Hameln-Pyrmont is a district (Landkreis) in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Schaumburg, Hanover, Hildesheim and Holzminden, and by the state of North Rhine-Westphalia.

The County of Waldeck was a state of the Holy Roman Empire and its successors from the late 12th century until 1929. In 1349 the county gained Imperial immediacy and in 1712 was raised to the rank of Principality. After the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 it was a constituent state of its successors: the Confederation of the Rhine, the German Confederation, the North German Confederation, the German Empire and, until 1929, the Weimar Republic. It comprised territories in present-day Hesse and Lower Saxony (Germany).
Waldeck-Frankenberg is a Kreis (district) in the north of Hesse, Germany. Neighbouring districts are Höxter, Kassel, Schwalm-Eder, Marburg-Biedenkopf, Siegen-Wittgenstein, Hochsauerland.

The Province of Hesse-Nassau was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1868 to 1918, then a province of the Free State of Prussia until 1944.
Free state is a term occasionally used in the official titles of some states throughout the world with varying meanings depending on the context. In principle, the title asserts and emphasises a particular freedom of the state in question, but this is not always reflected in practice. Some states use the title to assert sovereignty or independence from foreign domination, while others have used it to assert autonomy within a larger nation-state. Sometimes "free state" is used as a synonym for "republic".
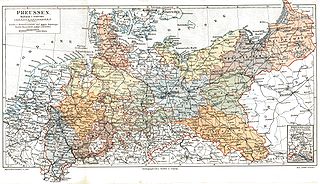
The Provinces of Prussia were the main administrative divisions of Prussia from 1815 to 1946. Prussia's province system was introduced in the Stein-Hardenberg Reforms in 1815, and were mostly organized from duchies and historical regions. Provinces were divided into several Regierungsbezirke, sub-divided into Kreise (districts), and then into Gemeinden (townships) at the lowest-level. Provinces constituted the highest level of administration in the Kingdom of Prussia and Free State of Prussia until 1933, when Nazi Germany established de facto direct rule over provincial politics, and were formally abolished in 1946 following World War II. The Prussian provinces became the basis for many federal states of Germany, and the states of Brandenburg, Lower Saxony, and Schleswig-Holstein are direct successors of provinces.

Bad Arolsen is a small town in northern Hesse, Germany, in Waldeck-Frankenberg district. From 1655 until 1918 it served as the residence town of the Princes of Waldeck-Pyrmont and then until 1929 as the capital of the Waldeck Free State. The International Tracing Service has its headquarters in Bad Arolsen. In 2003, the town hosted the 43rd Hessentag state festival.

Bad Pyrmont is a town in the district of Hamelin-Pyrmont, in Lower Saxony (Niedersachsen), Germany, with a population close to 19,000. It is located on the River Emmer, about 10 km west of the Weser. Bad Pyrmont is a popular spa resort that gained its reputation as a fashionable place for princely vacations in the 17th and 18th centuries. The town is also the center of the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers) in Germany.

The Free State of Prussia was a state of Germany from 1918 to 1947.

The Province of Schleswig-Holstein was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.

The Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine was a grand duchy in western Germany that existed from 1806 to the end of the German Empire in 1918. The grand duchy originally formed on the basis of the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1806 as the Grand Duchy of Hesse. After the end of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815, it changed its name in 1816 to distinguish itself from the Electorate of Hesse, which had formed from neighboring Hesse-Kassel. Colloquially, the grand duchy continued to be known by its former name of Hesse-Darmstadt. It joined the German Empire in 1871 and became a republic after the German defeat in World War I in 1918.

The Free State of Mecklenburg-Schwerin was a state in the Weimar Republic that was established in 1918 following the abdication of the Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin following the German Revolution. In 1933, after the onset of Nazi rule, it was united with the smaller neighbouring state of Mecklenburg-Strelitz to form the united state of Mecklenburg on December 31, 1933.

The Free State of Bottleneck was a short-lived quasi-state that existed from 10 January 1919 until 25 February 1923. It was formed out of part of the Prussian province of Hesse-Nassau as a consequence of the occupation of the Rhineland following World War I. The Bottleneck is now part of the modern German states of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate.

Josias, Hereditary Prince of Waldeck and Pyrmont was the heir apparent to the throne of the Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont and a general in the SS. From 1946 until his death, he was the head of the Princely House of Waldeck and Pyrmont. After World War II, he was sentenced to life in prison at the Buchenwald Trial for his part in the "common plan" to violate the Laws and Usages of War in connection with prisoners of war held at Buchenwald concentration camp, but was released after serving about three years in prison.

Princess Pauline Emma Auguste Hermine of Waldeck and Pyrmont was a member of the House of Waldeck and Pyrmont and a Princess of Waldeck and Pyrmont. Through her marriage to Alexis, Prince of Bentheim and Steinfurt, Pauline was also a member of the Princely House of Bentheim and Steinfurt and Princess consort of Bentheim and Steinfurt from 28 September 1890 to 21 January 1919.
Alexis Carl Ernst Louis Ferdinand Eugen Bernhard, Prince of Bentheim and Steinfurt was a Lieutenant General, statesman, and the Prince of Bentheim and Steinfurt from 28 September 1890 to 21 January 1919.

The Evangelical Church of Hesse Electorate-Waldeck is a United Protestant church body in former Hesse-Cassel and the Waldeck part of the former Free State of Waldeck-Pyrmont.
The German Evangelical Church Confederation was a formal federation of 28 regional Protestant churches (Landeskirchen) of Lutheran, Reformed or United Protestant administration or confession. It existed during the Weimar Republic from 1922 until being replaced by the German Evangelical Church in 1933. It was a predecessor body to the Evangelical Church in Germany.

Heringhausen in the area of Waldeck, Upland and Sauerland, is a village in the municipality Diemelsee in northern Hesse. In 2023, the place has a 1000-year history. Heringhausen is a recognized health resort.