Gallery
- CAS-TAS conversion
- An E6B flight computer commonly used by student pilots.
- nm-km conversion on a CRP-5 flight computer
A flight computer is a form of slide rule used in aviation and one of a very few analog computers in widespread use in the 21st century. Sometimes it is called by the make or model name like E6B, CR, CRP-5 or in German, as the Dreieckrechner. [1]
They are mostly used in flight training, but many professional pilots still carry and use flight computers. They are used during flight planning (on the ground before takeoff) to aid in calculating fuel burn, wind correction, time en route, and other items. In the air, the flight computer can be used to calculate ground speed, estimated fuel burn and updated estimated time of arrival. The back is designed for wind correction calculations, i.e., determining how much the wind is affecting one's speed and course.
One of the most useful parts of the E6B, is the technique of finding distance over time. Take the number 60 on the inner circle which usually has an arrow, and sometimes says rate on it. 60 is used in reference to the number of minutes in an hour, by placing the 60 on the airspeed in knots, on the outer ring the pilot can find how far the aircraft will travel in any given number of minutes. Looking at the inner ring for minutes traveled and the distance traveled will be above it on the outer ring. This can also be done backwards to find the amount of time the aircraft will take to travel a given number of nautical miles. On the main body of the flight computer it will find the wind component grid, which it will use to find how much crosswind the aircraft will actually have to correct for.
The crosswind component is the amount of crosswind in knots that is being applied to the airframe and can be less than the actual speed of the wind because of the angle. Below that the pilot will find a grid called crosswind correction, this grid shows the difference the pilot needs to correct for because of wind. On either side of the front it will have rulers, one for statute miles and one for nautical miles on their sectional map.
Another very useful part is the conversion scale on the front outer circle, which helps convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius. The back of the E6B is used to find ground speed and determine how much wind correction it needs. [2]

Flight instruments are the instruments in the cockpit of an aircraft that provide the pilot with data about the flight situation of that aircraft, such as altitude, airspeed, vertical speed, heading and much more other crucial information in flight. They improve safety by allowing the pilot to fly the aircraft in level flight, and make turns, without a reference outside the aircraft such as the horizon. Visual flight rules (VFR) require an airspeed indicator, an altimeter, and a compass or other suitable magnetic direction indicator. Instrument flight rules (IFR) additionally require a gyroscopic pitch-bank, direction and rate of turn indicator, plus a slip-skid indicator, adjustable altimeter, and a clock. Flight into instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) require radio navigation instruments for precise takeoffs and landings.

Wind shear /ʃɪr/, sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude.

The airspeed indicator (ASI) or airspeed gauge is a flight instrument indicating the airspeed of an aircraft in kilometres per hour (km/h), knots, miles per hour (MPH) and/or metres per second (m/s). The recommendation by ICAO is to use km/h, however knots (kt) is currently the most used unit. The ASI measures the pressure differential between static pressure from the static port, and total pressure from the pitot tube. This difference in pressure is registered with the ASI pointer on the face of the instrument.

In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air it is flying through. It is difficult to measure the exact airspeed of the aircraft, but other measures of airspeed, such as indicated airspeed and Mach number give useful information about the capabilities and limitations of airplane performance. The common measures of airspeed are:

The true airspeed of an aircraft is the speed of the aircraft relative to the air mass through which it is flying. The true airspeed is important information for accurate navigation of an aircraft. Traditionally it is measured using an analogue TAS indicator, but as the Global Positioning System has become available for civilian use, the importance of such air-measuring instruments has decreased. Since indicated, as opposed to true, airspeed is a better indicator of margin above the stall, true airspeed is not used for controlling the aircraft; for these purposes the indicated airspeed – IAS or KIAS – is used. However, since indicated airspeed only shows true speed through the air at standard sea level pressure and temperature, a TAS meter is necessary for navigation purposes at cruising altitude in less dense air. The IAS meter reads very nearly the TAS at lower altitude and at lower speed. On jet airliners the TAS meter is usually hidden at speeds below 200 knots (370 km/h). Neither provides for accurate speed over the ground, since surface winds or winds aloft are not taken into account.

Indicated airspeed (IAS) is the airspeed of an aircraft as measured by its pitot-static system and displayed by the airspeed indicator (ASI). This is the pilots' primary airspeed reference.

A crosswind is any wind that has a perpendicular component to the line or direction of travel. This affects the aerodynamics of many forms of transport. Moving non-parallel to the wind direction creates a crosswind component on the object and thus increasing the apparent wind on the object; such use of cross wind travel is used to advantage by sailing craft, kiteboarding craft, power kiting, etc. On the other side, crosswind moves the path of vehicles sideways and can be a hazard.

