Related Research Articles

The Omo River in southern Ethiopia is the largest Ethiopian river outside the Nile Basin. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia, and it empties into Lake Turkana on the border with Kenya. The river is the principal stream of an endorheic drainage basin, the Turkana Basin.

The Mursi are a Surmic ethnic group in Ethiopia. They principally reside in the Debub Omo Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People's Region, close to the border with South Sudan. According to the 2007 national census, there are 11,500 Mursi, 848 of whom live in urban areas; of the total number, 92.25% live in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People's Region (SNNPR).
Sokoru is one of the woredas in the Oromia Region of Ethiopia. This woreda is named after the former awraja of the same name, and covering much of the same territory as the current woreda, as well as its administrative center, Sokoru. Part of the Jimma Zone, Sokoru is bordered on the south by Omo Nada, on the west by Tiro Afeta, and on the north and east by the Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples Region; the Gibe River defines the northern boundary. Other towns in this woreda include Deneba, Kumbi and Natri.
Tiro Afeta, also known as Nedi Gibe, is a woreda in Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Part of the Jimma Zone, Tiro Afeta is bordered on the south by Omo Nada, on the west by Kersa, on the north by Limmu Kosa, and on the east by Sokoru. The administrative center of the woreda is Dimtu.
Kersa is a woreda in the Jimma Zone of the Oromia Region of Ethiopia. It is bordered on the south by Dedo, on the southwest by Seka Chekorsa, on the west by Mana, on the north by Limmu Kosa, on the northeast by Tiro Afeta, and on the southeast by Omo Nada. Towns and cities in Kersa include Jimma, the zone's capital, and Serbo.
Omo Nada is one of the woredas in the Oromia region of Ethiopia. Part of the Jimma Zone, Omo Nada is bordered on the south by the Gojeb River, which separates it from the Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples Region (SNNPR), on the west by Dedo, on the northwest by Kersa, on the north by Tiro Afeta, on the northeast by Sokoru, and on the east by the Omo River which separates it from the SNNPR. Nada is the administrative center of the district; other towns in Omo Nada include Asendabo.

The Gibe River is by far the largest tributary of the Omo River in Ethiopia and typically flowing south-southeast. The confluence of the large Gibe River at 8°19′N37°28′E with the smaller Wabe River forms the even larger Omo River. Consequently, the whole drainage basin is sometimes called the Omo-Gibe River Basin with the Gibe and the Omo draining the upper and lower reaches, respectively.
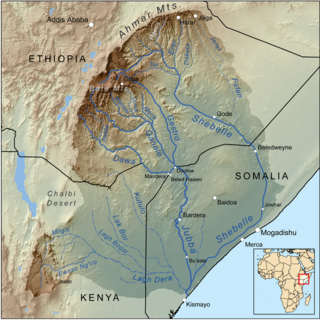
The Dawa River is found in East Africa, covering an area of, 58,961 km2. It flows through three major countries: Kenya, Ethiopia, and Somalia, with 81% falling into Ethiopian territory. It is known for its complex geological environment, evident through its diverse lithology and structural framework, coming from the river's closeness to multiple volcanic-tectonic events. The wide river has gentle slopes either side of its exposed bedrock. The Dawa river flows south east to form part of the Ethiopia - Somalia border and part of Ethiopia - Kenya border. Awata, Digati, and Mormora are the only significant off-flowing rivers to Dawa.
ELC Electroconsult (ELC) is a historic Italian engineering firm established in 1955 by the major Italian private companies leading and pioneering since 1905 in planning, design and construction of hydropower schemes in the Alps. The company is based in Milan (Italy).
Wabe River is a west-southwest flowing river of south-central Ethiopia, entirely confined within the reaches of Gurage Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region.
Energy in Ethiopia is energy and electricity production, consumption, transport, exportation, and importation in Ethiopia.
The Gilgel Gibe I Dam is a rock-filled embankment dam on the Gilgel Gibe River in Ethiopia. It is located about 57 km (35 mi) northeast of Jimma in Oromia Region. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production. The Gilgel Gibe I hydroelectric powerplant has an installed capacity of 184 MW, enough to power over 123,200 households. The dam is 1,700 m (5,600 ft) long and 40 m (130 ft) tall. Construction on the dam began in 1988 but work was halted in 1994. In 1995 construction restarted with a new construction firm. The power station was commissioned in 2004.

