
Groep fan Auwerk ("Group of Aurich") is a political activism organization that advocates for an independent Frisian state (Frisia). The group is active in politics and promotes a stronger Frisian identity.[ citation needed ]

Groep fan Auwerk ("Group of Aurich") is a political activism organization that advocates for an independent Frisian state (Frisia). The group is active in politics and promotes a stronger Frisian identity.[ citation needed ]
Groep fan Auwerk was founded in 2003 and organized its platform. In 2005 they made an application for the Frisian nationality to be recognized by the provincial house of parliament in Leeuwarden and ultimately the Frisian nationality was accepted by the European Union. After that, they made a "FRL" (Friesland) license plate sticker to replace the official "NL" (Netherlands). [1]
On 23 September 2006, Groep fan Auwerk presented a proposal for an Inter-Frisian flag, intended to represent all Frisian regions, but was rejected by the Interfrisian Council in June 2007. However, the Council adopted the idea of a common flag. [2] The flag of the Groep fan Auwerk previously advised, particularly in East Frisia under criticism because it had been prepared by the group in secret and then propagated massively. [3] [ failed verification ]
In September 2008, Groep fan Auwerk replaced several traffic signs with Frisian-language versions. On 25 September 2009, Groep fan Auwerk, in cooperation with Frije Fryske Grûn (Free Frisian Foundation) removed the Dutch versions in Wymbritseradiel. The municipality had already decided that the signs should be in Frisian but the activists did not feel that the municipality had effected the change quickly enough. [4] [ better source needed ]

The Frisian languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 400,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and foreign influences.
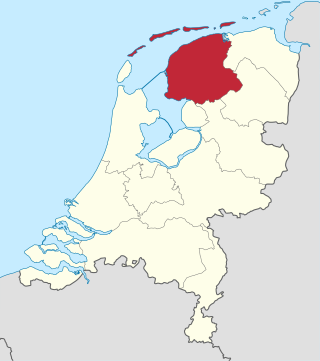
Friesland, historically and traditionally known as Frisia, named after the Frisians, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of Flevoland, northeast of North Holland, and south of the Wadden Sea. As of January 2023, the province had a population of about 660,000, and a total area of 5,753 km2 (2,221 sq mi).
The Frisians are an ethnic group indigenous to the coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark, and during the Early Middle Ages in the north-western coastal zone of Flanders, Belgium. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany, East Frisia and North Frisia.

Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. Wider definitions of ‘Frisia’ may include the island of Rem and the other Danish Wadden Sea Islands. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Germanic ethnic group.
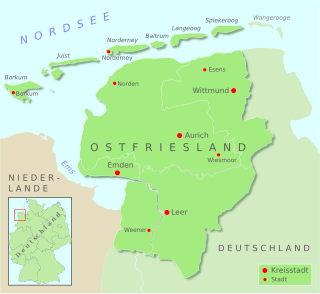
East Frisia or East Friesland is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia and to the west of Landkreis Friesland.

Radbod was the king of Frisia from c. 680 until his death. He is often considered the last independent ruler of Frisia before Frankish domination. He defeated Charles Martel at Cologne. Eventually, Charles prevailed and compelled the Frisians to submit. Radbod died in 719, but for some years his successors struggled against the Frankish power.

Stadsfries or Town Frisian is a set of dialects spoken in certain cities in the province of Friesland in the northern Netherlands, namely Leeuwarden, Sneek, Bolsward, Franeker, Dokkum, Harlingen, Stavoren, and to some extent in Heerenveen. For linguistic reasons, the outlying and insular dialects of Midsland (Terschelling), Ameland, Het Bildt, and Kollum are also sometimes tied to Stadsfries.

Saterland Frisian, also known as Sater Frisian, Saterfrisian or Saterlandic, is the last living dialect of the East Frisian language. It is closely related to the other Frisian languages: North Frisian, spoken in Germany as well, and West Frisian, spoken in the Dutch province of Friesland.

Sportclub Heerenveen is a Dutch professional football club from Heerenveen. They currently play in the Eredivisie, the top level of football in the Netherlands. The club is known for its Frisian identity.

The Flag of the province of Friesland or Frisian flag, is the official flag of the Netherlands province of Friesland.

