
In geometry, the circumference is the perimeter of a circle or ellipse. The circumference is the arc length of the circle, as if it were opened up and straightened out to a line segment. More generally, the perimeter is the curve length around any closed figure. Circumference may also refer to the circle itself, that is, the locus corresponding to the edge of a disk. The circumference of a sphere is the circumference, or length, of any one of its great circles.
In mechanics, the virial theorem provides a general equation that relates the average over time of the total kinetic energy of a stable system of discrete particles, bound by a conservative force, with that of the total potential energy of the system. Mathematically, the theorem states that where T is the total kinetic energy of the N particles, Fk represents the force on the kth particle, which is located at position rk, and angle brackets represent the average over time of the enclosed quantity. The word virial for the right-hand side of the equation derives from vis, the Latin word for "force" or "energy", and was given its technical definition by Rudolf Clausius in 1870.

In geometry, a solid angle is a measure of the amount of the field of view from some particular point that a given object covers. That is, it is a measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. The point from which the object is viewed is called the apex of the solid angle, and the object is said to subtend its solid angle at that point.

Stellar dynamics is the branch of astrophysics which describes in a statistical way the collective motions of stars subject to their mutual gravity. The essential difference from celestial mechanics is that the number of body
The Plummer model or Plummer sphere is a density law that was first used by H. C. Plummer to fit observations of globular clusters. It is now often used as toy model in N-body simulations of stellar systems.

A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base to a point called the apex or vertex that is not contained in the base.

Messier 108 is a barred spiral galaxy about 46 million light-years away from Earth in the northern constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 or 1782. From the Earth, this galaxy is seen almost edge-on.

In geometry, a spherical cap or spherical dome is a portion of a sphere or of a ball cut off by a plane. It is also a spherical segment of one base, i.e., bounded by a single plane. If the plane passes through the center of the sphere, so that the height of the cap is equal to the radius of the sphere, the spherical cap is called a hemisphere.

In modern models of physical cosmology, a dark matter halo is a basic unit of cosmological structure. It is a hypothetical region that has decoupled from cosmic expansion and contains gravitationally bound matter. A single dark matter halo may contain multiple virialized clumps of dark matter bound together by gravity, known as subhalos. Modern cosmological models, such as ΛCDM, propose that dark matter halos and subhalos may contain galaxies. The dark matter halo of a galaxy envelops the galactic disc and extends well beyond the edge of the visible galaxy. Thought to consist of dark matter, halos have not been observed directly. Their existence is inferred through observations of their effects on the motions of stars and gas in galaxies and gravitational lensing. Dark matter halos play a key role in current models of galaxy formation and evolution. Theories that attempt to explain the nature of dark matter halos with varying degrees of success include cold dark matter (CDM), warm dark matter, and massive compact halo objects (MACHOs).
In classical mechanics, the shell theorem gives gravitational simplifications that can be applied to objects inside or outside a spherically symmetrical body. This theorem has particular application to astronomy.
For most numbered asteroids, almost nothing is known apart from a few physical parameters and orbital elements. Some physical characteristics can only be estimated. The physical data is determined by making certain standard assumptions.
The Hubble–Reynolds law models the surface brightness of elliptical galaxies as
de Vaucouleurs's law, also known as the de Vaucouleurs profile or de Vaucouleurs model, describes how the surface brightness of an elliptical galaxy varies as a function of apparent distance from the center of the galaxy:

The Sérsic profile is a mathematical function that describes how the intensity of a galaxy varies with distance from its center. It is a generalization of de Vaucouleurs' law. José Luis Sérsic first published his law in 1963.
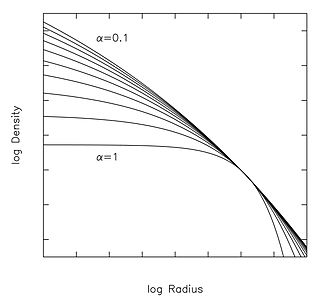
The Einasto profile is a mathematical function that describes how the density of a spherical stellar system varies with distance from its center. Jaan Einasto introduced his model at a 1963 conference in Alma-Ata, Kazakhstan.

Osipkov–Merritt models are mathematical representations of spherical stellar systems. The Osipkov–Merritt formula generates a one-parameter family of phase-space distribution functions that reproduce a specified density profile in a specified gravitational potential. The density and potential need not be self-consistently related. A free parameter adjusts the degree of velocity anisotropy, from isotropic to completely radial motions. The method is a generalization of Eddington's formula for constructing isotropic spherical models.

NGC 5982 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Draco. It is located at a distance of circa 130 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5982 is about 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on May 25, 1788.

NGC 765 is an intermediate spiral galaxy located in the constellation Aries. It is located at a distance of circa 220 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 765 is about 195,000 light years across. It was discovered by Albert Marth on October 8, 1864. The galaxy has an extensive hydrogen (HI) disk with low surface brightness, whose diameter is estimated to be 240 kpc.

ESO 383-76 is an elongated, X-ray luminous supergiant elliptical galaxy, residing as the dominant, brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) of the Abell 3571 galaxy cluster, the sixth-brightest in the sky at X-ray wavelengths. It is located at the distance of 200.6 megaparsecs from Earth, and is possibly a member of the large Shapley Supercluster. With a diameter of about 540.9 kiloparsecs, it is one of the largest galaxies known. It also contains a supermassive black hole, one of the most massive known with mass estimates varying from 2 billion M☉ to 28 billion M☉.
In applied sciences, the equivalent radius is the radius of a circle or sphere with the same perimeter, area, or volume of a non-circular or non-spherical object. The equivalent diameter is twice the equivalent radius.





















