| Greenleaf Peak | |
|---|---|
Southeast slope of Greenleaf Peak, Red Bluffs and the Columbia River from Bonneville Dam | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 3,424 ft (1,044 m) NAVD 88 [1] |
| Coordinates | 45°42′50″N121°58′01″W / 45.713974956°N 121.966995881°W Coordinates: 45°42′50″N121°58′01″W / 45.713974956°N 121.966995881°W [1] |
| Geography | |
| Location | Skamania County, Washington, U.S. |
| Parent range | Cascade Range |
| Topo map | USGS Bonneville Dam |
Greenleaf Peak is a mountain in the Cascade Range in the U.S. state of Washington, located on the north side of the Columbia River near Table Mountain, in the Columbia River Gorge. The peak lies within the Columbia River Gorge National Scenic Area near Bonneville Dam. It is 3,424 feet (1,044 m) in elevation. [1] Botanist David Douglas climbed to the summit in September 1825, making this the first recorded mountain ascent in what is now Washington state. [2]

The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades. The small part of the range in British Columbia is referred to as the Canadian Cascades or, locally, as the Cascade Mountains. The latter term is also sometimes used by Washington residents to refer to the Washington section of the Cascades in addition to North Cascades, the more usual U.S. term, as in North Cascades National Park. The highest peak in the range is Mount Rainier in Washington at 14,411 feet (4,392 m).

In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are currently 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory and shares its sovereignty with the federal government. Due to this shared sovereignty, Americans are citizens both of the federal republic and of the state in which they reside. State citizenship and residency are flexible, and no government approval is required to move between states, except for persons restricted by certain types of court orders. Four states use the term commonwealth rather than state in their full official names.

The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. It flows northwest and then south into the US state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state of Oregon before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The river is 1,243 miles (2,000 km) long, and its largest tributary is the Snake River. Its drainage basin is roughly the size of France and extends into seven US states and a Canadian province. The fourth-largest river in the United States by volume, the Columbia has the greatest flow of any North American river entering the Pacific.

Just south of the summit of Greenleaf Peak there is a dramatic escarpment called Red Bluffs, which connects Greenleaf Peak and Table Mountain. Approximately 1,300 feet (400 m) of the Eagle Creek formation are exposed at Red Bluffs. [3] The Red Bluffs escarpment was created by the repeated collapse of Greenleaf Peak and Table Mountain. Massive landslides have fallen from the mountains, creating a 12-to-14-square-mile (31 to 36 km2) area of debris called the Cascade Landslide Complex. The largest and most studied landslide is known as the Bonneville Slide, which created the Bridge of the Gods and Cascade Rapids [4] The topography of the landslide complex is uneven with roughly rolling hills and abrupt slopes. The whole area is inclined south toward and beyond the Columbia River. There may have been a cinder cone between Greenleaf Peak and Table Mountain which collapsed during the Bonneville Slide. [3]

An escarpment, or scarp, is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as an effect of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having differing elevations. Usually scarp and scarp face are used interchangeably with escarpment.

The Bridge of the Gods was a natural dam created by the Bonneville Slide, a major landslide that dammed the Columbia River near present-day Cascade Locks, Oregon in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. The river eventually breached the bridge and washed much of it away, but the event is remembered in local legends of the Native Americans as the Bridge of the Gods.
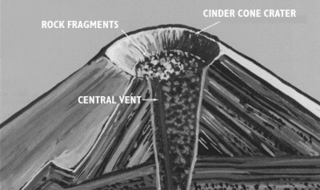
A cinder cone is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as either volcanic clinkers, cinders, volcanic ash, or cinder that has been built around a volcanic vent. They consist of loose pyroclastic debris formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30–40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit.

The propensity of the area south of Greenleaf Peak and Table Mountain to collapse in landslides is due to the Eagle Creek formation. The rocks of the formation cover approximately 30 miles (48 km) of the Columbia River Gorge east of Cape Horn and consist of a mixture of past landslides, volcanic mud flows and ash falls. The formation is topped with basalt. Water can percolate through the basalt and saturate the Eagle Creek formation. In places where the formation is relatively close to the surface and inclined downslope, such as near Greenleaf Peak and Table Mountain, water saturation can cause the formation's material to slide away, carrying the overlying basalt with it. [5]

Basalt is a mafic extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich lava exposed at or very near the surface of a terrestrial planet or a moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Basalt lava has a low viscosity, due to its low silica content, resulting in rapid lava flows that can spread over great areas before cooling and solidification. Flood basalt describes the formation in a series of lava basalt flows.
Between Greenleaf Peak and Table Mountain, and above the Red Bluffs, lies Greenleaf Basin. The basin averages 2,040 feet (620 m) in elevation and is covered with forested wetlands. Greenleaf Creek flows south through the basin before plunging as a waterfall over the Red Bluffs escarpment.
In the winter of 2007-2008, there was a large landslide on the south slope of Greenleaf Peak, in the state-owned Table Mountain Natural Resources Conservation Area. Some 3 to 5 acres (12,000 to 20,000 m2) of a timbered rocky cliff slid, burying approximately 30 acres (120,000 m2) of forest under rubble. The slide was estimated to be about 750 feet (230 m) wide and 0.5 miles (0.80 km) long. [5]





















