 |
|---|
The government of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) conducts its own foreign relations. Since independence in 1986, the FSM has established diplomatic relations with 92 countries, including all of its Pacific neighbors.
 |
|---|
The government of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) conducts its own foreign relations. Since independence in 1986, the FSM has established diplomatic relations with 92 countries, including all of its Pacific neighbors.
Regional cooperation through various multilateral organizations is a key element in FSM's foreign policy. FSM is a full member of the Pacific Islands Forum, the South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission, the Pacific Regional Environment Programme and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community. The country also is one of the eight signatories of the Nauru Agreement Concerning Cooperation In The Management Of Fisheries Of Common Interest which collectively controls 25-30% of the world's tuna supply and approximately 60% of the western and central Pacific tuna supply. [1]
List of countries with which the Federated States of Micronesia maintains diplomatic relations with:
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| # | Country | Date [2] |
| 1 | 3 November 1986 | |
| 2 | 26 February 1987 | |
| 3 | 10 April 1987 | |
| 4 | 3 March 1988 | |
| 5 | 30 June 1988 | |
| 6 | 6 July 1988 | |
| 7 | 5 August 1988 | |
| 8 | 5 August 1988 | |
| 9 | 21 September 1988 | |
| 10 | 23 November 1988 | |
| 11 | 9 December 1988 | |
| 12 | 10 January 1989 | |
| 13 | 1 August 1989 | |
| 14 | 11 September 1989 | |
| 15 | 13 March 1990 | |
| 16 | 31 March 1990 | |
| 17 | 5 April 1990 | |
| 18 | 19 April 1990 | |
| 19 | 5 April 1991 | |
| 20 | 16 July 1991 | |
| 21 | 26 August 1991 | |
| 22 | 24 October 1991 | |
| 23 | 23 February 1992 | |
| 24 | 20 March 1992 | |
| 25 | 21 April 1992 | |
| 26 | 5 May 1992 | |
| 27 | 7 May 1992 | |
| 28 | 11 May 1992 | |
| 29 | 1 July 1992 | |
| 30 | 6 July 1992 | |
| 31 | 17 August 1992 | |
| 32 | 31 August 1992 | |
| 33 | 8 September 1992 | |
| 34 | 27 November 1992 | |
| 35 | 5 February 1993 | |
| 36 | 13 March 1993 | |
| 37 | 27 July 1993 | |
| – | 27 January 1994 | |
| 38 | 1 October 1994 | |
| 39 | 24 March 1995 | |
| 40 | 2 May 1995 | |
| 41 | 22 September 1995 | |
| 42 | 15 April 1996 | |
| 43 | 30 April 1996 | |
| 44 | 28 October 1996 | |
| 45 | 29 November 1996 | |
| 46 | 12 December 1996 | |
| – | 12 November 1997 | |
| 47 | 3 March 1998 | |
| – | 9 March 1999 | |
| 48 | 17 September 1999 | |
| 49 | 30 September 1999 | |
| 50 | 27 September 2001 | |
| 51 | 22 April 2003 | |
| 52 | 27 September 2004 | |
| 53 | 6 October 2004 | |
| 54 | 27 October 2004 | |
| 55 | 30 November 2004 | |
| 56 | 13 September 2006 | |
| 57 | 22 September 2006 | |
| 58 | 6 December 2006 | |
| 59 | 5 October 2007 | |
| 60 | 24 April 2008 | |
| 61 | 3 May 2010 | |
| 62 | 25 September 2010 | |
| 63 | 13 October 2010 | |
| 64 | 25 October 2010 | |
| 65 | 29 March 2011 | |
| 66 | 12 August 2011 | |
| 67 | 7 September 2011 | |
| 68 | 5 September 2013 | |
| 69 | 10 September 2013 | |
| – | 17 September 2013 | |
| 70 | 4 November 2013 | |
| 71 | 6 December 2013 | |
| – | 24 September 2014 | |
| 72 | 25 February 2015 | |
| 73 | 6 March 2015 | |
| 74 | 9 September 2015 | |
| 75 | 27 October 2015 | |
| 76 | 2 September 2016 | |
| 77 | 14 September 2016 | |
| 78 | 21 September 2017 | |
| 79 | 10 October 2017 | |
| 80 | 11 October 2017 | |
| 81 | 29 January 2018 [3] | |
| 82 | 12 April 2018 | |
| 83 | 29 August 2018 | |
| 84 | 25 September 2018 | |
| 85 | 25 September 2018 | |
| 86 | 30 October 2018 | |
| 87 | 5 February 2019 | |
| 88 | 11 December 2019 | |
| 89 | 20 September 2022 | |
| 90 | 21 September 2022 | |
| 91 | 20 October 2022 | |
| 92 | 19 April 2023 | |
| 93 | 7 November 2023 | |
The FSM maintains permanent embassies in four nations: China, Fiji, Japan and the United States. The FSM also maintains a resident consulate in Hawaii, Portland, Oregon and Guam. The FSM maintains non-resident embassies for four nations: Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore (all in Japan) and Israel in Fiji. Four nations maintain permanent embassies in the FSM: Australia, China, Japan and the United States. Additionally, 15 nations maintain non-resident embassies with the FSM. France and the United Kingdom have non-resident embassies for the FSM in Fiji. Canada, Italy and South Africa have non-resident embassies for the FSM in Australia. Indonesia has a non-resident embassy for the FSM in Japan. Chile has its non-resident embassies for the FSM in the United States. Croatia has its non-resident embassy for the FSM in Indonesia. Czech Republic, Finland, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, and Switzerland have non-resident embassies in the Philippines. New Zealand has its non-resident embassy for the FSM in Kiribati.
| Country | Notes |
|---|---|
| See Australia–Federated States of Micronesia relations | |
