
Adelaide of Italy, also called Adelaide of Burgundy, was Holy Roman Empress by marriage to Emperor Otto the Great. She was crowned with him by Pope John XII in Rome on 2 February 962. She was the first empress designated consors regni, denoting a "co-bearer of royalty" who shared power with her husband. She was essential as a model for future consorts regarding both status and political influence. She was regent of the Holy Roman Empire as the guardian of her grandson in 991–995.

The Ottonian dynasty was a Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman Emperors named Otto, especially its first Emperor Otto I. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German stem duchy of Saxony. The family itself is also sometimes known as the Liudolfings, after its earliest known member Count Liudolf and one of its most common given names. The Ottonian rulers were successors of the Germanic king Conrad I, who was the only Germanic king to rule in East Francia after the Carolingian dynasty and before this dynasty.
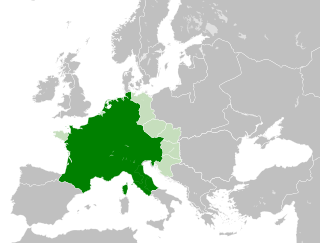
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the Roman Empire from the Byzantine Empire to Western Europe. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire.
A queen consort is the wife of a reigning king, and usually shares her spouse's social rank and status. She holds the feminine equivalent of the king's monarchical titles and may be crowned and anointed, but historically she does not formally share the king's political and military powers, unless on occasion acting as regent.

Hedwige of Saxony, a member of the Ottonian dynasty, was Duchess consort of the Franks by her marriage to the Robertian duke Hugh the Great. Upon her husband's death in 956, she acted as a regent during the minority of their son Hugh Capet, the founder of the Elder House of Capet.
Louis the Blind was the king of Provence from 11 January 887, King of Italy from 12 October 900, and briefly Holy Roman Emperor, as Louis III, between 901 and 905. His father was a Bosonid and his mother was a Carolingian. He was blinded after a failed invasion of Italy in 905.

Ealhswith or Ealswitha was wife to King Alfred the Great. She was one of the most powerful noble women in early medieval England during the time of the Vikings. She was mother to King Edward the Elder who succeeded King Alfred to the Anglo-Saxon throne. Her father was a Mercian nobleman, Æthelred Mucel, Ealdorman of the Gaini, which is thought to be an old Mercian tribal group. Her mother was Eadburh, a member of the Mercian royal family and her lineage was one of the primary reasons for Alfred taking Ealhswith as his wife. Her legacy persists; after her death in the nunnery she founded and in the estates left to her by Alfred.

Ermentrude of Orléans was the Queen of the Franks by her marriage to Charles II.

Hugh, known as Hugh of Arles or Hugh of Provence, was the king of Italy from 926 until his death. He belonged to the Bosonid family. During his reign, he empowered his relatives at the expense of the aristocracy and tried to establish a relationship with the Byzantine Empire. He had success in defending the realm from external enemies, but his domestic habits and policies created many internal foes and he was removed from power before his death.
Rudolph I was King of Upper Burgundy from his election in 888 until his death.
The House of Capet ruled the Kingdom of France from 987 to 1328. It was the most senior line of the Capetian dynasty – itself a derivative dynasty from the Robertians.

Boso was a Frankish nobleman of the Bosonid family who was related to the Carolingian dynasty and who rose to become King of Lower Burgundy and Provence.

Otto, called the Illustrious by later authors, was a notable member of the Ottonian dynasty and Duke of Saxony from 880 until his death in 912. He played an important role in early medieval history of Germany during the 9th and 10th centuries, known for his military campaigns and diplomatic efforts.

The Kingdom of Upper Burgundy was a Frankish dominion established in 888 by the Welf king Rudolph I of Burgundy within the territory of former Middle Francia. It grew out of the Carolingian margraviate of Transjurane Burgundy southeast of the Jura Mountains together with the adjacent County of Burgundy (Franche-Comté) in the northwest. The adjective 'upper' refers to its location upstream in the Rhône river valley, as distinct from Lower Burgundy and also from the Duchy of Burgundy west of the Saône river. Upper Burgundy reunited with the Kingdom of Lower Burgundy in 933 to form the Kingdom of Burgundy, later known as Kingdom of Arles or Arelat.
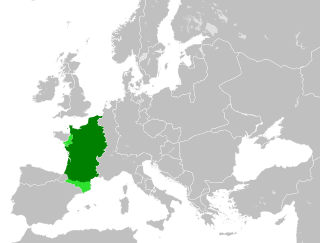
In medieval historiography, West Francia or the Kingdom of the West Franks constitutes the initial stage of the Kingdom of France and extends from the year 843, from the Treaty of Verdun, to 987, the beginning of the Capetian dynasty. It was created from the division of the Carolingian Empire following the death of Louis the Pious, with its neighbor East Francia eventually evolving into the Kingdom of Germany.
Ermengard of Italy was Queen of Provence as the spouse of King Boso. She was the second and only surviving child of Emperor Louis II. In her early life, she was betrothed to Constantine, the junior Byzantine emperor, but whether the marriage actually occurred or not is still debated among historians. In 871, Ermengard and her family were taken hostage by Adelchis of Benevento but were later freed. In 876, Ermengard married Boso, a nobleman with connections to the Carolingian dynasty, and became queen upon his accession to the throne of Provence in 879. After her husband's death in 887, she served as regent of the kingdom during the minority of her son Louis the Blind.
Ælfflæd was the second wife of the English king Edward the Elder.

King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds the powers of government without control, or the entire sovereignty over a nation; he is a limited monarch if his power is restrained by fixed laws; and he is an absolute, when he holds the whole legislative, judicial, and executive power, or when the legislative or judicial powers, or both, are vested in other people by the king. Kings are hereditary sovereigns when they hold the powers of government by right of birth or inheritance, and elective when raised to the throne by choice.

Louis IV, called d'Outremer or Transmarinus, reigned as King of West Francia from 936 to 954. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, he was the only son of king Charles the Simple and his second wife Eadgifu of Wessex, daughter of King Edward the Elder of Wessex. His reign is mostly known thanks to the Annals of Flodoard and the later Historiae of Richerus.