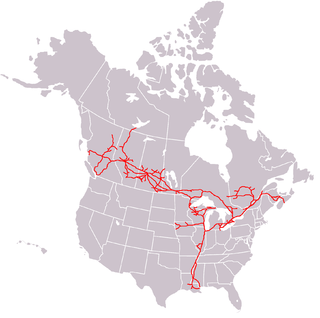
The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.

BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad in the United States. One of six North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 36,000 employees, 33,400 miles (53,800 km) of track in 28 states, and over 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.

The Kansas City Southern Railway Company was an American Class I railroad. Founded in 1887, it operates in 10 Midwestern and Southeastern U.S. states: Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Tennessee, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana and Texas. KCS owns the shortest north-south rail route between Kansas City, Missouri, and several key ports along the Gulf of Mexico.

Kansas City Southern (KCS) was a transportation holding company with railroad investments in the United States, Mexico, and Panama and operated from 1887 to 2023. The KCS rail network included about 7,299 miles (11,747 km) of track in the U.S. and Mexico.

The Chicago, Missouri and Western Railway was a Class II railroad that operated in the midwest of the United States between 1987 and 1989. Never financially stable, less than a year after it was created it was bankrupt and sold off its lines piecemeal to other railroads in 1989.

The Alton Railroad was the final name of a railroad linking Chicago to Alton, Illinois; St. Louis, Missouri; and Kansas City, Missouri. Its predecessor, the Chicago and Alton Railroad, was purchased by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad in 1931 and was controlled until 1942 when the Alton was released to the courts. On May 31, 1947, the Alton Railroad was merged into the Gulf, Mobile and Ohio Railroad. Jacob Bunn had been one of the founding reorganizers of the Chicago & Alton Railroad Company during the 1860s.
The Fort Smith and Western Railway was a railroad that operated in the states of Arkansas and Oklahoma.

The Toledo, Peoria and Western Railway is a short line railroad that operates 247 miles (398 km) of track from Mapleton, Illinois, through Peoria across Illinois to Logansport, Indiana. TP&W has trackage rights between Galesburg, Illinois, and Peoria, between Logansport and Kokomo, Indiana, and between Reynolds, Indiana, and Lafayette, Indiana. TPW has connections with UP, BNSF, NS, CSXT, CN, CP, BL, CERA, CIM, KBSR and T&P. The railroad is now owned by Genesee & Wyoming Inc. The railroad's traffic comes largely from agricultural products, including both raw and processed grain products, as well as chemicals and completed tractors. The TPW hauled around 26,000 carloads in 2008.

The Terminal Railroad Association of St. Louis is a Class III switching and terminal railroad that handles traffic in the St. Louis metropolitan area. It is co-owned by five of the six Class I railroads that reach the city.
The Gateway Eastern Railway was a railroad subsidiary of the Kansas City Southern Railway (KCS), owning a 17-mile (27 km) main line between East Alton and East St. Louis, Illinois, United States. Originally created in 1994 as a subsidiary of the Gateway Western Railway, which acquired the East St. Louis-Kansas City line of the Chicago, Missouri and Western Railway in 1990. It was acquired by KCS along with its parent in 1997.
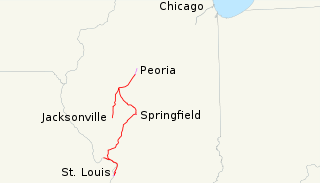
The Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad (CP&StL) was a railroad in the U.S. state of Illinois that operated a main line between Pekin and Madison via Springfield. Its property was sold at foreclosure to several new companies in the 1920s; the portion north of Springfield has since become the Illinois and Midland Railroad, while the remainder has been abandoned, except for a portion near St. Louis that is now owned by the Norfolk Southern Railway.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.
The Chicago and Southern Railroad built a rail line in northeastern Illinois, extending south from Chicago to Thornton. It now mainly forms part of the Grand Trunk Western Railroad, while the north end has been operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, the Illinois Northern Railway, and most recently the Central Illinois Railroad.
The Chicago and Illinois River Railroad was a predecessor of the Alton Railroad that built a line from Joliet southwest through Coal City, Illinois, to the Mazon River. A portion is now a second main track on the BNSF Railway's Southern Transcon.

The Wabash Railroad was a Class I railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. It served a large area, including track in the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, and Missouri and the province of Ontario. Its primary connections included Chicago, Illinois; Kansas City, Missouri; Detroit, Michigan; Buffalo, New York; St. Louis, Missouri; and Toledo, Ohio.

The Joliet Subdivision is a railroad subdivision of the Canadian National Railway in the Chicago metropolitan area. The 33-mile route runs from Joliet, Illinois to Chicago's Bridgeport neighborhood, largely paralleling the route of the Illinois and Michigan Canal. Union Pacific has trackage rights over the route, which meets the Union Pacific Joliet Subdivision at Joliet to reach Bloomington and St. Louis. The line also hosts Metra's Heritage Corridor commuter service, and Amtrak's Lincoln and Texas Eagle service. From Bridgeport, services reach Chicago Union Station via Canadian National's Freeport Subdivision.

Canadian Pacific Kansas City Limited, doing business as CPKC, is a Canadian railway holding company. Through its primary operating railway subsidiaries, Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) and Kansas City Southern Railway (KCS), it operates about 32,000 kilometres (20,000 mi) of rail in Canada, Mexico, and the United States, and is the only single-line rail corporation ever to connect the three countries. CPKC is headquartered in Calgary and led by President and CEO Keith Creel.