The People's Republic of China has close relations with the FSM in terms of both trade and foreign aid. Chinese aid projects have included among others the Giant Clam Farm Project in Kosrae, the Pilot Farm Project in Madolenihmw, the construction of a gymnasium on Pohnpei (officially named the FSM-China Friendship Sports Center), donation of police vehicles for the Yap state police, a facility to house the FSM's Tuna Commission, an expansion of the Chuuk State Airport Terminal, a biogas project on Chuuk, the construction of the Pohnpei Administration Building, and the construction of Kosrae High School Project. [4] China is the FSM's third largest trade partner (after the United States and Japan), a fact marked by the rapid increase in trade between the two nations. As the Chinese Ambassador to the FSM Zhang Weidong observed on the 20th anniversary of relations between the two countries, trade between China and the FSM had gone from "almost zero to $9.5 million in 2007." [5] | |
| Micronesia was one of ten Pacific countries to send a government member to the first Cuba-Pacific Islands ministerial meeting, held in Havana in September 2008. [6] [7] The aim of the meeting was to "strengthen cooperation" between Micronesia and Cuba, notably on addressing the impact of climate change. [8] | |
| See India–Federated States of Micronesia relations India and Micronesia have maintained diplomatic relations with each other since 1996. India gave 'Development assistance' to the country of about US$73,145 in 2009 for the purchase of machinery for the coconut industry. India also made a grant of 3 ITEC scholarships in 2010–11. As per the Ministry of External Affairs of the Government of India, "Micronesia has been supportive of issues of importance to India, particularly Indian candidatures to international organizations and supported India's candidature for the UNSC non-permanent seat in 2011–12. As per information available, there is one Indian family in Micronesia." [9] | |
| See Israel–Federated States of Micronesia relations The FSM is one of the most consistent supporters of Israel (along with the United States) in international affairs. Throughout the history of the United Nations General Assembly, it is claimed by some there has always been an "automatic majority" against Israel. [10] The United States has consistently opposed what it perceives as "unbalanced" "anti-Israel" resolutions and, in recent years, one other nation has joined Israel's defense — Micronesia. The foreign policy goals of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) are primarily linked to achieving economic development and protecting their vast marine environment. Israel was one of the first to welcome the FSM into the family of nations, even before the FSM became a member of the U.N. According to the FSM U.N. deputy ambassador, Micronesia has since sought close bilateral relations with Israel in areas such as agriculture, technical training and health care training. Israel has assisted the FSM in its early development. As one Micronesian diplomat said, "We need Israeli expertise, so I don't see a change in our policy anytime soon."[ citation needed ] | |
| The Federated States of Micronesia officially recognized the independence of the Republic of Kosovo on 5 December 2008. [11] [12] Kosovo and Micronesia established diplomatic relations on 19 September 2013. [13] | |
| See Marshall Islands–Federated States of Micronesia relations The Federated States of Micronesia and the Marshall Islands share very good relations, as they are both bound by Compacts of Free Association with the United States.[ citation needed ] | |
| See Federated States of Micronesia–Palau relations The Federated States of Micronesia and Palau share very good relations, as they are both bound by Compacts of Free Association with the United States.[ citation needed ] | |
The Federated States of Micronesia and The Republic of Korea (South Korea) were established diplomatic relations in April 1991. [15] | |
The islands of the FSM were once part of the Spanish East Indies.
| |
| See Micronesia-United States relations The Governments of the FSM and the U.S. signed the final version of the Compact of Free Association on October 1, 1982. The Compact went into effect on November 3, 1986, and the FSM became a sovereign nation in free association with the United States. Under the Compact, the U.S. has full authority and responsibility for the defense of the FSM. This security relationship can be changed or terminated by mutual agreement. The Compact provides U.S. grant funds and federal program assistance to the FSM. The basic relationship of free association continues indefinitely, but certain economic and defense provisions of the Compact expire in 2001, subject to renegotiation. Negotiations on extending the Compact began in November 1999. The United States is the FSM's largest trading partner. The relationship is heavily imbalanced. Of the FSM-US total balance of trade in goods in 2010 of US$38.3 million, the FSM imported $42.5 million in goods from the United States while exporting only US$4.2 million to the United States. [17] (see Economy of the Federated States of Micronesia). |

