
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus Vibrio; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves.

Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words luciferin and luciferase, for the substrate and enzyme, respectively. Both words are derived from the Latin word lucifer, meaning "lightbearer", which in turn is derived from the Latin words for "light" (lux) and "to bring or carry" (ferre).

Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a subclass of the class Hexanauplia. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and ostracods.

Luciferin is a generic term for the light-emitting compound found in organisms that generate bioluminescence. Luciferins typically undergo an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with molecular oxygen. The resulting transformation, which usually involves splitting off a molecular fragment, produces an excited state intermediate that emits light upon decaying to its ground state. The term may refer to molecules that are substrates for both luciferases and photoproteins.

Noctiluca scintillans is a marine species of dinoflagellate that can exist in a green or red form, depending on the pigmentation in its vacuoles. It can be found worldwide, but its geographical distribution varies depending on whether it is green or red. This unicellular microorganism is known for its ability to bioluminesce, giving the water a bright blue glow seen at night. However, blooms of this species can be responsible for environmental hazards, such as toxic red tides. They may also be an indicator of anthropogenic eutrophication.

The Cyclopoida are an order of small crustaceans from the subclass Copepoda. Like many other copepods, members of Cyclopoida are small, planktonic animals living both in the sea and in freshwater habitats. They are capable of rapid movement. Their larval development is metamorphic, and the embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite.

Malacosteus niger, commonly known as the black dragon fish, is a species of deep sea fish. Some additional common names for this species include: Northern Stoplight Loosejaw, Lightless Loosejaw, Black Loosejaw, and Black Hinged-Head. It belongs to the order of fishes called the dragonfishes, or scientifically known as the Stomiidae. It is among the top predators of the open mesopelagic zone. M. Niger is a circumglobal species, which means that it inhabits waters ranging from the tropics to the subarctics. Not many studies have been conducted on its feeding habits, but recent research suggests that M. niger primarily feed on a calanoid copopods which is a form of zooplankton. Indeed, it appears that M. niger primarily prey on zooplankton despite its apparent morphological adaptations for the consumption of relatively large prey. Another unique adaptation for this species is its ability to produce both red and blue bioluminescence. Most mesopelagic species aren’t capable of producing red bioluminescence. This is advantageous because most other species cannot perceive red light, therefor allowing M. niger to camouflage part of itself to its prey and predators.

Coelenterazine is a luciferin, a molecule that emits light after reaction with oxygen, found in many aquatic organisms across eight phyla. It is the substrate of many luciferases such as Renilla reniformis luciferase (Rluc), Gaussia luciferase (Gluc), and photoproteins, including aequorin, and obelin. All these proteins catalyze the oxidation of this substance, a reaction catalogued EC 1.13.12.5.

Vargulin, also called Cypridinid luciferin, Cypridina luciferin, or Vargula luciferin, is the luciferin found in the ostracod Cypridina hilgendorfii, also named Vargula hilgendorfii. These bottom dwelling ostracods emit a light stream into water when disturbed presumably to deter predation. Vargulin is also used by the midshipman fish, Porichthys.
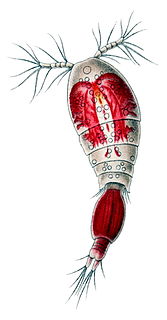
Oncaea is a genus of copepods. The genus contains bioluminescent species. Unlike other bioluminescent copepods, Oncaea have an internal (non-secreted) bioluminescence. Oncaea contains the following species:

Ommatokoita is a monotypic genus of copepods, the sole species being Ommatokoita elongata. However, a specimen has been found on the skin of Etmopterus princeps assigned to the genus but not species.
Stygotantulus is a genus of crustacean with the sole species Stygotantulus stocki, that lives as an ectoparasite on harpacticoid copepods of the families Tisbidae and Canuellidae. It is the smallest arthropod in the world, at a length of less than 0.1 millimetres (0.004 in). The specific name stocki commemorates Jan Hendrik Stock, a Dutch carcinologist. Another contender for the world's smallest arthropod is Tantulacus dieteri, with a total body length of only 85 micrometres (0.0033 in).
Gaussia is a genus of copepods. The genus contains bioluminescent species. It is a "characteristic genus of the mesopelagial", occurring at depths of 0–3,000 metres (0–9,843 ft). The genus Gaussia contains the following species:
Metridinidae is a family of copepods, comprising three genera – Gaussia, Metridia and Pleuromamma. It has also been referred to as "Metridiidae", but following a petition to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature, that name has been restricted to the family Metridiidae Carlgren, 1893, based on the anthozoan genus Metridium. All species in the family can produce blue-green bioluminescence; the light is produced in glands, whose position varies between genera.
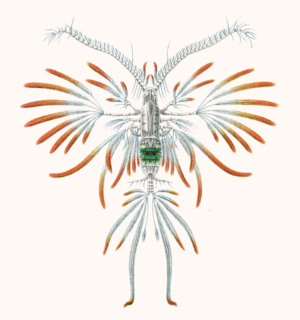
Euaugaptilus is a genus of copepods.
Cardiodectes is a genus of copepods in the family Pennellidae. Species are parasites of fish.

Peniculus is a genus of marine copepods in the family Pennellidae. They occur worldwide and typically parasitize coastal or epipelagic fish, with the exception of Peniculus hokutoae that was found parasitizing a mesopelagic myctophid, Symbolophorus evermanni.

Peniculus hokutoae is a species of parasitic pennellid copepod. It was described in 2018 from a single female. The type-host is the myctophid fish Symbolophorus evermanni and the type-locality is off Japan. The Japanese name of this species is hokuto-kozutsu-hijikimushi.
A micronekton is a group of organisms of 2 to 20 cm in size which are able to swim independently of ocean currents. The word 'nekton' is derived from the Greek νήκτον, translit. nekton, meaning "to swim", and was coined by Ernst Haeckel in 1890.













