The study of galaxy formation and evolution is concerned with the processes that formed a heterogeneous universe from a homogeneous beginning, the formation of the first galaxies, the way galaxies change over time, and the processes that have generated the variety of structures observed in nearby galaxies. Galaxy formation is hypothesized to occur from structure formation theories, as a result of tiny quantum fluctuations in the aftermath of the Big Bang. The simplest model in general agreement with observed phenomena is the Lambda-CDM model—that is, that clustering and merging allows galaxies to accumulate mass, determining both their shape and structure. Hydrodynamics simulation, which simulates both baryons and dark matter, is widely used to study galaxy formation and evolution.
Guinevere Alice Mei-Ing Kauffmann was born in California. She is an astrophysicist and is known for her work studying galaxies among other subjects.

The Ooty Radio Telescope (ORT) is located in Muthorai near Ooty, in South Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is part of the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA) of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), which is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Atomic Energy. The radio telescope is a 530-metre (1,740 ft) long and 30-metre (98 ft) tall cylindrical parabolic antenna. It operates at a frequency of 326.5 MHz with a maximum bandwidth of 15 MHz at the front end.

HW Virginis, abbreviated HW Vir, is an eclipsing binary system, approximately 563 light-years away based on the parallax measured by the Gaia spacecraft, in the constellation of Virgo. The system comprises an eclipsing B-type subdwarf star and red dwarf star. The two stars orbit each other every 0.116795 days.
HD 27274, also known as Gliese 167, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern constellation Dorado. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.63, making it readily visible in binoculars, but not to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the star is known to be located 42.5 light-years away from the Solar System However, it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −23 km/s. At its current distance, HD 27274 is dimmed down by 0.05 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
An exocomet, or extrasolar comet, is a comet outside the Solar System, which includes rogue comets and comets that orbit stars other than the Sun. The first exocomets were detected in 1987 around Beta Pictoris, a very young A-type main-sequence star. There are now a total of 27 stars around which exocomets have been observed or suspected.

Theta Muscae is a multiple star system in the southern constellation Musca, containing a Wolf-Rayet star and two massive companions. With an apparent magnitude of 5.5, it is the second-brightest Wolf–Rayet star in the sky, although much of the visual brightness comes from the massive companions and it is not one of the closest of its type.

Alan R. Duffy is a British and Australian professional astronomer and science communicator. He was born in England, raised in Northern Ireland, and is currently based in Australia. He is a professor at the Centre for Astrophysics and Supercomputing at Swinburne University of Technology, and is the Lead Scientist at the Royal Institution of Australia.
Benedetta Ciardi is an Italian astrophysicist.
PKS 1353−341, also known as LEDA 88936 is a quasar located in the southern constellation Centaurus. It has an apparent magnitude of 18.5, making it only visible in powerful telescopes. Based on the object's luminosity, it is estimated to be 3.7 billion light years distant from the Solar System. It is receding from the Milky Way with a heliocentric radial velocity of 59,531 km/s

NGC 4324 is a lenticular galaxy located about 85 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on March 4, 1862. NGC 4324 has a stellar mass of 5.62 × 1010M☉, and a baryonic mass of 5.88 × 1010M☉. The galaxy's total mass is around 5.25 × 1011M☉. NGC 4324 is notable for having a ring of star formation surrounding its nucleus. It was considered a member of the Virgo II Groups until 1999, when its distance was recalculated and it was placed in the Virgo W Group.

Gamma3 Octantis, Latinized from γ3 Octantis, is a solitary star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It is faintly visible to the naked eye as an orange-hued star with an apparent magnitude of 5.28. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 264 light years but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 15 km/s. At its current distance, Gamma3 Octantis' brightness is diminished by two tenths of a magnitude due to interstellar dust and Eggen (1993) lists it as a member of the old disk population. It has an absolute magnitude of +0.83.

WZ Columbae, also known as HD 38170, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the southern constellation Columba, the dove. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.28, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is about 365 light years distant. It appears to be receding from the Solar System, having a heliocentric radial velocity of 36.3 km/s.

AF Columbae, also known as HD 42682, is a solitary, red hued variable star located in the southern constellation Columba, the dove. It has an apparent magnitude that fluctuates between 5.6 and 5.71. Nevertheless, it is faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft place the star relatively far at a distance of 820 light years. However, it is approaching the Solar System with a poorly constrained radial velocity of −19 km/s.
HD 34255, also known HR 1720, is a star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis, the giraffe. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.60, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The object is located relatively far at a distance of about 1.65 kly but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −7.7 km/s.
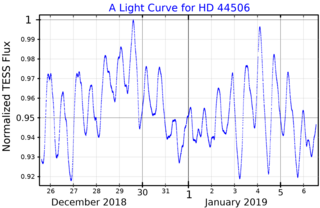
HD 44506 is a solitary, blue hued star located in the southern constellation Columba. The object is also called HR 2288, which is its Bright Star Catalog designation. It has an average apparent magnitude of 5.52, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. HD 44506 is located relatively far at a distance of 1,800 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 54 km/s.

8 Leonis Minoris is a solitary, red hued star located in the northern constellation Leo Minor. It has an apparent magnitude 5.37, making it faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia satellite, the object is estimated to be 492 light years distant. It is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 40 km/s. At its current distance, 8 LMi is diminshed by 0.12 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

PW Telescopii, also known as HD 183806 or simply PW Tel, is a solitary variable star located in the southern constellation Telescopium. It has an average apparent magnitude of 5.58, making it faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia satellite, the star is estimated to be 395 light years distant. It appears to be approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −10 km/s. The value is somewhat constrained, having an uncertainty of 26%. At its current distance, PW Tel's brightness is diminished by 0.05 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 197630, also known as HR 7933 or rarely 23 G. Microscopii, is a probable astrometric binary located in the southern constellation Microscopium. The visible component is a bluish-white hued star that is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 5.47. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia satellite, the system is estimated to be 328 light years away. However, it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −30 km/s. At its current distance, HD 197630's brightness is diminished by 0.11 magnitudes due to interstellar dust. A 2012 multiplicity survey failed to confirm the velocity variations.