The Gilgel Gibe III Dam is a 250m high roller-compacted concrete dam with an associated hydroelectric power plant on the Omo River in Ethiopia. It is located about 62 km (39 mi) west of Sodo in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region. Once fully commissioned, it will be the third largest hydroelectric plant in Africa with a power output of about 1870 Megawatt (MW), thus more than doubling total installed capacity in Ethiopia from its 2007 level of 814 MW. The Gibe III dam is part of the Gibe cascade, a series of dams including the existing Gibe I dam and Gibe II power station as well as the planned Gibe IV and Gibe V dams. The existing dams are owned and operated by the state-owned Ethiopian Electric Power, which is also the client for the Gibe III Dam.
Ethiopia is called the water tower of Africa due to its combination of mountainous areas with a comparatively large share of water resources in Africa. Only a fraction of this potential has been harnessed so far, 1% at the beginning of the 21st century. In order to become the powerhouse of Africa, Ethiopia is actively exploiting its water resources by building dams, reservoirs, irrigation and diversion canals and hydropower stations. The benefits of the dams are not only limited to hydropower. Many dams are multi-purpose dams that are also designed to provide water for irrigation, drinking water and flood control. However, hydropower is expected to be the main benefit of the dams.
The Gilgel Gibe II Power Station is a hydroelectric power station on the Omo River in Ethiopia. It is located about 80 km (50 mi) east of Jimma in Wolaita/Dawro Region. The power station receives water from a tunnel entrance 7°55′27″N37°23′16″E on the Gilgel Gibe River. It has an installed capacity of 420 MW and was inaugurated on January 14, 2010. Almost two weeks after inauguration, a portion of the head race tunnel collapsed causing the station to shut down. Repairs were completed on December 26, 2010.

Wolayita or Wolaita is an administrative zone in Ethiopia. It is named for the Welayta people, whose homeland is in the zone. Wolayita is bordered on the south by Gamo Gofa, on the west by the Omo River which separates it from Dawro, on the northwest by Kembata Tembaro, on the north by Hadiya, on the northeast by the Oromia Region, on the east by the Bilate River which separates it from Sidama Region, and on the south east by the Lake Abaya which separates it from Oromia Region. The administrative centre of Wolayita is Sodo. Other major towns are Areka, Boditi, Tebela, Bele, Gesuba, Gununo, Bedessa and Dimtu.

The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, formerly known as the Millennium Dam and sometimes referred to as the Hidase Dam, is a gravity dam on the Blue Nile River in Ethiopia under construction since 2011. The dam is in the Benishangul-Gumuz Region of Ethiopia, about 45 km (28 mi) east of the border with Sudan.
Friends of Lake Turkana (FoLT) is a nonprofit organization in Kenya that was founded in 2007 by Kenyan environmentalist Ikal Angelei. The organization has worked to stop the construction of the Ethiopian Gilgel Gibe III Dam on the Omo River, Lake Turkana's primary source of water. Due to FoLT and other partner's advocacy work on saving Lake Turkana, the Lake was added to the list of world Heritage sites in Danger by UNESSCO in June 2018.

Ethiopia's industrial sectors classified into four basic groups: agriculture, food processing, construction, resources and energy and tourism. Agriculture constitutes over 50% of economic sector in Ethiopia, and the largest dependable economic activity. It includes production of livestock products, beverages, leather and textiles industry. Besides, Ethiopia is the largest exporter of coffee involving over 15 million active workers.
References
- ↑ "Gilgel Gibe Resettlement Project in Ethiopia". Archived from the original on November 12, 2004. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ↑ "New Hydroelectric Power Plant in Gilgel-Gibe Inaugurated by Prime Minister Meles Zenawi" (accessed 22 April 2006)
- ↑ "New Hydroelectric Power Plant on Gilgel Gibe" (All Africa), subscription required; accessed 21 July 2006