Related Research Articles

Francis II and I was the last Holy Roman Emperor as Francis II from 1792 to 1806, and the first Emperor of Austria as Francis I from 1804 to 1835. He was also King of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia, and served as the first president of the German Confederation following its establishment in 1815.

The Geheime Staatspolizei, abbreviated Gestapo, was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.

The House of Habsburg, also known as the House of Austria, is one of the most prominent and important dynasties in European history.
The history of Austria covers the history of Austria and its predecessor states. In the late Iron Age Austria was occupied by people of the Hallstatt Celtic culture, they first organized as a Celtic kingdom referred to by the Romans as Noricum, dating from c. 800 to 400 BC. At the end of the 1st century BC, the lands south of the Danube became part of the Roman Empire. In the Migration Period, the 6th century, the Bavarii, a Germanic people, occupied these lands until it fell to the Frankish Empire established by the Germanic Franks in the 9th century. The name Ostarrîchi (Austria) has been in use since 996 AD when it was a margravate of the Duchy of Bavaria and from 1156 an independent duchy of the Holy Roman Empire.
Sicherheitsdienst, full title Sicherheitsdienst des Reichsführers-SS, or SD, was the intelligence agency of the SS and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany. Established in 1931, the SD was the first Nazi intelligence organization and the Gestapo was considered its sister organization through the integration of SS members and operational procedures. The SD was administered as an independent SS office between 1933 and 1939. That year, the SD was transferred over to the Reich Security Main Office, as one of its seven departments. Its first director, Reinhard Heydrich, intended for the SD to bring every single individual within the Third Reich's reach under "continuous supervision".

Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his death in 1916. In the early part of his reign, his realms and territories were referred to as the Austrian Empire, but were reconstituted as the dual monarchy of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1867. From 1 May 1850 to 24 August 1866, he was also president of the German Confederation.

Leopold II was the 44th Holy Roman Emperor, King of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia, and Archduke of Austria from 1790 to 1792, and Grand Duke of Tuscany from 1765 to 1790. He was a son of Empress Maria Theresa and Emperor Francis I, and the brother of Queen Marie Antoinette of France, Queen Maria Carolina, Duchess Maria Amalia of Parma, and Emperor Joseph II. Leopold was a moderate proponent of enlightened absolutism. He granted the Academy of Georgofili his protection. Unusually for his time, he opposed the death penalty and torture and abolished it in Tuscany on 30 November 1786 during his rule there, making it the first nation in modern history to do so. This act has been commemorated since 2000 by a regional custom known as the Feast of Tuscany, held every 30 November. Despite his brief reign, he is highly regarded. The historian Paul W. Schroeder called him "one of the most shrewd and sensible monarchs ever to wear a crown".

Ferdinand III was Archduke of Austria from 1621, King of Hungary from 1625, King of Croatia and of Bohemia from 1627 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1637 to his death.

Charles I or Karl I was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, King of Croatia, King of Bohemia, and the last of the monarchs belonging to the House of Habsburg-Lorraine to rule over Austria-Hungary. The son of Archduke Otto of Austria and Princess Maria Josepha of Saxony, Charles became heir presumptive of Emperor Franz Joseph when his uncle Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated in 1914. In 1911, he married Princess Zita of Bourbon-Parma. He is venerated in the Catholic Church, was beatified by Pope John Paul II on 3 October 2004, and is known to the Catholic Church as Blessed Karl of Austria.

Secret police are police, intelligence, or security agencies that engage in covert operations against a government's political, religious, or social opponents and dissidents. Secret police organizations are characteristic of authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. They protect the political power of a dictator or regime and often operate outside the law to repress dissidents and weaken political opposition, frequently using violence. They may enjoy legal sanction to hold and charge suspects without ever identifying their organization.

