
Sengbe Pieh, also known as Joseph Cinqué or Cinquez and sometimes referred to mononymously as Cinqué, was a West African man of the Mende people who led a revolt of many Africans on the Spanish slave ship La Amistad in July 1839. After the ship was taken into custody by the US Revenue-Marine, Cinqué and his fellow Africans were eventually tried for mutiny and killing officers on the ship, in a case known as United States v. The Amistad. This reached the U.S. Supreme Court, where Cinqué and his fellow Africans were found to have rightfully defended themselves from being enslaved through the illegal Atlantic slave trade and were released. The US government did not provide any aid to the acquitted Mende People. The United Missionary Society, a black group founded by James W.C. Pennington, helped raise money for the return of thirty-five of the survivors to Sierra Leone in 1842.
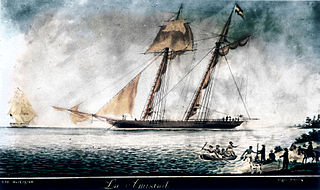
La Amistad was a 19th-century two-masted schooner owned by a Spaniard colonizing Cuba. It became renowned in July 1839 for a slave revolt by Mende captives who had been captured and sold to European slave traders and illegally transported by a Portuguese ship from West Africa to Cuba, in violation of European treaties against the Atlantic slave trade. Spanish plantation owners Don José Ruiz and Don Pedro Montes bought 53 captives in Havana, Cuba, including four children, and were transporting them on the ship to their plantations near Puerto Príncipe. The revolt began after the schooner's cook jokingly told the slaves that they were to be "killed, salted, and cooked." Sengbe Pieh unshackled himself and the others on the third day and started the revolt. They took control of the ship, killing the captain and the cook. Three Africans were also killed in the melee.

USS Hope was a 19th-century wooden yacht schooner, designed and built in 1861 by Henry Steers for Captain Thomas B. Ives of Providence, Rhode Island. She was acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was placed into service as a gunboat assigned to support the fleet blockading the ports of the Confederate States of America. However, at times, Hope was assigned extra tasks, such as that of a dispatch boat, supply runner and salvage ship. She was a pilot boat from 1866 to 1891 and in 1891 she was replaced by the Herman Oelrichs, when the Hope was wrecked ashore the Sandy Hook Point.

The Phantom was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built in 1867 from the designs by Dennison J. Lawlor. The schooner was considered a model for her type with a reputation for being very fast. She helped rescue the passengers on the steamship SS Oregon when it sank in 1886. She was one of the pilot-boats that was lost in the Great Blizzard of 1888. The Phantom was replaced by the pilot-boat William H. Bateman.

The Thomas S. Negus was a 19th-century two-masted Sandy Hook pilot boat, built by C. & R. Poillon shipyard in Brooklyn in 1873 for the New Jersey maritime pilots. She was built to replace the pilot boat Jane, No. 1, which sank in early 1873. She was the winner of a $1,000 prize at the Cape May Regatta in 1873. She was named for Thomas S. Negus, president of the N. J. Pilots' Commissioners. In 1897, she left the pilot service to prospect for gold during the Klondike Gold Rush.

The Ezra Nye was a 19th-century pilot boat, built in 1859 by the Wells & Webb shipyard in Greenpoint, Brooklyn for a group of New Jersey and Sandy Hook Pilots. She was one of the pilot-boats that was in the Great Blizzard of 1888, that was one of the most severe blizzards in American history. In 1896, in the age of steam, the Ezra Nye along with other pilot boats, were replaced with steamboats.
The Mary Ann, No. 13 was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built for the New York pilots. She helped transport maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. In 1860, the Mary Ann, was one of only twenty-one pilot boats in the New York and New Jersey fleet. She went ashore outside Sandy Hook in 1863.

The Nettle was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built in 1844 by S. Hall of East Boston, Massachusetts for the New York Pilots. She helped transport maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. In 1868, she found the wreck of the bark Henry Trowbridge, and towed her to Sandy Hook. The Nettle, sank in 1876 in the Pensacola Bay. The sunken wreck was removed in 1878 to improve the Pensacola harbor.

