Related Research Articles

Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess of water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils is good enough to prevent severe waterlogging, but many soils need artificial drainage to improve production or to manage water supplies.

Greenup County is a county located along the Ohio River in the northeastern part of the U.S. state of Kentucky. The county was founded in 1803 and named in honor of Christopher Greenup. Its county seat is Greenup. Greenup County is part of the Huntington-Ashland, WV-KY-OH Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Oxisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy, best known for their occurrence in tropical rain forest within 25 degrees north and south of the Equator. In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB), they belong mainly to the ferralsols, but some are plinthosols or nitisols. Some oxisols have been previously classified as laterite soils.

Soil liquefaction occurs when a cohesionless saturated or partially saturated soil substantially loses strength and stiffness in response to an applied stress such as shaking during an earthquake or other sudden change in stress condition, in which material that is ordinarily a solid behaves like a liquid. In soil mechanics, the term "liquefied" was first used by Allen Hazen in reference to the 1918 failure of the Calaveras Dam in California. He described the mechanism of flow liquefaction of the embankment dam as:
If the pressure of the water in the pores is great enough to carry all the load, it will have the effect of holding the particles apart and of producing a condition that is practically equivalent to that of quicksand... the initial movement of some part of the material might result in accumulating pressure, first on one point, and then on another, successively, as the early points of concentration were liquefied.

Flatwoods, pineywoods, pine savannas and longleaf pine-wiregrass ecosystem are terms that refer to an ecological community in the Southeastern coastal plain of North America. Flatwoods are an ecosystem maintained by wildfire or prescribed fire and are dominated by longleaf pine, and slash pine in the tree canopy and saw palmetto, gallberry and other flammable evergreen shrubs in the understory, along with a high diversity of herb species. It was once one of the dominant ecosystem types of southeastern North America. Although grasses and pines are characteristic of this system, the precise composition changes from west to east, that is, from Texas to Florida. In Louisiana, savannas even differ between the east and west side of the Mississippi River. The key factor maintaining this habitat type is recurring fire. Without fire, the habitat is eventually invaded by other species of woody plants.

The Apalachicola National Forest is the largest U.S. National Forest in the state of Florida. It encompasses 632,890 acres and is the only national forest located in the Florida Panhandle. The National Forest provides water and land-based outdoors activities such as off-road biking, hiking, swimming, boating, hunting, fishing, horse-back riding, and off-road ATV usage.
This is an index of articles relating to soil.

The Flatwoods monster, in West Virginia folklore, is an entity reported to have been sighted in the town of Flatwoods in Braxton County, West Virginia, United States, on September 12, 1952, after a bright object crossed the night sky. Over 50 years later, investigators concluded that the light was a meteor and the creature was a barn owl perched in a tree, with shadows making it appear to be a large humanoid.

Osceola National Forest is a National Forest located in northeast Florida.

The frosted flatwoods salamander is a small, elongated species of mole salamander. It has a small, indistinct head, short legs, and a long, rounded tail. Typical coloration consists of a background of brownish- to purplish-black overlaid with narrow gray or silvery-white reticulations, bands, or diffuse spotting. The gilled aquatic larvae are distinctly colored, having a series of bold brown and yellow longitudinal stripes.

The Ogeechee River is a 294-mile-long (473 km) blackwater river in the U.S. state of Georgia. It heads at the confluence of its North and South Forks, about 2.5 miles (4.0 km) south-southwest of Crawfordville and flowing generally southeast to Ossabaw Sound about 16 miles (26 km) south of Savannah. Its largest tributary is the Canoochee River, which drains approximately 1,400 square miles (3,600 km2) and is the only other major river in the basin. The Ogeechee has a watershed of 5,540 square miles (14,300 km2). It is one of the state's few free-flowing streams.

Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs in the vadose zone below plant roots and, is often expressed as a flux to the water table surface. Groundwater recharge also encompasses water moving away from the water table farther into the saturated zone. Recharge occurs both naturally and through anthropogenic processes, where rainwater and or reclaimed water is routed to the subsurface.

A Pocosin is a type of palustrine wetland with deep, acidic, sandy, peat soils. Groundwater saturates the soil except during brief seasonal dry spells and during prolonged droughts. Pocosin soils are nutrient-deficient (oligotrophic), especially in phosphorus.
Acid sulfate soils are naturally occurring soils, sediments or organic substrates that are formed under waterlogged conditions. These soils contain iron sulfide minerals or their oxidation products. In an undisturbed state below the water table, acid sulfate soils are benign. However, if the soils are drained, excavated or exposed to air by a lowering of the water table, the sulfides react with oxygen to form sulfuric acid.
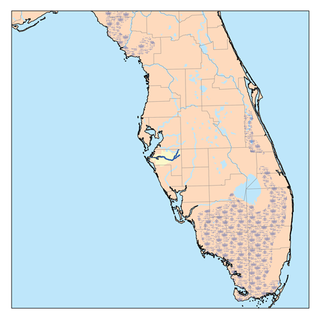
The Manatee River is a 36-mile-long (58 km) river in Manatee County, Florida. The river forms in the northeastern corner of Manatee County and flows into the Gulf of Mexico at the southern edge of Tampa Bay.

Myakka soil is the official state soil of Florida, which has more than 1,500,000 acres (6,100 km2) of land composed partly or entirely of Myakka soils, out of its total acreage of 42,084,928 acres (170,311.66 km2). Its name derives from a Native American word that means "Big Waters". This soil is primarily located in broad flatwoods in irregularly shaped areas ranging from 5 to 500 acres in size. The organic matter content and fertility of the soil is low. Most areas where this soil occurs are native range or improved pasture, although some is used for citrus or vegetable farming. Some counties in Florida where this soil occurs are Hendry, Collier, Glades, and Lee.
Drainage research is the study of agricultural drainage systems and their effects to arrive at optimal system design.

Colt Creek State Park is a Florida State Park in Central Florida, 16 miles (26 km) north of Lakeland off of State Road 471. This 5,067 acre park nestled within the Green Swamp Wilderness Area and named after one of the tributaries that flows through the property was opened to the public on January 20, 2007. Composed mainly of pine flatwoods, cypress domes and open pasture land, this piece of pristine wilderness is home to many animal species including the American bald eagle, Southern fox squirrel, gopher tortoise, white-tailed deer, wild turkey and bobcat.

The environmental effects of irrigation relate to the changes in quantity and quality of soil and water as a result of irrigation and the subsequent effects on natural and social conditions in river basins and downstream of an irrigation scheme. The effects stem from the altered hydrological conditions caused by the installation and operation of the irrigation scheme.

Paludification is the most common process by which peatlands in the boreal zone are formed.
References
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on September 29, 2006. Retrieved September 14, 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Official Series Description – FLATWOODS Series Archived 2008-09-28 at the Wayback Machine