A lubricant is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity.

An air gun, air rifle or airgun, is a gun that shoots projectiles pneumatically with compressed air or other gases that are mechanically pressurized without involving any chemical reactions, in contrast to a firearm, which pressurizes gases chemically via oxidation of combustible propellants that generates propulsive energy by breaking molecular bonds.
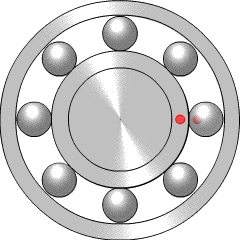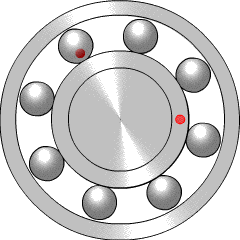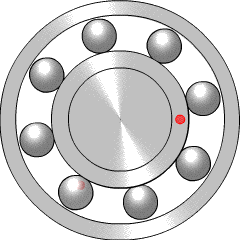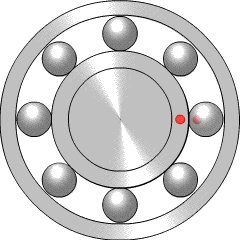
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.

A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion, and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free rotation around a fixed axis; or, it may prevent a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts. Most bearings facilitate the desired motion by minimizing friction. Bearings are classified broadly according to the type of operation, the motions allowed, or to the directions of the loads (forces) applied to the parts.
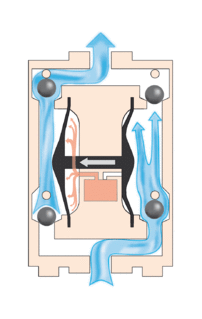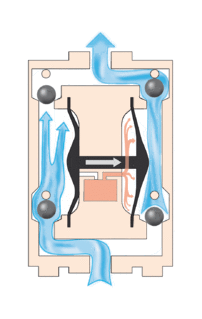
A diaphragm pump is a positive displacement pump that uses a combination of the reciprocating action of a rubber, thermoplastic or teflon diaphragm and suitable valves on either side of the diaphragm (check valve, butterfly valves, flap valves, or any other form of shut-off valves) to pump a fluid.

Cutting fluid is a type of coolant and lubricant designed specifically for metalworking processes, such as machining and stamping. There are various kinds of cutting fluids, which include oils, oil-water emulsions, pastes, gels, aerosols (mists), and air or other gases. Cutting fluids are made from petroleum distillates, animal fats, plant oils, water and air, or other raw ingredients. Depending on context and on which type of cutting fluid is being considered, it may be referred to as cutting fluid, cutting oil, cutting compound, coolant, or lubricant.

Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology.

Spray painting is a painting technique in which a device sprays coating material through the air onto a surface. The most common types employ compressed gas—usually air—to atomize and direct the paint particles. Spray guns evolved from airbrushes, and the two are usually distinguished by their size and the size of the spray pattern they produce. Airbrushes are hand-held and used instead of a brush for detailed work such as photo retouching, painting nails, or fine art. Air gun spraying uses generally larger equipment. It is typically used for covering large surfaces with an even coating of liquid. Spray guns can be either automated or hand-held and have interchangeable heads to allow for different spray patterns. Single color aerosol paint cans are portable and easy to store.

A staple gun or powered stapler is a hand-held machine used to drive heavy metal staples into wood, plastic, or masonry. Staple guns are used for many different applications and to affix a variety of materials, including insulation, house wrap, roofing, wiring, carpeting, upholstery, and hobby and craft materials. These devices are also known as trigger tackers.
Grease is a solid or semisolid lubricant formed as a dispersion of thickening agents in a liquid lubricant. Grease generally consists of a soap emulsified with mineral or vegetable oil.
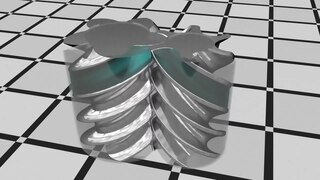
A rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas compressor, such as an air compressor, that uses a rotary-type positive-displacement mechanism. These compressors are common in industrial applications and replace more traditional piston compressors where larger volumes of compressed gas are needed, e.g. for large refrigeration cycles such as chillers, or for compressed air systems to operate air-driven tools such as jackhammers and impact wrenches. For smaller rotor sizes the inherent leakage in the rotors becomes much more significant, leading to this type of mechanism being less suitable for smaller compressors than piston compressors.

A grease fitting, grease nipple, Zerk fitting, grease zerk, or Alemite fitting is a metal fitting used in mechanical systems to feed lubricants, usually lubricating grease, into a bearing under moderate to high pressure using a grease gun.
The following are terms related to firearms and ammunition topics.

Lincoln Industrial Corporation (Lincoln) is a manufacturer of automated lubrication systems, manual lubrication equipment and industrial pumping systems, and subsidiary of Svenska Kullagerfabriken AB (SKF). Founded in 1910, the company has been responsible for many of the inventions that established modern lubrication practices in automotive maintenance and industry.

A paper cartridge is one of various types of small arms ammunition used before the advent of the metallic cartridge. These cartridges consisted of a paper cylinder or cone containing the bullet, gunpowder, and in some cases, a primer or a lubricating and anti-fouling agent. Combustible cartridges are paper cartridges that use paper treated with oxidizers to allow them to burn completely upon ignition.

Graco is an American manufacturer of fluid-handling systems and products based in Minneapolis, Minnesota.

The M3 is an American .45-caliber submachine gun adopted for U.S. Army service on 12 December 1942, as the United States Submachine Gun, Cal. .45, M3. The M3 was chambered for the same .45 ACP round fired by the Thompson submachine gun, but was cheaper to produce and lighter, although, contrary to popular belief, it was less accurate. The M3 was commonly referred to as the "Grease Gun" or simply "the Greaser", owing to its visual similarity to the mechanic's tool.

An Automatic Lubrication System (ALS), sometimes referred to as a Centralized Lubrication System (CLS),is a system that delivers controlled amounts of lubricant to multiple locations on a machine while the machine is operating. Even though these systems are usually fully automated, a system that requires a manual pump or button activation is still identified as a centralized lubrication system. The system can be classified into two different categories that can share a lot of the same components.

Firearm maintenance is a series of periodic preventive maintenance procedures aiming to ensure the proper function of a firearm, often with the use of a variety of specialized tools and chemical solutions. Typically such maintenance is performed by the owner of the firearm using either simple methods such as cleaning the firearm with oil or other cleaning solutions, or more sophisticated practices such as lubricating moving parts with oil/grease and recoating exposed surfaces with protective finishes such as varnishing or bluing.

Spiral groove bearings are self-acting, or hydrodynamic bearings used to reduce friction and wear without the use of pressurized lubricants. They have this ability due to special patterns of grooves. Spiral groove bearings are self-acting because their own rotation builds up the pressure needed to separate the bearing surfaces. For this reason, they are also contactless bearings.

