A slip is an aerodynamic state where an aircraft is moving somewhat sideways as well as forward relative to the oncoming airflow or relative wind. In other words, for a conventional aircraft, the nose will be pointing in the opposite direction to the bank of the wing(s). The aircraft is not in coordinated flight and therefore is flying inefficiently.
Ground speed is the horizontal speed of an aircraft relative to the Earth’s surface. It is vital for accurate navigation that the pilot has an estimate of the ground speed that will be achieved during each leg of a flight.

In air navigation, the 1 in 60 rule is a rule of thumb which states that if a pilot has traveled sixty miles then an error in track of one mile is approximately a 1° error in heading, and proportionately more for larger errors. The rule is used by pilots with many other tasks to perform, often in a basic aircraft without the aid of an autopilot, who need a simple process that can be performed in their heads. This rule is also used by air traffic controllers to quickly determine how much to turn an aircraft for separation purposes.
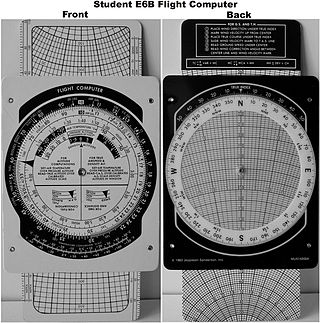
The E6B flight computer is a form of circular slide rule used in aviation. It is an instance of an analog calculating device still being used in the 21st century.
A tailwind is a wind that blows in the direction of travel of an object, while a headwind blows against the direction of travel. A tailwind increases the object's speed and reduces the time required to reach its destination, while a headwind has the opposite effect.

Flight planning is the process of producing a flight plan to describe a proposed aircraft flight. It involves two safety-critical aspects: fuel calculation, to ensure that the aircraft can safely reach the destination, and compliance with air traffic control requirements, to minimise the risk of midair collision. In addition, flight planners normally wish to minimise flight cost through the appropriate choice of route, height, and speed, and by loading the minimum necessary fuel on board. Air Traffic Services (ATS) use the completed flight plan for separation of aircraft in air traffic management services, including tracking and finding lost aircraft, during search and rescue (SAR) missions.
The clock code is a method of mentally computing the sine of an angle between zero and sixty degrees. Pilots sometimes need to do this to estimate the heading correction due to the wind, and sailors may find it useful to do the same thing to allow for the current due to the tides.
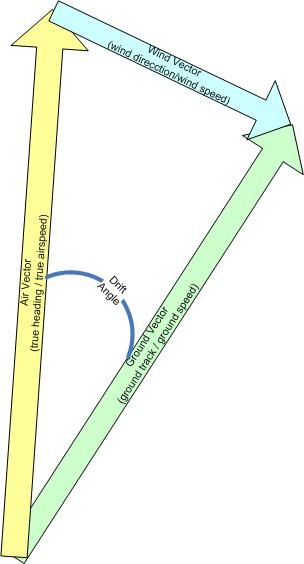
In air navigation, the wind triangle is a graphical representation of the relationship between aircraft motion and wind. It is used extensively in dead reckoning navigation.

Lufthansa Flight 2904 was an Airbus A320-200 flying from Frankfurt, Germany to Warsaw, Poland that overran the runway at Okęcie International Airport on 14 September 1993.

TRACON is a series of game software programs that simulate an air traffic control environment on a personal computer. The games were originally sold by Texas-based Wesson International as an offshoot to their line of professional air traffic control simulation products. TRACON and RAPCON were released in 1989, and TRACON II was released in 1990. Wesson was merged into Adacel in 2001.

China Airlines Flight 605 was a daily non-stop flight departing from Taipei, Taiwan at 6:30 a.m. and arriving in Hong Kong at 7:00 a.m. local time. On November 4, 1993, the plane went off the runway and overran attempting to land during a storm. It was the first hull loss of a Boeing 747-400.

Modern United States Navy aircraft carrier air operations include the operation of fixed-wing and rotary aircraft on and around an aircraft carrier for performance of combat or noncombat missions. The flight operations are highly evolved, based on experiences dating back to 1922 with USS Langley.
Crosswind kite power is power derived from airborne wind-energy conversion systems or crosswind kite power systems (CWKPS). The kite system is characterized by energy-harvesting parts flying transversely to the direction of the ambient wind, i.e., to crosswind mode; sometimes the entire wing set and tether set are flown in crosswind mode. From toy to power-grid-feeding sizes, these systems may be used as high-altitude wind power (HAWP) devices or low-altitude wind power (LAWP) devices without having to use towers. Flexible wings or rigid wings may be used in the kite system. A tethered wing, flying in crosswind at many times wind speed, harvests wind power from an area that exceeds the wing's total area by many times.