In psychology, libido is psychological drive or energy, usually conceived as sexual in nature, but also includes other forms of desire. The term was originally used in psychoanalytic theory, where the neurologist and pioneering psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud began by employing the term in reference to the energy of the sexual drive, later generalising the concept to refer to the fundamental energy of all expressions of love, pleasure, and self-preservation.

Paroxetine, sold under the brand names Paxil and Seroxat among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder. It has also been used in the treatment of premature ejaculation and hot flashes due to menopause. It is taken orally.
Sexual desire is an emotion and motivational state characterized by an interest in sexual objects or activities, or by a drive to seek out sexual objects or to engage in sexual activities. It is an aspect of sexuality, which varies significantly from one person to another and also fluctuates depending on circumstances.

Bupropion, sold under the brand name Wellbutrin among others, is an atypical antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the cases of "incomplete response" to the first-line selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant. Bupropion has several features that distinguish it from other antidepressants: it does not usually cause sexual dysfunction; it is not associated with weight gain and sleepiness, and it is more effective than SSRIs at improving symptoms of hypersomnia and fatigue. Bupropion, particularly the immediate release formulation, carries a higher risk of seizure than many other antidepressants, hence caution is recommended in patients with a history of seizure disorder.
Persistent genital arousal disorder (PGAD), previously called persistent sexual arousal syndrome, is spontaneous, persistent, unwanted and uncontrollable genital arousal in the absence of sexual stimulation or sexual desire, and is typically not relieved by orgasm. Instead, multiple orgasms over hours or days may be required for relief.
Hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD), hyposexuality or inhibited sexual desire (ISD) is sometimes considered a sexual dysfunction, and is characterized as a lack or absence of sexual fantasies and desire for sexual activity, as judged by a clinician. For this to be regarded as a disorder, it must cause marked distress or interpersonal difficulties and not be better accounted for by another mental disorder, a drug, or some other medical condition. A person with ISD will not start, or respond to their partner's desire for, sexual activity. HSDD affects approximately 10% of all pre-menopausal women in the United States, or about 6 million women.
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction as a "person's inability to participate in a sexual relationship as they would wish". This definition is broad and is subject to many interpretations. A diagnosis of sexual dysfunction under the DSM-5 requires a person to feel extreme distress and interpersonal strain for a minimum of six months. Sexual dysfunction can have a profound impact on an individual's perceived quality of sexual life. The term sexual disorder may not only refer to physical sexual dysfunction, but to paraphilias as well; this is sometimes termed disorder of sexual preference.
Sexual arousal disorder is characterized by a lack or absence of sexual fantasies and desire for sexual activity in a situation that would normally produce sexual arousal, or the inability to attain or maintain typical responses to sexual arousal. The disorder is found in the DSM-IV. The condition should not be confused with a sexual desire disorder.

Buspirone, sold under the brand name Buspar, among others, is a medication primarily used to treat anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder. Benefits support its short-term use. It is taken orally, and takes two to six weeks to be fully effective.
Sexual medicine or Psychosexual medicine as defined by Masters and Johnsons in their classic Textbook of Sexual Medicine, is "that branch of medicine that focuses on the evaluation and treatment of sexual disorders, which have a high prevalence rate." Examples of disorders treated with sexual medicine are erectile dysfunction, hypogonadism, and prostate cancer. Sexual medicine often uses a multidisciplinary approach involving physicians, mental health professionals, social workers, and sex therapists. Sexual medicine physicians often approach treatment with medicine and surgery, while sex therapists often focus on behavioral treatments.

Trazodone, sold under many brand names, is an antidepressant medication. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and difficulties with sleep. The medication is taken orally.
Delayed ejaculation (DE) describes a man's inability or persistent difficulty in achieving orgasm, despite typical sexual desire and sexual stimulation. Generally, a man can reach orgasm within a few minutes of active thrusting during sexual intercourse, whereas a man with delayed ejaculation either does not have orgasms at all or cannot have an orgasm until after prolonged intercourse which might last for 30–45 minutes or more. Delayed ejaculation is closely related to anorgasmia.

Flibanserin, sold under the brand name Addyi, is a medication approved for the treatment of pre-menopausal women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD). The medication improves sexual desire, increases the number of satisfying sexual events, and decreases the distress associated with low sexual desire. The most common side effects are dizziness, sleepiness, nausea, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep and dry mouth.
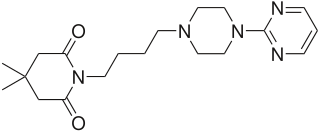
Gepirone is an antidepressant and anxiolytic drug of the azapirone group that was synthesized by Bristol-Myers Squibb in 1986 and has been under development for the treatment of depression but has yet to be marketed. It has been under development in the U.S. in an extended release form, but despite completing phase III clinical trials and demonstrating efficacy, it has been rejected multiple times by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) during the drug approval process. However, in March 2016, the FDA reversed course and ruled favorably on the efficacy of gepirone.
Robert Taylor Segraves is an American psychiatrist who works on sexual dysfunction and its pharmacologic causes and treatments.

Norepinephrine and dopamine disinhibitors (NDDIs) are a class of drugs which act at specific sites to disinhibit downstream norepinephrine and dopamine release in the brain.
Sexual anhedonia, also known as pleasure dissociative orgasmic disorder, is a condition in which an individual cannot feel pleasure from an orgasm. It is thought to be a variant of hypoactive sexual desire disorder.

Cindy Meston is a Canadian-American clinical psychologist well-known for her research on the psychophysiology of female sexual arousal. She is a Full Professor of Clinical Psychology at the University of Texas at Austin, Director of the Female Sexual Psychophysiology Laboratory, and author of Why Women Have Sex. In 2016, the BBC, London, England named Meston one of the 100 most influential and inspirational women in the world.
Buspirone/testosterone (tentative brand name Lybridos) is a combination of buspirone, a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist, α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist, and D2 autoreceptor antagonist, and testosterone, an androgen or androgen receptor agonist, which is under development by the pharmaceutical company Emotional Brain for the treatment of female sexual dysfunction. Both buspirone and testosterone have individually been found to be effective in the treatment of female sexual dysfunction in clinical studies, and so their combination could be anticipated to be even more effective. As of January 2016, the combination is in phase II clinical trials, with a phase III trial being planned in the United States and Europe.
Drugs and sexual desire is about sexual desire being manipulated through drugs from various approaches. Sexual desire is generated under the effects from sex hormones and microcircuits from brain regions. Neurotransmitters play essential roles in stimulating and inhibiting the processes that lead to libido production in both men and women. For instance, a positive stimulation is modulated by dopamine from the medial preoptic area in the hypothalamus and norepinephrine. At the same time, inhibition occurs when prolactin and serotonin are released for action.







