Related Research Articles

The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), Dow Jones, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index of 30 prominent companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States.

A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often follow speculation and economic bubbles.

The 1997 Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided.

The Bear Stearns Companies, Inc. was an American investment bank, securities trading, and brokerage firm that failed in 2008 during the 2007–2008 financial crisis and the Great Recession. After its closure it was subsequently sold to JPMorgan Chase. The company's main business areas before its failure were capital markets, investment banking, wealth management, and global clearing services, and it was heavily involved in the subprime mortgage crisis.
The Doha Development Round or Doha Development Agenda (DDA) is the trade-negotiation round of the World Trade Organization (WTO) which commenced in November 2001 under then director-general Mike Moore. Its objective was to lower trade barriers around the world, and thus increase global trade.
Deglobalization or deglobalisation is the process of diminishing interdependence and integration between certain units around the world, typically nation-states. It is widely used to describe the periods of history when economic trade and investment between countries decline. It stands in contrast to globalization, in which units become increasingly integrated over time, and generally spans the time between periods of globalization. While globalization and deglobalization are antitheses, they are not mirror images.

The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus, and Western Canadian Select (WCS). Oil prices are determined by global supply and demand, rather than any country's domestic production level.

The American subprime mortgage crisis was a multinational financial crisis that occurred between 2007 and 2010 that contributed to the 2007–2008 global financial crisis. The crisis led to a severe economic recession, with millions losing their jobs and many businesses going bankrupt. The U.S. government intervened with a series of measures to stabilize the financial system, including the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) and the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA).

The Great Depression was a period of severe global economic downturn that occurred from 1929 to 1939. It was characterised by high unemployment rates, crisies of liquidity, and widespread business failures around the world. The economic contagion began around September 1929 in the United States, the largest economy in the world. Economic historians usually consider the devastating Wall Street stock market crash of October 1929, often referred to as "Black Tuesday," to have been the catalyst of the Great Depression.

The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country. At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression.

A global recession is a recession that affects many countries around the world—that is, a period of global economic slowdown or declining economic output.
The European recession is part of the Great Recession that began in mid-2007. The crisis spread rapidly and affected much of the region, with several countries already in recession as of February 2009, and most others suffering marked economic setbacks. The global recession was first seen in Europe, as Ireland was the first country to fall into recession from Q2-Q3 2007 – followed by temporary growth in Q4 2007 – and then a two-year-long recession.
While beginning in the United States, the Great Recession spread to Asia rapidly and has affected much of the region.
North America was one of the focal points of the global Great Recession. While Canada has managed to return its economy nearly to the levels it enjoyed prior to the recession, the United States and Mexico are still under the influence of the worldwide economic slowdown. The cost of staple items dropped dramatically in the United States as a result of the recession.
The Great Recession in Oceania was the great recession of the late 2000s and early 2010s in Oceania. The Oceanic countries suffered minimal impact during this time, in comparison with the impact that North America and Europe felt.

Panic selling is a large-scale selling of an investment that causes a sharp decline in prices. Specifically, an investor wants to sell an investment with little regard to the price obtained. The sale is problematic because the investor is reacting to emotion and fear, rather than evaluating the fundamentals.
The Great Recession in South America, as it mainly consists of commodity exporters, was not directly affected by the financial turmoil, even if the bond markets of Brazil, Argentina, Colombia and Venezuela have been hit.
This information is related to the effects of the Great Recession that happened worldwide from 2007 to 2012.

The 2007–2008 financial crisis, or the global financial crisis (GFC), was the most severe worldwide economic crisis since the Great Depression. Predatory lending in the form of subprime mortgages targeting low-income homebuyers, excessive risk-taking by global financial institutions, a continuous buildup of toxic assets within banks, and the bursting of the United States housing bubble culminated in a "perfect storm", which led to the Great Recession.
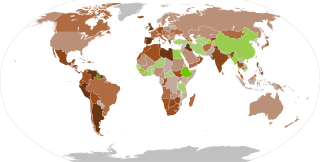
The COVID-19 recession was a global economic recession caused by COVID-19 lockdowns. The recession began in most countries in February 2020. After a year of global economic slowdown that saw stagnation of economic growth and consumer activity, the COVID-19 lockdowns and other precautions taken in early 2020 drove the global economy into crisis. Within seven months, every advanced economy had fallen to recession.