Related Research Articles

The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.
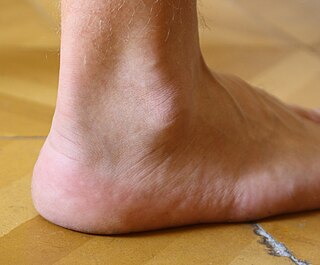
The ankle, the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.

The extensor hallucis longus muscle is a thin skeletal muscle, situated between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It extends the big toe and dorsiflects the foot. It also assists with foot eversion and inversion.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
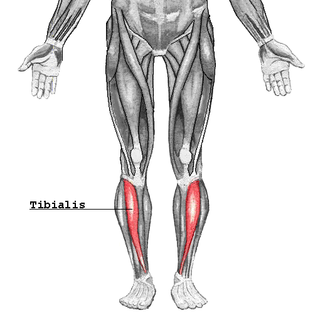
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.
The posterior tibial artery of the lower limb is an artery that carries blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar surface of the foot. It branches from the popliteal artery via the tibial-fibular trunk.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The flexor hallucis longus muscle (FHL) attaches to the plantar surface of phalanx of the great toe and is responsible for flexing that toe. The FHL is one of the three deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg, the others being the flexor digitorum longus and the tibialis posterior. The tibialis posterior is the most powerful of these deep muscles. All three muscles are innervated by the tibial nerve which comprises half of the sciatic nerve.

The flexor digitorum longus muscle is situated on the tibial side of the leg. At its origin it is thin and pointed, but it gradually increases in size as it descends. It serves to flex the second, third, fourth, and fifth toes.

In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.
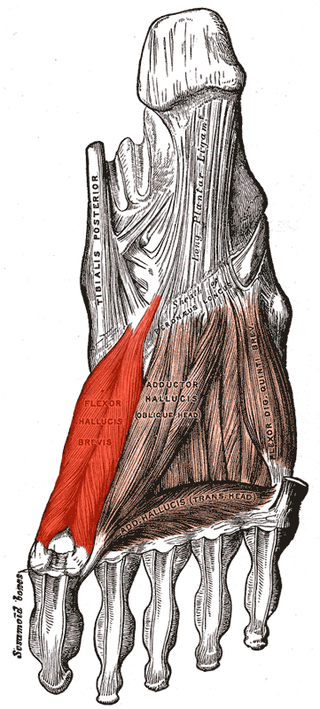
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe.

In humans, the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect.

The inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot is a Y-shaped band placed in front of the ankle-joint, the stem of the Y being attached laterally to the upper surface of the calcaneus, in front of the depression for the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament; it is directed medialward as a double layer, one lamina passing in front of, and the other behind, the tendons of the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus.

The superior extensor retinaculum of the foot is the upper part of the extensor retinaculum of foot which extends from the ankle to the heelbone.

A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.
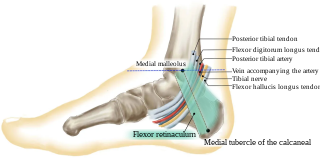
The tarsal tunnel is a passage found along the inner leg underneath the medial malleolus of the ankle.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 489 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 489 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- 1 2 Lowe, Whitney; Chaitow, Leon (2009-01-01), Lowe, Whitney; Chaitow, Leon (eds.), "Chapter 6 - Foot, ankle, and lower leg", Orthopedic Massage (Second Edition), Edinburgh: Mosby, pp. 77–115, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06812-6.00006-4, ISBN 978-0-443-06812-6 , retrieved 2021-03-02
- ↑ Fowler, Timothy J.; Scadding, John W. (28 November 2003). Clinical Neurology (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 60. ISBN 0-340-80798-9.
- ↑ Katirji, Bashar (2007-01-01), Katirji, Bashar (ed.), "Case 6", Electromyography in Clinical Practice (Second Edition), Philadelphia: Mosby, pp. 125–132, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-02899-8.50015-x, ISBN 978-0-323-02899-8 , retrieved 2021-03-02