
Hawaii is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, it is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics.
The terms multiracial people refer to people who are of multiple races, and the terms multi-ethnic people refer to people who are of more than one ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for multiracial people in a variety of contexts, including multiethnic, polyethnic, occasionally bi-ethnic, Métis, Muwallad, Melezi, Coloured, Dougla, half-caste, ʻafakasi, mestizo, mutt, Melungeon, quadroon, octoroon, sambo/zambo, Eurasian, hapa, hāfu, Garifuna, pardo, and Gurans. A number of these once-acceptable terms are now considered offensive, in addition to those that were initially coined for pejorative use.

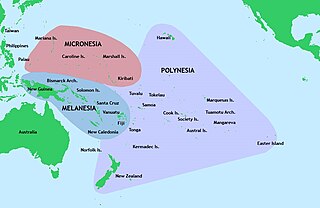
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, Pacificans, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania or any other island located in the Pacific Ocean.
Polynesians are an ethnolinguistic group comprising closely related ethnic groups native to Polynesia, which encompasses the islands within the Polynesian Triangle in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Southeast Asia and are part of the larger Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, with an Urheimat in Taiwan. They speak the Polynesian languages, a branch of the Oceanic subfamily within the Austronesian language family. The Indigenous Māori people form the largest Polynesian population, followed by Samoans, Native Hawaiians, Tahitians, Tongans, and Cook Islands Māori.

Native Hawaiians are the Indigenous Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.

European exploration and settlement of Oceania began in the 16th century, starting with the Spanish (Castilian) landings and shipwrecks in the Mariana Islands, east of the Philippines. This was followed by the Portuguese landing and settling temporarily in some of the Caroline Islands and Papua New Guinea. Several Spanish landings in the Caroline Islands and New Guinea came after. Subsequent rivalry between European colonial powers, trade opportunities and Christian missions drove further European exploration and eventual settlement. After the 17th century Dutch landings in New Zealand and Australia, with no settlement in these lands, the British became the dominant colonial power in the region, establishing settler colonies in what would become Australia and New Zealand, both of which now have majority European-descended populations. States including New Caledonia (Caldoche), Hawaii, French Polynesia, and Norfolk Island also have considerable European populations. Europeans remain a primary ethnic group in much of Oceania, both numerically and economically.
Samoan Americans are Americans of Samoan origin, including those who emigrated from the United States Territory of American Samoa and immigrants from the Independent State of Samoa to the United States. Samoan Americans are Pacific Islanders in the United States census, and are the second largest Pacific Islander group in the US, after Native Hawaiians.

The Indigenous peoples of Oceania are Aboriginal Australians, Papuans, and Austronesians. These indigenous peoples have a historical continuity with pre-colonial societies that developed on their territories. With the notable exceptions of Australia, New Zealand, Hawaii, New Caledonia, Guam, and Northern Mariana Islands, indigenous peoples make up the majority of the populations of Oceania.
The United States has a racially and ethnically diverse population. At the federal level, race and ethnicity have been categorized separately. The most recent United States census recognized five racial categories, as well as people who belong to two or more of the racial categories. The United States also recognizes the broader notion of ethnicity. The 2000 census and 2010 American Community Survey inquired about the "ancestry" of residents, while the 2020 census allowed people to enter their "origins". The Census Bureau also classified respondents as either Hispanic or Latino, identifying as an ethnicity, which comprises the minority group in the nation.
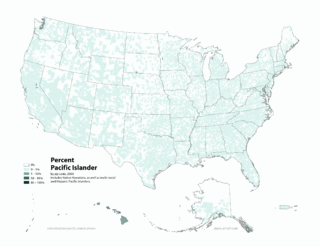
Pacific Islander Americans are Americans who are of Pacific Islander ancestry. For its purposes, the United States census also counts Aboriginal Australians as part of this group.
Pitcairn Islanders, also referred to as Pitkerners and Pitcairnese, are the native inhabitants of the Pitcairn Islands, a British Overseas Territory including people whose families were previously inhabitants and maintaining cultural connections. Most Pitcairn Islanders are descendants of the Bounty mutineers and Tahitians.
Asian people are the people of the continent of Asia. The term may also refer to their descendants.

The Tahitians are the Indigenous Polynesian people of Tahiti and thirteen other Society Islands in French Polynesia. The numbers may also include the modern population in these islands of mixed Polynesian and French ancestry. Indigenous Tahitians are one of the largest Polynesian ethnic groups, behind the Māori, Samoans and Hawaiians.

The Kingdom of Tahiti or the Tahitian Kingdom was a Polynesian monarchy founded by paramount chief Pōmare I, who, with the aid of British missionaries and traders, and European weaponry, unified the islands of Tahiti, Moʻorea, Teti‘aroa, and Mehetiʻa. The kingdom eventually annexed the Tuamotus, and the Austral Islands.

Asian/Pacific American (APA) or Asian/Pacific Islander (API) or Asian American and Pacific Islanders (AAPI) or Asian American and Native Hawaiians/Pacific Islander (AANHPI) is a term sometimes used in the United States when including both Asian and Pacific Islander Americans.

Tongan Americans are Americans who can trace their ancestry to Tonga, officially known as the Kingdom of Tonga. There are approximately 57,000 Tongan Americans living in the United States, as of 2012. Tongans are considered to be Pacific Islanders in the United States census, and are the country's fourth largest Pacific Islander American group in terms of population, after Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and Guamanian/Chamorro Americans.
Most early Asian settlers to the United States particularly the Japanese went to Hawaii. Most of these early immigrants moved to the islands as laborers to work on the pineapple, coconut, and sugarcane plantations. These early migrants have tended to stay, although a handful returned to their home countries. Most people in Hawaii of Asian ancestry/origin are Filipino, Japanese, or Chinese. There has also been recent immigration to Hawaii from more ethnic Asian groups, including Thai, Indian, Indonesian, and Vietnamese.
Pacific Islanders have a particular place in the history of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Its first non-English-speaking mission was in the region in 1844, less than twenty years after the church's founding, and there are currently six temples among the Pacific Island regions of Polynesia, Melanesia, and Micronesia. In 2015 the Latter-day Saint population in the area was increasing in percentage and absolute numbers.
Norfolk Islanders, also referred to as just Islanders, are the inhabitants or residents of Norfolk Island, an external territory of Australia. The Islanders have their own unique identity and are predominantly people of Pitcairn and English descent and to a lesser extent of Scottish and Irish.










