
The Sea of Azov is an inland shelf sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow Strait of Kerch, and is sometimes regarded as a northern extension of the Black Sea. The sea is bounded by Russia on the east, and by Ukraine on the northwest and southwest, currently under Russian occupation. It is an important access route for Central Asia, from the Caspian Sea via the Volga-Don Canal.

Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The Oxford Dictionary states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."

Atyrau, known until 1991 as Guryev, is a city in Kazakhstan and the capital of Atyrau Region. Atyrau is a transcontinental city, at the mouth of the Ural River on the Caspian Sea, between Europe and Asia, 2,700 kilometres west of Almaty and 351 kilometres east of the Russian city of Astrakhan.

The Port of London Authority (PLA) is a self-funding public trust established on 31 March 1909 in accordance with the Port of London Act 1908 to govern the Port of London. Its responsibility extends over the Tideway of the River Thames and its continuation. It maintains and supervises navigation, and protects the river's environment.

Rostov-on-Don is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East European Plain on the Don River, 32 kilometers (20 mi) from the Sea of Azov, directly north of the North Caucasus. The southwestern suburbs of the city lie above the Don river delta. Rostov-on-Don has a population of over one million people, and is an important cultural centre of Southern Russia.

The national flag of Russia, also known as the State Flag of the Russian Federation, is a tricolour flag consisting of three equal horizontal fields: white on the top, blue in the middle, and red on the bottom. The flag was first used as an ensign for Russian merchant ships in 1696.

Kotka is a city in the southern part of the Kymenlaakso province on the Gulf of Finland. Kotka is a major port and industrial city and also a diverse school and cultural city, which was formerly part of the old Kymi parish; later, Kymi with the Haapasaari island and Karhula, the latter of which once separate from Kymi as the market town, were incorporated into Kotka. The neighboring municipalities of Kotka are Hamina, Kouvola and Pyhtää. Kotka belongs to the Kotka-Hamina subdivision, and with Kouvola, Kotka is one of the capital center of the Kymenlaakso region. It is the 19th largest city in terms of population as a single city, but the 12th largest city of Finland in terms of population as an urban area.

Perm, previously known as Yagoshikha (Ягошиха) (1723–1781), and Molotov (Молотов) (1940–1957), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Perm Krai, Russia. The city is located on the banks of the Kama River, near the Ural Mountains, covering an area of 799.68 square kilometres, with a population of over one million residents. Perm is the fifteenth-largest city in Russia, and the fifth-largest city in the Volga Federal District.

The koch was a special type of small one or two mast wooden sailing ships designed and used in Russia for transpolar voyages in ice conditions of the Arctic seas, popular among the Pomors.

Makhachkala, previously known as Petrovskoye and Port-Petrovsk, or by the local Kumyk name of Anji, is the capital and largest city of Dagestan, Russia. The city is located on the Caspian Sea, covering an area of 468.13 square kilometres, with a population of over 603,518 residents, while the urban agglomeration covers over 3,712 square kilometres, with a population of roughly 1 million residents. Makhachkala is the fourth-largest city in the Caucasus, the largest city in the North Caucasus and the North Caucasian Federal District, as well as the third-largest city on the Caspian Sea. The city is extremely ethnically diverse, with a minor ethnic Russian population.

Berdiansk or Berdyansk is a port city in Zaporizhzhia Oblast, south-eastern Ukraine. It is on the northern coast of the Sea of Azov, which is connected to the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Berdiansk Raion. The city is named after the Berda River's Berdianska Spit, at the foot of which it is located. Its population is 106,311.

Dwarka is a town and municipality of Devbhumi Dwarka district in the state of Gujarat. It is located on the western shore of the Okhamandal Peninsula on the right bank of the Gomti river at the mouth of the Gulf of Kutch facing the Arabian Sea.

In military tactics, a flanking maneuver is a movement of an armed force around an enemy force's side, or flank, to achieve an advantageous position over it. Flanking is useful because a force's fighting strength is typically concentrated in its front, therefore, to circumvent an opposing force's front and attack its flank is to concentrate one's own offense in the area where the enemy is least able to concentrate defense.
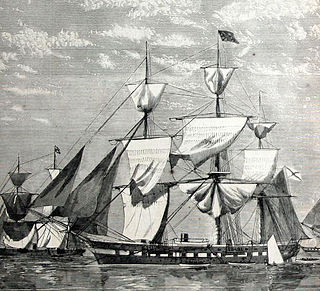
Alexander Nevsky was a large screw frigate of the Russian Imperial Navy. The ship was designed as part of a challenge being offered by the Russian Empire to the Royal Navy, but was lost in a shipwreck in 1868 while Grand Duke Alexei, son of Tsar Alexander II, was aboard.

The Imperial Chinese Navy was the modern navy of the Qing dynasty of China established in 1875. An Imperial naval force in China first came into existence from 1132 during the Song dynasty and existed in some form until the end of the Qing dynasty in 1912. However, the "Imperial Chinese Navy" usually only refers to the Qing navy, which existed between 1875 and 1912.

Oryol was a frigate that served in the Russian Navy. It was commissioned by Tsar Alexis I to protect Russian trading ships on the Caspian Sea and became the first Russian-built warship. The ship was built between 1667 and 1669 by the developing shipyard in Dedinovo on the Oka River. Although Oryol was captured and burned in 1670, it has achieved lasting importance as a symbol of the birth of Russian naval power.
John J. Collins is the Holmes Professor of Old Testament Criticism and Interpretation at Yale Divinity School. He is noted for his research in the Hebrew Bible, as well as the apocryphal works of the Second Temple period including the sectarian works found in Dead Sea Scrolls and their relation to Christian origins. Collins has published and edited over 300 scholarly works, and a number of popular level articles and books. Among his best known works are the Between Athens and Jerusalem: Jewish Identity in the Hellenistic Diaspora ; Daniel in the Hermeneia commentary series ; The Scepter and the Star. The Messiahs of the Dead Sea Scrolls and Other Ancient Literature ; and The Bible after Babel: Historical Criticism in a Postmodern Age.

The fences in Saint Petersburg, Russia are highly varied, with many notable examples remaining in use today from different periods in Russian architectural history.

The coat of arms of Saint Petersburg is the official symbol of the city and was adopted in 23 April 2003.

The Åland War is the Finnish term for the operations of a British-French naval force against military and civilian facilities on the coast of the Grand Duchy of Finland in 1854–1856, during the Crimean War between the Russian Empire and the allied France and Britain. The war is named after the Battle of Bomarsund in Åland. Although the name of the war refers to Åland, skirmishes were also fought in other coastal towns of Finland in the Gulf of Bothnia and the Gulf of Finland.



















