Related Research Articles

Cromarty is a town, civil parish and former royal burgh in Ross and Cromarty, in the Highland area of Scotland. Situated at the tip of the Black Isle on the southern shore of the mouth of Cromarty Firth, it is 5 miles (8 km) seaward from Invergordon on the opposite coast. In the 2001 census, it had a population of 719.

Cromartyshire is a historic county in the Highlands of Scotland, comprising the medieval "old shire" around the county town of Cromarty and 22 enclaves and exclaves transferred from Ross-shire in the late 17th century. The largest part, six times the size of the old shire, is Coigach, northwest from Ullapool. In 1890, Cromartyshire was merged with Ross-shire into the administrative county of Ross and Cromarty, which in 1975 was merged into the new council area of Highland.

Dingwall is a town and a royal burgh in the Highland council area of Scotland. It has a population of 5,491. It was an east-coast harbour that now lies inland. Dingwall Castle was once the biggest castle north of Stirling. On the town's present-day outskirts lies Tulloch Castle, parts of which may date back to the 12th century. In 1411 the Battle of Dingwall is said to have taken place between the Clan Mackay and the Clan Donald.
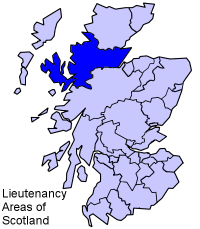
Ross and Cromarty, also referred to as Ross-shire and Cromartyshire, is a variously defined area in the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. There is a registration county and a lieutenancy area in current use, the latter of which is 8,019 square kilometres in extent. Historically there has also been a constituency of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, a local government county, a district of the Highland local government region and a management area of the Highland Council. The local government county is now divided between two local government areas: the Highland area and Na h-Eileanan Siar. Ross and Cromarty border Sutherland to the north and Inverness-shire to the south.
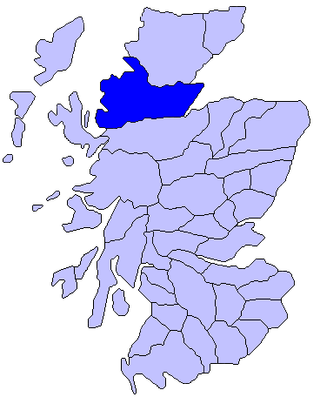
Ross is a region of Scotland. One of the provinces of Scotland from the 9th century, it gave its name to a later earldom and to the counties of Ross-shire and, later, Ross and Cromarty. The name Ross allegedly derives from a Gaelic word meaning "headland", perhaps a reference to the Black Isle. Another possible origin is the West Norse word for Orkney – Hrossey – meaning horse island; the area once belonged to the Norwegian earldom of Orkney. Ross is a historical comital region, perhaps predating the Mormaerdom of Ross. It is also a region used by the Kirk, with the Presbytery of Ross being part of the Synod of Ross, Sutherland and Caithness.
The Black Isle is a peninsula within Ross and Cromarty, in the Scottish Highlands. It includes the towns of Cromarty and Fortrose, and the villages of Culbokie, Jemimaville, Rosemarkie, Avoch, Munlochy, Tore, and North Kessock, as well as numerous smaller settlements. About 12,000 people live on the Black Isle, depending on the definition.

The Free Church of Scotland is an evangelical, Calvinist denomination in Scotland. It was historically part of the original Free Church of Scotland that remained outside the union with the United Presbyterian Church of Scotland in 1900. Now, it remains a distinct Presbyterian denomination in Scotland.

Evanton is a small village in Easter Ross, in the Highland council area of Scotland. It lies between the River Sgitheach and the Allt Graad, is 24 kilometres (15 mi) north of Inverness, some 6.5 km (4.0 mi) south-west of Alness, and 10 km (6.2 mi) northeast of Dingwall.
Cromartyshire was a county constituency of the House of Commons of Great Britain from 1708 until 1800, and of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1832.
Conon Bridge is a small village in the Highland region of Scotland. The current Gaelic name is likely a neologism: the bridge was not built until the early 19th century and some early gravestones show the name sgudal or scuddle. One suggested source is the Old Norse "sku dal", valley of the fine views.

