
Finance is a term for matters regarding the management, creation, and study of money and investments. Specifically, it deals with the questions of how and why an individual, company or government acquires the money needed – called capital in the company context – and how they spend or invest that money. Finance is then often split per the following major categories: corporate finance, personal finance and public finance.

The Federal Farm Loan Act of 1916 was a United States federal law aimed at increasing credit to rural family farmers. It did so by creating a federal farm loan board, twelve regional farm loan banks and tens of farm loan associations. The act was signed into law by President of the United States Woodrow Wilson.

The money market is a component of the economy which provides short-term funds. The money market deals in short-term loans, generally for a period of less than or equal to 365 days.

The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) is an independent bureau within the United States Department of the Treasury that was established by the National Currency Act of 1863 and serves to charter, regulate, and supervise all national banks and thrift institutions and the federally licensed branches and agencies of foreign banks in the United States. The acting Comptroller of the Currency is Brian P. Brooks, who took office in May 2020.
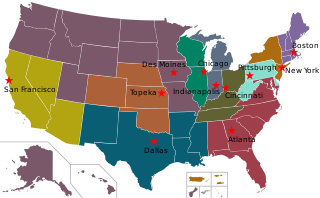
The Federal Home Loan Banks are 11 U.S. government-sponsored banks that provide reliable liquidity to member financial institutions to support housing finance and community investment. With their members, the FHLBanks represents the largest collective source of home mortgage and community credit in the United States.

A collateralized debt obligation (CDO) is a type of structured asset-backed security (ABS). Originally developed as instruments for the corporate debt markets, after 2002 CDOs became vehicles for refinancing mortgage-backed securities (MBS). Like other private label securities backed by assets, a CDO can be thought of as a promise to pay investors in a prescribed sequence, based on the cash flow the CDO collects from the pool of bonds or other assets it owns. Distinctively, CDO credit risk is typically assessed based on a probability of default (PD) derived from ratings on those bonds or assets.
Deposit insurance is a measure implemented in many countries to protect bank depositors, in full or in part, from losses caused by a bank's inability to pay its debts when due. Deposit insurance systems are one component of a financial system safety net that promotes financial stability.

The Farm Credit Act of 1933 established the Farm Credit System (FCS) as a group of cooperative lending institutions to provide short-, intermediate-, and long-term loans for agricultural purposes. Specifically, it authorized the Farm Credit Administration (FCA) to create 12 Production Credit Associations (PCAs) and 12 Banks for Cooperatives (BCs) alongside the 12 established Federal Land Banks (FLBs), as well as a Central Bank for Cooperatives.

The Bank of Canada is a Crown corporation and Canada's central bank. Chartered in 1934 under the Bank of Canada Act, it is responsible for formulating Canada's monetary policy, and for the promotion of a safe and sound financial system within Canada. The Bank of Canada is the sole issuing authority of Canadian banknotes, provides banking services and money management for the government, and loans money to Canadian financial institutions. The contract to produce the banknotes has been held by the Canadian Bank Note Company since 1935.
The Farm Credit System (FCS) in the United States is a nationwide network of borrower-owned lending institutions and specialized service organizations. The Farm Credit System provides more than $304 billion in loans, leases, and related services to farmers, ranchers, rural homeowners, aquatic producers, timber harvesters, agribusinesses, and agricultural and rural utility cooperatives.
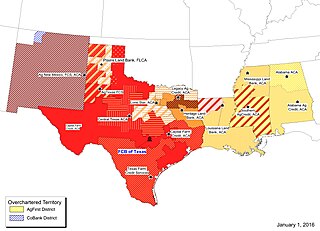
Farm Credit Bank of Texas, part of the US Farm Credit System, serves as a wholesale lender and business-service provider to 14 local borrower-owned Farm Credit associations in Alabama, Louisiana, Mississippi, New Mexico and Texas.

The Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989 (FIRREA), is a United States federal law enacted in the wake of the savings and loan crisis of the 1980s.

Flow of funds accounts are a system of interrelated balance sheets for a nation, calculated periodically. There are two types of balance sheets: those showing
Title 12 of the United States Code outlines the role of Banks and Banking in the United States Code.

The United States Postal Savings System was a postal savings system signed into law by President William Howard Taft and operated by the United States Post Office Department, predecessor of the United States Postal Service, from January 1, 1911, until July 1, 1967.

In United States federal agriculture legislation, the Agricultural Credit Act of 1987 was enacted in response to the severe financial crisis of the early- to mid-1980s, which affected both farmers and their lending institutions.

The Farm Credit Act of 1971 recodified all previous acts governing the Farm Credit System (FCS), a cooperatively owned government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) that provides credit primarily to farmers and ranchers.
The Resolution Funding Corporation (REFCORP) is a government-sponsored enterprise that provides funds to the Resolution Trust Corporation, which was established to finance the bailout of savings and loan associations in the wake of the savings and loan crisis of the 1980s in the United States. It was established by the United States Congress in the summer of 1989, as part of the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989. The Resolution Funding Corporation is a 501(c)(1) organization. As of July 1997, the Resolution Funding Corporation's debt stood at $30 billion.
The Australian government debt is the amount owed by the Australian federal government. The Australian Office of Financial Management, which is part of the Treasury Portfolio, is the agency which manages the government debt and does all the borrowing on behalf of the Australian government. Australian government borrowings are subject to limits and regulation by the Loan Council, unless the borrowing is for defence purposes or is a 'temporary' borrowing. Government debt and borrowings have national macroeconomic implications, and are also used as one of the tools available to the national government in the macroeconomic management of the national economy, enabling the government to create or dampen liquidity in financial markets, with flow on effects on the wider economy.
Smith v. Kansas City Title & Trust Co., 255 U.S. 180 (1921), was a United States Supreme Court case that helped define the range and scope of federal question jurisdiction in state corporate law matters. The case dealt with whether or not a district court had the power to uphold the constitutional validity of the Federal Farm Loan Act of 1916.