Fiji has experienced many coups recently, in 1987, 2000, and 2006. Fiji has been suspended various times from the Commonwealth of Nations, a grouping of mostly former British colonies. It was readmitted to the Commonwealth in December 2001, following the parliamentary election held to restore democracy in September that year, and has been suspended again because of the 2006 coup, but has been readmitted a second time after the 2014 election. Other Pacific Island governments have generally been sympathetic to Fiji's internal political problems and have declined to take public positions.

Kiribati is a full member of the Commonwealth, the IMF and the World Bank, and became a full member of the United Nations in 1999. Kiribati hosted the Thirty-First Pacific Islands Forum in October 2000. Kiribati has Least Developed Country Status and its interests rarely extend beyond the region. Through accession to the Lomé Convention, then Cotonou Agreement, Kiribati is also a member of the African Caribbean and Pacific Group. Kiribati maintains good relations with most countries and has particularly close ties to Pacific neighbours Japan, Australia, South Korea and New Zealand. Kiribati briefly suspended its relations with France in 1995 over that country's decision to renew nuclear testing in the South Pacific.

Vanuatu maintains diplomatic relations with many countries, and it has a small network of diplomatic missions. Australia, France, Japan, New Zealand, the People's Republic of China, South Korea and the United Kingdom maintain embassies, High Commissions, or missions in Port Vila. The British High Commission maintained a continued presence for almost a century, though closed from 2005 until reopening in 2019.