The Thomas H. Smith, or T. H. Smith, was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built for the New York pilots around 1820. She helped transport maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. In 1840, she was one of only eight pilot boats in the New York fleet. In 1857, she went ashore and sank six miles from Barnegat.

The Edward E. Barrett, or Edward E. Bartlett, was a 19th-century two-masted Sandy Hook pilot boat, built by C. & R. Poillon in 1883 and designed by William Townsend. She helped transport New Jersey maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. She was one of the pilot boats that survived the Great Blizzard of 1888. In the age of steam, the Barrett ended her pilot commission and was sold in 1904.

Edmund Blunt was a 19th-century New York pilot boat built in 1858 by Edward F. Williams for the New York Pilots. She helped transport New York City maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. She survived the Great Blizzard of 1888. In the age of steam, the Blunt along with other pilot boats, were replaced with steamboats. She was built to replace the Jacob L. Westervelt, which sank in 1857.

The Anthony B. Neilson was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat, built in 1854 by George Steers for a company of New York Sandy Hook pilots. She was considered to be the fastest boat in the piloting business. She helped transport New York City maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. She survived the Great Blizzard of 1888. In 1859, the Neilson was sold to a group of New Orleans pilots. The New York pilots then replaced the Neilson, with a new pilot boat, the John D. Jones.

The Enchantress was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built in 1851 by John Maginn who named her after one of the cast in the opera The Enchantress. She was launched from the Westervelt & McKay shipyard. The Enchantress was one of the oldest pilot-boats in the service. She was Cornelius Vanderbilt's favorite pilot boat. The Enchantress went down with all hands in the Great Blizzard of 1888. The pilot boat James Stafford was built to replace her.
The Blossom was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built for the New York pilots around 1837. She helped transport maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. In 1839, she came across the Slave ship La Amistad. In 1840, there were only eight New York pilot boats, the Blossom being No. 5. Pilot Thomas Freeborn of the Blossom boarded the packet ship John Minturn and tried to guide the ship in bad weather. He was one of thirty-eight passengers that died near the Jersey Shore in 1846.

The Joseph N. Lord was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built in 1840 at the Jabez Williams shipyard in East River, for New York pilots. She helped transport maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. The Joseph N. Lord was lost at sea in 1845 at Port-au-Platt, Dominican Republic.

The Virginia was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat. She came from Savannah to New York City in 1838. In 1840, the Virginia was No. 8 in the list of only eight pilot boats in the New York fleet. She went ashore in 1860 and was replaced by the pilot boat William H. Aspinwall in 1861.

Thomas D. Harrison was a 19th-century New York pilot boat built for New Jersey pilots. She was launched from the Jacob S. Ellis & Son shipyard, at Tottenville, Staten Island in 1875. The Harrison went ashore in the Great Blizzard of 1888 with no lives lost. She continued as a pilot boat with Pilot Stephen Cooper in command. She was purchased in 1897 by Allerton D. Hitch and used for coastal trade in the Cape Verde islands off the west African coast.

Favorite or Favorita, was a 19th-century New York Sandy Hook pilot boat built in the early 1820s. She helped transport New York City maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. Favorite collided with a United States steamer and sank in 1865 near Barnegat Lighthouse.

W. W. Story was a 19th-century New Jersey pilot boat built in 1874 at the Samuel H. Pine shipyard in Greenpoint, New York. She sank off Sandy Hook horseshoe during the Blizzard of 1888. She was raised and turned into a fishing smack. On November 13, 1896, she was reported missing along with her crew after being last seen along Absecon, New Jersey when she was caught up in a hurricane.

The John McKeon was a 19th-century New Jersey pilot boat built in 1838 by Webb & Allen for the New Jersey Pilots Association. She helped transport maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. Her short career ended in 1839, when the John McKeon was shipwrecked in a hurricane that swept the New York coast. The pilot boat Gratitude was lost in the same storm.


















