floor. It is named after physicist Léon Foucault, most famous for the Foucault pendulum.

File: Franz is a small lunar impact crater identified during the Apollo mission in August 1971 and located along the eastern edge of the Sinus Amoris, a bay that forms a northern extension to the Mare Tranquillitatis. Its diameter is 25 km. It was named after German astronomer Julius Heinrich Franz. It lies to the southwest of the prominent crater Macrobius. To the north is the smaller Carmichael, and to the northwest is the diminutive Theophrastus.

Chalonge is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the southwest of the larger crater Lewis, in the outer skirt of ejecta that surrounds the Mare Orientale impact basin. To the southeast are the Montes Cordillera, a ring of mountains that encircle the Mare Orientale formation.

Donner is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located just to the northeast of the Mare Australe, behind the southeastern limb of the Moon. During favorable librations this part of the lunar surface can be brought into view of the Earth, but the site is viewed from the edge and so not much detail can be seen.





