Nauru, following independence from the United Kingdom, became a sovereign, independent republic on 31 January 1968. Nauru has established diplomatic relations with a number of nations, including most of its Pacific neighbors with which it maintains economic, cultural and administrative ties.
From 1916 to 1975, Tuvalu was part of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands colony of the United Kingdom. A referendum was held in 1974 to determine whether the Gilbert Islands and Ellice Islands should each have their own administration. As a consequence of the referendum, the separate British colonies of Kiribati and Tuvalu were formed. Tuvalu became fully independent as a sovereign state within the Commonwealth on 1 October 1978. On 5 September 2000, Tuvalu became the 189th member of the United Nations.

Tonga, by a modification of its treaty of friendship with the United Kingdom in July 1970, is responsible for its own external affairs. It maintains cordial relations with most countries and has close relations with its Pacific neighbours and the United Kingdom. In 1998, it recognized the People's Republic of China and broke relations with Taiwan.
The Cook Islands maintains diplomatic relations with various countries and is a member of multilateral organisations. While the country is in free association with New Zealand, which can act on the Cook Islands' "delegated authority [...] to assist the Cooks Islands" in foreign affairs, the Cook Islands nevertheless enters into treaty obligations and otherwise "interacts with the international community as a sovereign and independent state."

Alik L. Alik is a diplomat and politician from the Federated States of Micronesia who was the Vice President of the Federated States of Micronesia from May 11, 2007 to May 11, 2015.
Cuban-Pacific relations are diplomatic, economic, cultural, and other relations between the Cuba and countries situated in Oceania. In the 2000s, Cuba has been strengthening its relations with Pacific nations, which have, for the most part, responded favorably to Cuban medical aid in particular. The first Cuba-Pacific Islands ministerial meeting was held in September 2008 in Havana, with government members from ten Pacific countries—Kiribati, Tuvalu, Nauru, Solomon Islands, Fiji, Tonga, Vanuatu, Samoa, the Federated States of Micronesia and Papua New Guinea—attending. The meeting was a consolidation rather than a starting point of Cuban-Pacific relations.
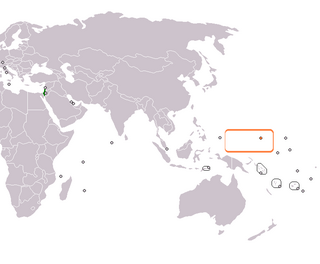
Israel – Micronesia relations are diplomatic and other relations between the State of Israel and the Federated States of Micronesia. Israel was among the first countries to establish formal diplomatic relations with Micronesia.

Diplomatic relations between China and the Federated States of Micronesia were established on September 11, 1989. The Chinese government first established an embassy in the capital of Palikir in 1990, and dispatched its first ambassador in 1991. In April 2023, the Chinese government allegedly threatened to assassinate the Micronesian president, David Panuelo, and so, Micronesia severed official relations between the two countries. It said it decided to increase relations with Taiwan and it accused China of bribing officials and trying to control the United States’ influence in the region. Initially, the Micronesian ambassador to Tokyo, Japan also served as Micronesia's ambassador to China, before Micronesia established an embassy in Beijing in 2007. President John Haglelgam was the first senior government agent from Micronesia to visit China, doing so in 1990. The current Chinese ambassador to Micronesia is Zhang Weidong, while the Micronesian ambassador to Beijing is Akillino H. Susaia.

The political status of the Cook Islands and Niue is formally defined as being states in free association within the Realm of New Zealand, which is made up of the Cook Islands, Niue, and New Zealand and its territories, Tokelau and the Ross Dependency. The Cook Islands and Niue do not have full constitutional independence from New Zealand but act as independent countries. Some countries have recognised them as sovereign entities and established diplomatic relations. However, New Zealand may carry out defence and foreign affairs on behalf of the two associated states when requested.

India–Federated States of Micronesia relations are the international relations that exist between the Republic of India and the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). The Embassy of India in Manila, Philippines is concurrently accredited to FSM.

Australia – Marshall Islands are bilateral relations between Australia and the Marshall Islands. The Marshall Islands are located approximately halfway between Australia and Hawaii. The two countries are members of the Pacific Islands Forum.