Related Research Articles

The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh and even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.

The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the "glutes".

The gluteus medius, one of the three gluteal muscles, is a broad, thick, radiating muscle. It is situated on the outer surface of the pelvis.

The gluteus minimus, or glutæus minimus, the smallest of the three gluteal muscles, is situated immediately beneath the gluteus medius.
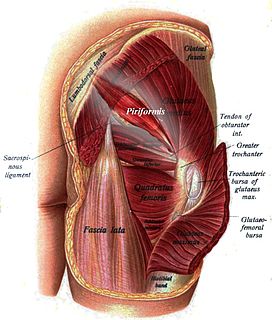
The piriformis muscle is a muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.

In vertebrate anatomy, hip refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.

The gluteal sulcus is an area of the body of humans and anthropoid apes, described by a horizontal crease formed by the inferior aspect of the buttocks and the posterior upper thigh. The gluteal sulcus is formed by the posterior horizontal skin crease of the hip joint and overlying fat and is not formed by the lower border of the gluteus maximus muscle, which crosses the fold obliquely. It is one of the major defining features of the buttocks. Children with developmental dysplasia of the hips are born with uneven gluteal folds and can be diagnosed with physical examination and sonogram.

Trendelenburg's sign is found in people with weak or paralyzed abductor muscles of the hip, namely gluteus medius and gluteus minimus. It is named after the German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg. It is often incorrectly referenced as Trendelenburg test which is a test for vascular insufficiency in the lower extremities.
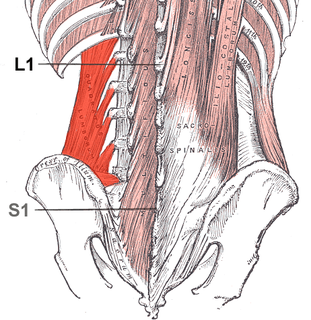
The quadratus lumborum muscle, informally called the QL, is a paired muscle of the left and right posterior abdominal wall. It is the deepest abdominal muscle, and commonly referred to as a back muscle. Each is irregular and quadrilateral in shape.

The tensor fasciae latae is a muscle of the thigh. Together with the gluteus maximus, it acts on the iliotibial band and is continuous with the iliotibial tract, which attaches to the tibia. The muscle assists in keeping the balance of the pelvis while standing, walking, or running.

The gluteal muscles, often called glutes are a group of three muscles which make up the gluteal region commonly known as the buttocks: the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus. The three muscles originate from the ilium and sacrum and insert on the femur. The functions of the muscles include extension, abduction, external rotation, and internal rotation of the hip joint.
Trendelenburg gait, named after Friedrich Trendelenburg, is an abnormal gait. It is caused by weakness or ineffective action of the gluteus medius muscle and the gluteus minimus muscle.

In human anatomy, the muscles of the hip joint are those muscles that cause movement in the hip. Most modern anatomists define 17 of these muscles, although some additional muscles may sometimes be considered. These are often divided into four groups according to their orientation around the hip joint: the gluteal group; the lateral rotator group; the adductor group; and the iliopsoas group.

The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a sensory nerve in the thigh. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum.

The inferior gluteal nerve is the main motor neuron that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle. It is responsible for the movement of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs. Injury to this nerve is rare but often occurs as a complication of posterior approach to the hip during hip replacement. When damaged, one would develop gluteus maximus lurch, which is a gait abnormality which causes the individual to 'lurch' backwards to compensate lack in hip extension.

The superior gluteal nerve is a nerve that originates in the pelvis. It supplies the gluteus medius muscle, the gluteus minimus muscle, the tensor fasciae latae muscle, and the piriformis muscle.

The superior gluteal artery is the largest and final branch of the internal iliac artery. It is the continuation of the posterior division of that vessel. It is a short artery which runs backward between the lumbosacral trunk and the first sacral nerve. It divides into a superficial and a deep branch after passing out of the pelvis above the upper border of the piriformis muscle.

The inferior gluteal artery, the smaller of the two terminal branches of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery, is distributed chiefly to the buttock and back of the thigh.
In medicine, physiotherapy, chiropractic, and osteopathy the hip examination, or hip exam, is undertaken when a patient has a complaint of hip pain and/or signs and/or symptoms suggestive of hip joint pathology. It is a physical examination maneuver.

The hip bone is a large irregular bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.
References
- ↑ Moore, Keith L.; Agur, Anne M. R.; Dalley, Arthur F.; Tank, Patrick W.; Gest, Thomas R. (2011). Essential Clinical Anatomy / Atlas of Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781451116700 . Retrieved 24 April 2018.