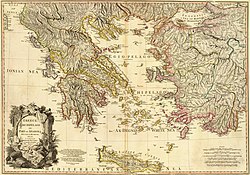
Ancient Greece was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity, that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period.
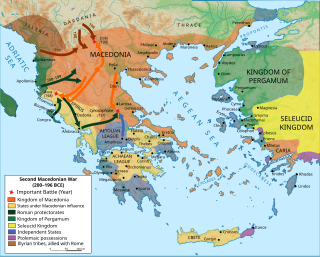
The Second Macedonian War was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. During their intervention, although the Romans declared the "freedom of the Greeks" against the rule from the Macedonian kingdom, the war marked a significant stage in increasing Roman intervention in the affairs of the eastern Mediterranean, which would eventually lead to Rome's conquest of the entire region.

Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period in which ancient Greece and ancient Rome flourished and wielded major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia.
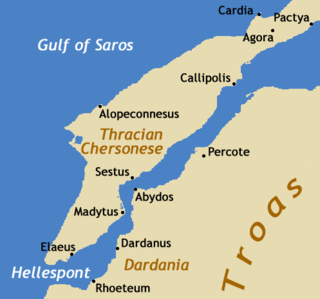
Sestos was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.

Athens is one of the oldest named cities in the world, having been continuously inhabited for perhaps 5,000 years. Situated in southern Europe, Athens became the leading city of Ancient Greece in the first millennium BC, and its cultural achievements during the 5th century BC laid the foundations of Western civilization.

In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII, followed by the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word Hellas was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word Hellenistic was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great.

Nicopolis or Actia Nicopolis was the capital city of the Roman province of Epirus Vetus. It is located near Preveza, Greece. The city was founded in 29 BC by Octavian in commemoration of his victory in 31 BC over Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium nearby.

Achaia, sometimes spelled Achaea, was a province of the Roman Empire, consisting of the Peloponnese, Attica, Boeotia, Euboea, the Cyclades and parts of Phthiotis, Aetolia-Acarnania and Phocis. In the north, it bordered on the provinces of Epirus vetus and Macedonia. The region was annexed by the Roman Republic in 146 BC following the sack of Corinth by the Roman general Lucius Mummius, who was awarded the surname "Achaicus". Initially part of the Roman province of Macedonia, it was made into a separate province by Augustus.

The history of Greece encompasses the history of the territory of the modern nation-state of Greece as well as that of the Greek people and the areas they inhabited and ruled historically. The scope of Greek habitation and rule has varied throughout the ages and as a result, the history of Greece is similarly elastic in what it includes. Generally, the history of Greece is divided into the following periods:

Hellenistic Greece is the historical period of the country following Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the annexation of the classical Greek Achaean League heartlands by the Roman Republic. This culminated at the Battle of Corinth in 146 BC, a crushing Roman victory in the Peloponnese that led to the destruction of Corinth and ushered in the period of Roman Greece. Hellenistic Greece's definitive end was with the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, when the future emperor Augustus defeated Greek Ptolemaic queen Cleopatra VII and Mark Antony, the next year taking over Alexandria, the last great center of Hellenistic Greece.

Byzantine Greece has a history that mainly coincides with that of the Byzantine Empire itself.

The Macedonian Wars were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Greece and the rest of the eastern Mediterranean basin, in addition to their hegemony in the western Mediterranean after the Punic Wars. Traditionally, the "Macedonian Wars" include the four wars with Macedonia, in addition to one war with the Seleucid Empire, and a final minor war with the Achaean League. The most significant war was fought with the Seleucid Empire, while the war with Macedonia was the second, and both of these wars effectively marked the end of these empires as major world powers, even though neither of them led immediately to overt Roman domination. Four separate wars were fought against the weaker power, Macedonia, due to its geographic proximity to Rome, though the last two of these wars were against haphazard insurrections rather than powerful armies. Roman influence gradually dissolved Macedonian independence and digested it into what was becoming a leading empire. The outcome of the war with the now-deteriorating Seleucid Empire was ultimately fatal to it as well, though the growing influence of Parthia and Pontus prevented any additional conflicts between it and Rome.
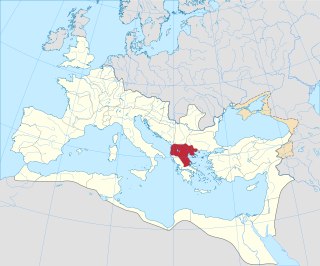
Macedonia was a province of ancient Rome, encompassing the territory of the former Antigonid Kingdom of Macedonia, which had been conquered by the Roman Republic in 168 BC at the conclusion of the Third Macedonian War. The province was created in 146 BC, after the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled King of Macedonia in the Fourth Macedonian War. The province incorporated the former Kingdom of Macedonia with the addition of Epirus, Thessaly, and parts of Illyria, Paeonia and Thrace.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to classical studies:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient Greece:

Achaea or Achaia is the northernmost region of the Peloponnese, occupying the coastal strip north of Arcadia. Its approximate boundaries are: to the south, Mount Erymanthus; to the south-east, Mount Cyllene; to the east, Sicyon; and to the west, the Larissos river. Apart from the plain around Dyme in the west, Achaea is generally a mountainous region.

The kingdom of Macedonia was an ancient state in what is now the Macedonian region of northern Greece, founded in the mid-7th century BC during the period of Archaic Greece and lasting until the mid-2nd century BC. Led first by the Argead dynasty of kings, Macedonia became a vassal state of the Achaemenid Empire of ancient Persia during the reigns of Amyntas I of Macedon and his son Alexander I of Macedon. The period of Achaemenid Macedonia came to an end in roughly 479 BC with the ultimate Greek victory against the second Persian invasion of Greece led by Xerxes I and the withdrawal of Persian forces from the European mainland.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Athens:
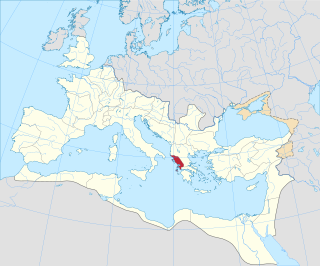
The province of Epirus was a province of the Roman Empire, covering the region of Ancient Epirus. Rome first annexed the region in 167 BC, in the aftermath of the Third Macedonian War, and initially put the region in the larger Roman province of Macedonia, which at the time covered the whole of the Hellenistic world in mainland Europe. In 27 BC, Epirus and Achaea were separated from Macedonia and grouped into the senatorial province of Achaea, with the exception of its northernmost part, which remained part of the province of Macedonia. Under Emperor Trajan, sometime between 103 and 114 AD, Epirus became a separate province, under a procurator Augusti. The new province extended from the Gulf of Aulon (Vlorë) and the Acroceraunian Mountains in the north to the lower course of the Acheloos River in the south, and included the northern Ionian Islands of Corfu, Lefkada, Ithaca, Cephallonia, and Zakynthos.