Dingwall or Dingwell is a Scottish surname but is of Viking origin. One of the most prominent families by the name of Dingwall in Scotland were the Dingwalls of Kildun who were vassals of the Earl of Ross and also septs of the Clan Munro, a Scottish clan of the Scottish Highlands.

The Diocese of Ross was an ecclesiastical territory or diocese in the Highland region of Scotland during the Middle Ages and Early modern period. The Diocese was led by the Bishop of Ross, and the cathedral was, latterly, at Fortrose. The bishops of the Early Church were located at Rosemarkie. The diocese had only one Archdeacon, the Archdeacon of Ross, first attested in 1223 with the appearance of Archdeacon Robert, who was consecrated bishop of Ross on 21 June 1249 x 20 June 1250. There is only one known Dean of Christianty (sic.), one Donald Reid called the dean of christianty of Dingwall on 12 June 1530.

Easter Kinkell is a rural village, in the parish of Urquhart and Logie Wester, in the area known as Black Isle, in the county of Ross-shire, Scottish Highlands. It is also in the Scottish council area of Highland.
Rev. Donald Macfarlane (1834–1926) was the founding father of the Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland. It began as a separate denomination when he tabled a Protest against the Declaratory Act at 25 May 1893 meeting of the General Assembly of the Free Church of Scotland (1843–1900). The Act, originally passed in 1892, had allowed a watering-down of the Calvinism of the church and conservative Free Churchmen like Macfarlane believed it would prevent church discipline of those who opposed the Westminster Confession of Faith as a result of it. Macfarlane and those who followed him believed that it 'altered and vitiated' the constitution of the Free Church. On 28 July 1893, at a meeting in Portree, Isle of Skye, Macfarlane joined the Rev Donald Macdonald, Shieldaig and Alexander Macfarlane, a schoolmaster on Raasay, in forming a presbytery. Macfarlane was minister of the Free Church in Strathconon, Ross-shire (1873–1879), followed by Moy, Inverness-shire (1879–1889) and Kilmallie (1889–1893). As a Free Presbyterian minister he served in Raasay until 1903 when he was translated to the Dingwall congregation which he pastored until his death in 1926.
Murdoch MacQueen (1848–1912) was a minister of the Free Church of Scotland who served as Moderator of the General Assembly at the end of his career in 1904/05.

Alexander Ross FRIBA LLD was a 19th/20th century Scottish architect specialising in churches, especially for the Free Church of Scotland and the Scottish Episcopal Church. He was Provost of Inverness from 1889 to 1895.

Duncan Forbes of Culloden was a Scottish lawyer and Whig politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1721 to 1737. As Lord President and senior Scottish legal officer, he played a major role in helping the government suppress the 1745 Jacobite Rising.

Alexander Ross was a Scottish missionary with the United Presbyterian Church (Scotland) in Duke Town, Old Calabar, West Africa along with other notable missionaries including William Anderson, Hugh Goldie, and Mary Slessor. Making two separate expeditions in 1877 and 1878, Ross was the first white man to venture south of Old Calabar to the palm-oil town of Odobo. He discovered the Falls of Komè on the River Meme and recorded details of the places, customs and languages of Efut. In 1881 the Mission was torn apart by a schism between Ross and Anderson that was to be a crucial link in the chain of events which led to the annexation by Britain of the territory from Calabar to the Niger.

Murdo or Murdoch Mackenzie, also known as Murdo McRorie was a Scottish courtier and the builder of Fairburn Tower near Inverness.
References
- ↑ Shennan, Hay (1892). Boundaries of Counties and Parishes in Scotland: as settled by the Boundary Commissioners under the Local Government (Scotland) Act, 1889. Edinburgh: William Green & Sons. pp. 132–134 – via Internet Archive.
- ↑ Du Toit 2004.
- ↑ "An 18th century distillery at Mulchaich Farm, Ferintosh on the Black Isle, Ross-shire". North of Scotland Archaeological Society. Retrieved 14 July 2018.