
Abydos is one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt, and also of the eighth nome in Upper Egypt. It is located about 11 kilometres west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of El Araba El Madfuna and El Balyana. In the ancient Egyptian language, the city was called Abedju (Arabic Abdu عبد-و). The English name Abydos comes from the Greek Ἄβυδος, a name borrowed by Greek geographers from the unrelated city of Abydos on the Hellespont. Abydos name in hieroglyphs

Sacred prostitution, temple prostitution, cult prostitution, and religious prostitution are purported rites consisting of paid intercourse performed in the context of religious worship, possibly as a form of fertility rite or divine marriage. Scholars prefer the terms "sacred sex" or "sacred sexual rites" in cases where payment for services is not involved.

Dodona in Epirus in northwestern Greece was the oldest Hellenic oracle, possibly dating to the 2nd millennium BCE according to Herodotus. The earliest accounts in Homer describe Dodona as an oracle of Zeus. Situated in a remote region away from the main Greek poleis, it was considered second only to the Oracle of Delphi in prestige.

Melqart was the tutelary god of the Phoenician city-state of Tyre and a major deity in the Phoenician and Punic pantheons. He may have been central to the founding-myths of various Phoenician colonies throughout the Mediterranean, as well as the source of several myths concerning the exploits of Heracles. Many cities were thought to be founded and protected by Melqart, no doubt springing from the original Phoenician practice of building a Temple of Melqart at new colonies. Similar to Tammuz and Adonis, he symbolized an annual cycle of death and rebirth.
Cult is the care owed to deities and temples, shrines, or churches. Cult is embodied in ritual and ceremony. Its presence or former presence is made concrete in temples, shrines and churches, and cult images, including votive offerings at votive sites.

Astarte is the Hellenized form of the Ancient Near Eastern goddess ʿAṯtart. ʿAṯtart was the Northwest Semitic equivalent of the East Semitic goddess Ishtar.
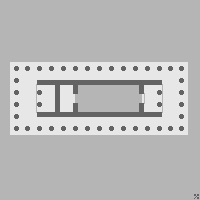
A cella or naos is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple in classical antiquity. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a biological cell in plants or animals.

Baetylus are sacred stones which were supposedly endowed with life, or gave access to a deity. According to ancient sources, at least some of these objects of worship were meteorites, which were dedicated to the gods or revered as symbols of the gods themselves.

The lectisternium was an ancient Roman propitiatory ceremony, consisting of a meal offered to gods and goddesses. The word derives from lectum sternere, "to spread a couch." The deities were represented by their busts or statues, or by portable figures of wood, with heads of bronze, wax or marble. It has also been suggested that the divine images were bundles of sacred herbs tied together in the form of a head, covered by a waxen mask so as to resemble a kind of bust, rather like the straw figures called Argei. A couch (lectus) was prepared by draping it with fabric. The figures or sacred objects pertaining to the deity were laid upon it. Each couch held a pair of deities, sometimes male with female equivalent. If the image was anthropomorphic, the left arms were rested on a cushion (pulvinus) in the attitude of reclining to eat, whence the couch itself was often called pulvinar) The couches were set out in the open street, or a temple forecourt, or in the case of ludi, in the pulvinar or viewing box, and a meal was served on a table before the couch.

The Heraion of Samos was a large sanctuary to the goddess Hera, on the island of Samos, Greece, 6 km southwest of the ancient city of Samos. It was located in the low, marshy basin of the Imbrasos river, near where it enters the sea. The late Archaic temple in the sanctuary was the first of the gigantic free-standing Ionic temples, but its predecessors at this site reached back to the Geometric Period of the 8th century BC, or earlier. As a testimony to the mercantile and naval power of Samos during Archaic Greece, and its exceptional architecture, the site of temple's ruins, with its sole standing column, was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site, along with the nearby archeological site Pythagoreion in 1992.

Pyrgi was originally an ancient Etruscan town and port in Latium, central Italy, to the north-west of Caere. Its location is now occupied by the borough of Santa Severa. It is notable for the discovery here of the gold tablets, an exceptional epigraphic document with rare texts in Phoenician and Etruscan languages, and also the exceptional terracotta pediment statues from the temple.