The Department for the Protection of Public Safety and Order, usually called the Guard Department and commonly abbreviated in modern English sources as the Okhrana was a secret police force of the Russian Empire and part of the police department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) in the late 19th century and early 20th century, aided by the Special Corps of Gendarmes.

Count Heinrich von Bellegarde, Viceroy of Lombardy-Venetia, of a noble Savoyard family, was born in Saxony, joined the Saxon army and later entered Habsburg military service, where he became a general officer serving in the Habsburg border wars, the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He became a Generalfeldmarschall and statesman.
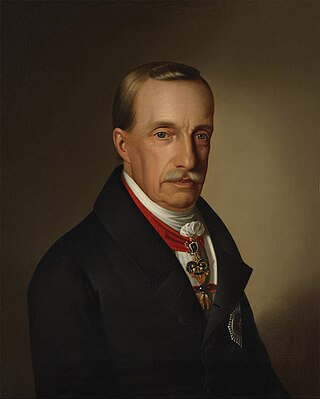
Archduke Joseph Anton of Austria was the 103rd and penultimate palatine of Hungary who served for more than fifty years from 1796 to 1847, after he had been appointed governor in 1795.

Archduke Franz Ferdinand Carl Ludwig Joseph Maria of Austria was the heir presumptive to the throne of Austria-Hungary. His assassination in Sarajevo was the most immediate cause of World War I.

The House of Habsburg-Lorraine originated from the marriage in 1736 of Francis III, Duke of Lorraine and Bar, and Maria Theresa of Austria, later successively Queen of Bohemia, Queen of Hungary, Queen of Croatia and Archduchess of Austria. Its members are the legitimate surviving line of both the House of Habsburg and the House of Lorraine and inherit their patrimonial possessions from their female line of the House of Habsburg and from the male line of the House of Lorraine.

The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand was one of the key events that led to World War I. Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir presumptive to the Austro-Hungarian throne, and his wife, Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, were assassinated on 28 June 1914 by Bosnian Serb student Gavrilo Princip. They were shot at close range while being driven through Sarajevo, the provincial capital of Bosnia-Herzegovina, formally annexed by Austria-Hungary in 1908.
A police state describes a state whose government institutions exercise an extreme level of control over civil society and liberties. There is typically little or no distinction between the law and the exercise of political power by the executive, and the deployment of internal security and police forces play a heightened role in governance. A police state is a characteristic of authoritarian, totalitarian or illiberal regimes. Such governments are typically one-party states, but police-state-level control may emerge in multi-party systems as well.

The Army of the Danube was a field army of the French Directory in the 1799 southwestern campaign in the Upper Danube valley. It was formed on 2 March 1799 by the simple expedient of renaming the Army of Observation, which had been observing Austrian movements on the border between French First Republic and the Holy Roman Empire. It was commanded by General Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, 1st Comte Jourdan (1762–1833).

Friedrich Freiherr (Baron) von Hotze, was a Swiss-born general in the Austrian army during the French Revolutionary Wars. He campaigned in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition and in Switzerland in the War of the Second Coalition, notably at Battle of Winterthur in late May 1799, and the First Battle of Zurich in early June 1799. He was killed at the Battle of Linth River.

Johann Anton Graf von Pergen was a diplomat and statesman of the Habsburg monarchy, serving under four consecutive monarchs for more than fifty years. He was one of the most influential individuals in the reformist administration of Joseph II (1780-1790).
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Adams, Jefferson (2009). Historical Dictionary of German Intelligence. Scarecrow Press. pp. 342–343. ISBN 0810863200.
- 1 2 3 Judson, Pieter M. (2016). The Habsburg Empire: A New History. Harvard University Press. pp. 83–84. ISBN 0674047761.
- ↑ Wagar, Chip (2018). Double Emperor: The Life and Times of Francis of Austria. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 119. ISBN 0761870784.
- ↑ Bernard, Paul P. (1979). The Limits of Enlightenment: Joseph II and the Law. University of Illinois Press. p. 97. ISBN 0252007352.