The Vetkopers and Schieringers were two opposing Frisian factional parties from the medieval period. They were responsible for a civil war that lasted for over a century (1350–1498) and which eventually led to the end of the so-called "Frisian freedom".

Frisian freedom was the absence of feudalism and serfdom in Frisia, the area that was originally inhabited by the Frisians. Historical Frisia included the modern provinces of Friesland and Groningen, and the area of West Friesland, in the Netherlands, and East Friesland in Germany. During the period of Frisian freedom the area did not have a sovereign lord who owned and administered the land. The freedom of the Frisians developed in the context of ongoing disputes over the rights of local nobility.
A grietenij was a municipal district, a forerunner to the gemeente or municipality in Frisia, particularly in Friesland, and also in the city Groningen which are now a part of the Netherlands. After the Saxon occupation, from about 1498 until 1851, there were a total of 30 grietenijen in Friesland and 11 cities.

Frisia has changed dramatically over time, both through floods and through a change in identity. It is part of the Nordwestblock which is a hypothetical historic region linked by language and culture,where they may have spoken an Indo-European language which was neither germanic nor celtic.

Almenum is a historic locality in the northern Netherlands, near Midlum, Friesland the site of the first Christian church in Friesland. Saint Boniface set up a local church in the locality in 754. The location of the church is on the Terp of Almenum, a mound of earth about five meters high. Almenum is named after the place where someone called "Allaman" lived. The -um suffix is derived from the West Frisian word "hiem" meaning "home". An alternative explanation for the name of the locality is that it originally meant common lands for grazing cattle. In Icelandic this kind of land still uses the term "almenningurheim".
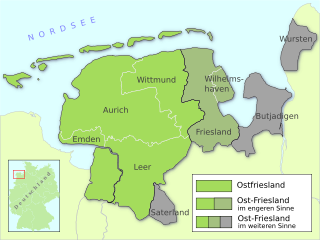
East Frisia is a collective term for all traditionally Frisian areas in Lower Saxony, Germany, which are primarily located on a peninsula between the Dollart and the Jade Bight. Along with West Frisia and North Frisia, it is one of the most commonly used subdivisions of Frisia.

The flags of Frisia are the flags that are used to represent Frisia, a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Some designs are in official use on a local or provincial level, while others are used unofficially on a regional, linguistic or international level.

The Interfrisian Council is a geopolitical organization that represents the common interests of the Frisians. The organization consists of three regional councils or "sections": North Frisia, East Frisia and West Frisia. Every three years, the presidency of the Interfrisian Council is handed over to another section. The council was established in 1956.

Frisian nationalism refers to the nationalism which views Frisians as a nation with a shared culture. Frisian nationalism seeks to achieve greater levels of autonomy for Frisian people, and also supports the cultural unity of all Frisians regardless of modern-day territorial borders. The Frisians derive their name from the Frisii, an ancient Germanic tribe which inhabited the northern coastal areas in what today is the northern Netherlands, although historical research has indicated a lack of direct ethnic continuity between the ancient Frisii and later medieval 'Frisians' from whom modern Frisians descend. In the Middle Ages, these Frisians formed the Kingdom of Frisia and later the Frisian freedom confederation, before being subsumed by stronger foreign powers up to this day.

The Wirmer Flag, also known commercially as the flag of German Resistance 20 July or the Stauffenberg flag, is a design by Josef Wirmer. Wirmer was a resistance fighter against the Nazi Regime and part of the 20 July plot. According to his idea, the flag was to become the new flag of Germany after the successful assassination attempt against Hitler and the transfer of power to the conspirators. First discussed by the Parlamentarischer Rat in 1948/49 as the federal flag, the design served in modified form as the party flag of the Christian Democratic Union of Germany (CDU) from 1953 until around 1970 and as the model for the Free Democratic Party's (FDP) party symbol. The flag then disappeared from public perception.
Einstimmig wurde beschlossen, eine zusätzliche gesamtfriesische Flagge gestalten zu lassen. Ein von der Group van Auwerk aus Westfriesland vorgestellter Flaggenentwurf wurde nicht übernommen, aber als Idee für eine weitere Entwicklung der Fahne begrüßt.[It was decided unanimously to have an additional all-Frisian flag designed. A flag design presented by the Group van Auwerk from West Friesland was not adopted, but was welcomed as an idea for further development of the flag.]