Related Research Articles

The aegis, as stated in the Iliad, is a device carried by Athena and Zeus, variously interpreted as an animal skin or a shield and sometimes featuring the head of a Gorgon. There may be a connection with a deity named Aex or Aix, a daughter of Helios and a nurse of Zeus or alternatively a mistress of Zeus.

Boudica or Boudicca (, known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh as Buddug was the wife of a king of the Iceni tribe of Celtic Britons, who led a failed uprising against the conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. According to Roman sources, shortly after the uprising failed, she poisoned herself or died of her wounds, although there is no actual evidence of either fate. She is considered a British national heroine and a symbol of the struggle for justice and independence.

The Horned God is one of the two primary deities found in Wicca and some related forms of Neopaganism. The term Horned God itself predates Wicca, and is an early 20th-century syncretic term for a horned or antlered anthropomorphic god partly based on historical horned deities.

In Greek mythology, a satyr, also known as a silenus or silenos, is a male nature spirit with ears and a tail resembling those of a horse, as well as a permanent, exaggerated erection. Early artistic representations sometimes include horse-like legs, but, by the sixth century BC, they were more often represented with human legs. Comically hideous, they have mane-like hair, bestial faces, and snub noses and are always shown naked. Satyrs were characterized by their ribaldry and were known as lovers of wine, music, dancing, and women. They were companions of the god Dionysus and were believed to inhabit remote locales, such as woodlands, mountains, and pastures. They often attempted to seduce or rape nymphs and mortal women alike, usually with little success. They are sometimes shown masturbating or engaging in bestiality.

In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Pan is the god of the wild, shepherds and flocks, rustic music and impromptus, and companion of the nymphs. He has the hindquarters, legs, and horns of a goat, in the same manner as a faun or satyr. With his homeland in rustic Arcadia, he is also recognized as the god of fields, groves, wooded glens and often affiliated with sex; because of this, Pan is connected to fertility and the season of spring.

Britannia is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin Britannia was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great Britain, and the Roman province of Britain during the Roman Empire. Typically depicted reclining or seated with spear and shield since appearing thus on Roman coins of the 2nd century AD, the classical national allegory was revived in the early modern period. On coins of the pound sterling issued by Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland, Britannia appears with her shield bearing the Union Flag. To symbolise the Royal Navy's victories, Britannia's spear became the characteristic trident in 1797, and a helmet was added to the coinage in 1825.

Thor is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred groves and trees, strength, the protection of mankind, hallowing, and fertility. Besides Old Norse Þórr, the deity occurs in Old English as Þunor, in Old Frisian as Thuner, in Old Saxon as Thunar, and in Old High German as Donar, all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *Þun(a)raz, meaning 'Thunder'.

Rogan josh also spelled roghan josh or roghan ghosht, is an aromatic curried meat dish of Kashmiri origin from the Kashmir. It is made with red meat—traditionally lamb, mutton, or goat—and coloured and flavoured primarily by alkanet flower and Kashmiri chilies. It is one of the signature recipes of Kashmiri cuisine.

The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geographer Ptolemy named the Brigantes as a people in Ireland also, where they could be found around what is now Wexford, Kilkenny and Waterford, while another people named Brigantii is mentioned by Strabo as a sub-tribe of the Vindelici in the region of the Alps.

Tyneham is a ghost village and former civil parish, now in the civil parish of Steeple with Tyneham, in south Dorset, England, near Lulworth on the Isle of Purbeck. In 2001 the civil parish had a population of 0. The civil parish was abolished on 1 April 2014 and merged with Steeple to form Steeple with Tyneham.

Akelarre is the Basque term meaning Witches' Sabbath. Akerra means male goat in the Basque language. Witches' sabbaths were envisioned as presided over by a goat.

Kukeri are elaborately costumed Bulgarian men, who perform traditional rituals intended to scare away evil spirits. This Bulgarian tradition has been practiced since Thracian times and is of a Thracian origin.

Bucknall is a village and civil parish in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. The village is situated approximately 5 miles (8 km) west from Horncastle and 5 miles (8 km) north from Woodhall Spa.

The Chimera of Arezzo is regarded as the best example of ancient Etruscan art. The British art historian David Ekserdjian described the sculpture as "one of the most arresting of all animal sculptures and the supreme masterpiece of Etruscan bronze-casting". Made entirely of bronze and measuring 78.5 cm high with a length of 129 cm, it was found alongside a small collection of other bronze statues in Arezzo, an ancient Etruscan and Roman city in Tuscany. The statue was originally part of a larger sculptural group representing a fight between a Chimera and the Greek hero Bellerophon. This sculpture is likely to have been created as a votive offering to the Etruscan god Tinia.

Antimilos is a Greek island in the Cyclades, 13 miles northwest of Milos. Administratively, it is part of the municipality of Milos. Antimilos is an uninhabited mass of trachyte, often called Erimomilos. It is a volcanic island and the crater is still obvious. Ancient inhabitants transformed the crater to an open rain tank. On the island lives a rare variation of the common goat called Capra aegagrus pictus. It is similar but not the same as the Cretan goat known as "kri-kri".

The Parisi were a British Celtic tribe located somewhere within the present-day East Riding of Yorkshire, in England, known from a single brief reference by Ptolemy in his Geographica of about AD 150. Many writers have connected them with the archaeological Arras culture and some with the more widely known Parisii of Gaul.
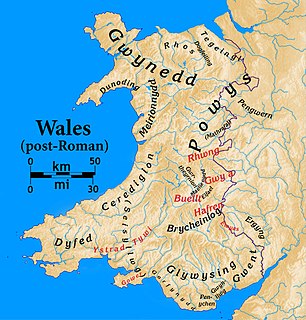
Wales in the early Middle Ages covers the time between the Roman departure from Wales c. 383 until the end of the 10th century. In that time there was a gradual consolidation of power into increasingly hierarchical kingdoms. The end of the early Middle Ages was the time that the Welsh language transitioned from the Primitive Welsh spoken throughout the era into Old Welsh, and the time when the modern England–Wales border would take its near-final form, a line broadly followed by Offa's Dyke, a late eighth-century earthwork. Successful unification into something recognisable as a Welsh state would come in the next era under the descendants of Merfyn Frych.

Toutatis or Teutates is a Celtic god who was worshipped in ancient Gaul and Britain. On the basis of his name's etymology, he has been widely interpreted to be a tribal protector.
Aizis was a Dacian town mentioned by Emperor Trajan in his work Dacica. Located at Dealul Ruieni, Fârliug, Caraș-Severin, Banat, Romania.
References
- ↑ Brown, Ian (2009). Beacons in the landscape : the hillforts of England and Wales. Oxford: Windgather Press. p. 222. ISBN 9781909686274.
- ↑ A.L.F. Rivet, C. Smith, The Place-names of Roman Britain, Batsford (1979)
- ↑ Helmut Birkhan, Germanen und Kelten bis zum Ausgang der Römerzeit, Böhlau (1970)
- ↑ K Jackson, Journal of Roman Studies XXXVIII (1948), 57