The Punic religion, Carthaginian religion, or Western Phoenician religion in the western Mediterranean was a direct continuation of the Phoenician variety of the polytheistic ancient Canaanite religion. However, significant local differences developed over the centuries following the foundation of Carthage and other Punic communities elsewhere in North Africa, southern Spain, Sardinia, western Sicily, and Malta from the ninth century BC onward. After the conquest of these regions by the Roman Republic in the third and second centuries BC, Punic religious practices continued, surviving until the fourth century AD in some cases. As with most cultures of the ancient Mediterranean, Punic religion suffused their society and there was no stark distinction between religious and secular spheres. Sources on Punic religion are poor. There are no surviving literary sources and Punic religion is primarily reconstructed from inscriptions and archaeological evidence. An important sacred space in Punic religion appears to have been the large open air sanctuaries known as tophets in modern scholarship, in which urns containing the cremated bones of infants and animals were buried. There is a long-running scholarly debate about whether child sacrifice occurred at these locations, as suggested by Greco-Roman and biblical sources.

Terracotta figurines are a wide range of small figurines made throughout the time span of Ancient Greece, and one of the main types of Ancient Greek pottery. Early figures are typically religious, modelled by hand, and often found in large numbers at religious sites, left as votive offerings. Psi and phi type figurines are two very early and simple types, dating as far back as 1400 BCE.

Animal mummification was common in ancient Egypt. Animals were an important part of Egyptian culture, not only in their role as food and pets, but also for religious reasons. Many different types of animals were mummified, typically for four main purposes: to allow people's beloved pets to go on to the afterlife, to provide food in the afterlife, to act as offerings to a particular god, and because some were seen as physical manifestations of specific deities that the Egyptians worshipped. Bastet, the cat goddess, is an example of one such deity. In 1888, an Egyptian farmer digging in the sand near Istabl Antar discovered a mass grave of felines, ancient cats that were mummified and buried in pits at great numbers.

The Temple of Eshmun is an ancient place of worship dedicated to Eshmun, the Phoenician god of healing. It is located near the Awali river, 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) northeast of Sidon in southwestern Lebanon. The site was occupied from the 7th century BC to the 8th century AD, suggesting an integrated relationship with the nearby city of Sidon. Although originally constructed by Sidonian king Eshmunazar II in the Achaemenid era to celebrate the city's recovered wealth and stature, the temple complex was greatly expanded by Bodashtart, Yatonmilk and later monarchs. Because the continued expansion spanned many centuries of alternating independence and foreign hegemony, the sanctuary features a wealth of different architectural and decorative styles and influences.

A votive offering or votive deposit is one or more objects displayed or deposited, without the intention of recovery or use, in a sacred place for religious purposes. Such items are a feature of modern and ancient societies and are generally made in order to gain favor with supernatural forces.

Ocriticum was an Italic and Roman town, the ruins of which are located in the comune of Cansano, in the province of L'Aquila in the Abruzzo region of Italy.
Bothros is the Ancient Greek word for "hole", "pit" or "trench". In contemporary use it can refer to a variety of holes or depressions found at ancient sites and referred to in literature, and has also been utilized in biological taxonomy to describe species or structures that have similar characteristics.

The Byblos figurines or Phoenician statuettes are approximately 1,500–2,000 ex-voto statuettes found in ancient Phoenician temples in Lebanon, primarily in Byblos, but also in Kamid al lawz. The statuettes date to the second millennium BC and are made of bronze, silver, or copper alloy. The Byblos figurines are considered to represent the best example of their kind across the Levant.

The Phoenician sanctuary of Kharayeb is a historic temple in the town of Kharayeb, situated in the hinterland of Tyre in Southern Lebanon. It was excavated during three archaeological missions. The first mission, led by then head of the Lebanon's Directorate General of Antiquities Maurice Chehab in 1946, revealed a Hellenistic period temple and thousands of clay figurines dating from the sixth to the first centuries BC. Subsequent excavations in 1969, carried out by Lebanese archaeologist Brahim Kaoukabani, and a more recent excavation in 2009, funded by the Italian government, yielded significant discoveries regarding cultic practices and a detailed reconstruction of the sanctuary's architecture and development.



















